Table of Contents
A plant cell diagram is a diagram showing all the structures, that represent cell walls and cell membranes. A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that can perform the fundamental processes required for the survival of an organism. Every living organism is made up of cells, including plants. These cells make up the structure of plants and help in their survival. It has various cell components that perform specialized functions.
The different components in a plant and animal cell diagram are called cell organelles. The nucleus, chloroplast, Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, etc. are some important cell organelles of a plant cell. The outermost layer of the cell is a tough cell wall made up of cellulose. It protects the cell and gives it structural support. Animal cells differ from plant cells in the sense that they do not possess this rigid cell wall.
What is a Plant Cell Diagram?
A plant cell diagram is the smallest fundamental unit specialized to play an important role in a plant. It is an eukaryotic cell with organelles present to play specific roles. Each organelle has a different structure and function. They are like organs in humans to plants. They help perform various functions in plant cells. Some of the functions include providing stability, photosynthesis, genetic control, and energy production. There are mainly three types of plant cells, namely, Parenchyma, Collenchyma, and Sclerenchyma cells.
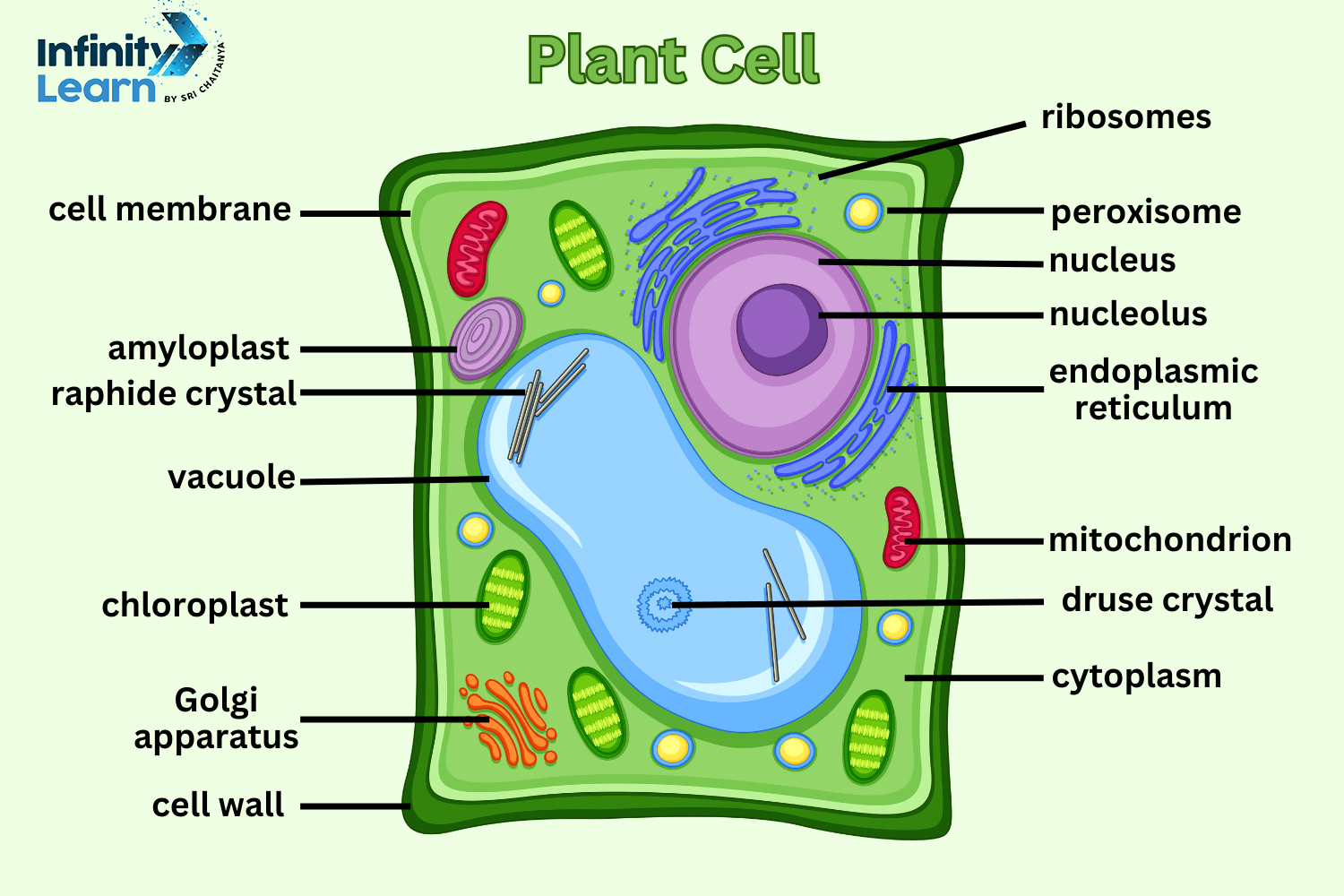
Plant Cell Diagram
A plant cell diagram is typically rectangular and quite large as compared to an animal cell. Both cells are eukaryotic and share many organelles in common, but also differ in their structure to an extent. Since each cell has its distinct functions, they have different structures. In a plant cell diagram class 9 includes the nucleus, cell wall, mitochondria, ribosomes, etc.
Components of a Plant Cell
In a plant cell diagram simple shows the basic structure of a plant cell. There are different components inside the plant cells called cell organelles. Cell wall, Cell Membrane, Cytoplasm, Nucleous, Plastids, Golgi Apparatus, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Ribosomes, Mitochondria, and Lysosomes are the cell organelles of a plant cell.
Cell wall
The cell wall is a hard layer made up of cellulose, hemicellulose, glycoproteins, etc. It is present outside the cell membrane and forms the outermost layer in a plant cell. The main function of the cell wall is to protect the cell against mechanical stress and give it a structure. It is a permeable layer, that filters and allows molecules in and out of the cell.
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane is located inside the cell wall and is made up of a thin layer of protein and fat. It is a semi-permeable membrane that allows only certain specific molecules to pass through it. It acts like a barrier layer that only allows the required minerals and prevents toxins from entering the cell. In the plant cell diagram class 8 textbook, the presence of the cell membrane is clearly visible.
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm of a plant cell is a jelly-like substance present inside the entire cell. It holds the other cell organelles, like the nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes, and Golgi apparatus. It contains amino acids, enzymes, glucose, nutrients, vitamins, and water to perform various cellular functions. Various metabolic activities, like photosynthesis, protein synthesis, glycolysis, etc., take place in the cytoplasm.
Nucleus
The nucleus is an important cell organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It is associated with the production of ribosomes. One of the major functions of the nucleus is to store genetic information as DNA, which is hence called the “control center” of the cell. There is a double membrane structure that surrounds the nucleus for its protection. It also contains small pores that help in molecular exchange between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
Plastids
Plastids are important cell organelles found in plant cells that help in the photosynthesis process. They also play an important role in producing and storing food. Plastids contain pigments that not only help in photosynthesis but also change the color of the cell. There are three types of plastids, i.e., chloroplasts, leucoplasts, and chromoplasts.
Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi Apparatus, also known as the Golgi body or Golgi complex, helps in the synthesis of macromolecules. It also helps in processing and distributing the synthesized macro-molecules to the different parts of the cell. The Golgi body also helps in intercellular transportation.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes that helps in protein synthesis and lipid metabolism. It is connected to the nucleus on one side and to the plasma membrane on the other. It is divided into two parts, the rough endoplasmic reticulum and the smooth endoplasmic reticulum. The rough endoplasmic reticulum helps in the transportation of proteins. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum helps in the detoxification of toxic substances.
Ribosomes
Ribosomes present in plant cells help in various functions of a plant. It is used in the synthesis of proteins in plant cells. They also contribute to regulating photosynthesis in plants and translating the genetic code stored in DNA.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria is the cell organelle in plant cells responsible for providing energy to the cell by breaking down carbs. Since it helps in providing energy, it is referred to as the “powerhouse of the cell.” A plant cell diagram labelled in detail shows the mitochondria clearly.
Specialized Cells in Plant Cell Diagram
Parenchyma Cells
Parenchyma cells are the living cells in the plant responsible for cell metabolism. These are thin and flexible cells and thus also help gaseous exchange.
Collenchyma Cells
The main function of the collenchyma cell is to give support to the plant when it is young. Hence, these cells are very hard. As the plants grow, these cells also grow along with them.
Sclerenchyma Cells
Sclerenchyma cells are the hardest cells present to provide maximum support to the plants. These cells are located in the roots of the plants and die as the plants grow.
FAQs on Plant Cell Diagram
Where does photosynthesis take place in the plant cells?
Photosynthesis in plants occurs within the chloroplast of the plant cell.
What are 3 types of plant cells?
The four types of plant cells are parenchyma cells, collenchyma cells, and sclerenchyma cells
Why are plant cells green?
The chloroplast in the plant cell has Chlorophyll that imparts a green color to the cell.
What is a plant cell?
A plant cell is a type of cell that has a real nucleus and some special parts for doing specific jobs. But, these special parts in plant cells are not the same as in other cells with a real nucleus.
What is the composition of a plant cell wall?
The plant's cell wall consists of cellulose, which is a long, straight chain of many glucose molecules.









