Table of Contents
CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets
CBSE class 6 science notes chapter 13 Fun with Magnets is an essential part of the curriculum, focusing on introducing students to the basics of magnets. These CBSE notes, aligned with CBSE syllabus and NCERT guidelines, are provided by Infinity Learn (IL) to make learning more effective and engaging. Notes play a crucial role in exam preparation, serving as a quick revision tool. Well-prepared notes from Infinity Learn can significantly enhance a student’s understanding and performance in exams.
Class 6 Science Chapter 13 – Fun with Magnets Notes
How Magnets Were Discovered
- Legend of a shepherd named Magnes who discovered natural magnets in ancient Greece.
- Magnetite, a natural magnet, was named after Magnes or the place Magnesia.
What is Magnet?
- A magnet is a material that can attract iron, nickel, and cobalt.
- Magnets can be natural (like magnetite) or artificial.
Types of Magnets
- Natural Magnet: Magnetite is called a natural magnet.
- Artificial Magnets: Man-made magnets, e.g., bar magnets, horseshoe magnets.
- Temporary magnets: They are called temporary magnets that retain their magnetic properties only for a short period.
- Permanent magnets: Magnets that retain their magnetic properties for a long period are called permanent magnets.
Properties of Magnet
- Attracts magnetic materials like iron, nickel, cobalt.
- Has two poles: North Pole and South Pole.
- Opposite poles attract each other; like poles repel each other.
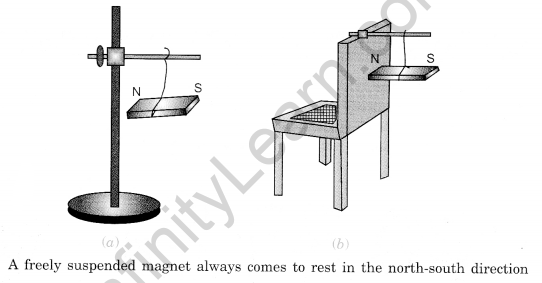
- A freely suspended magnet always aligns itself in the North-South direction.
Also Check: Class 6 Science Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets Extra Questions
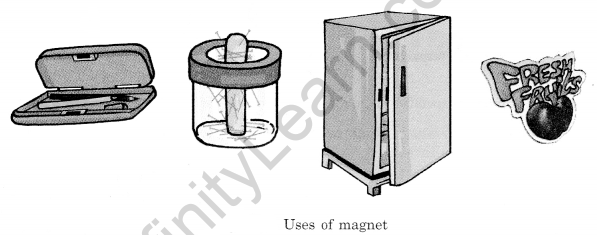
Applications of Magnet
- Used in various devices like compasses, motors, generators, and magnetic locks.
- Utilized in industries for separating magnetic materials from non-magnetic materials.
- Credit cards, ATM cards, and identity cards have a strip of magnetic material that stores information.
- Television and computer monitors use magnets.
- Computer hard discs and audio and video cassettes have magnetic material that stores information.
- Magnets are used in picking up substances made of iron from a scrapyard.
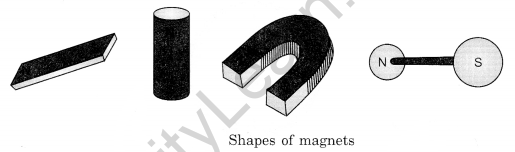
Shapes of Magnets
Magnets are made of different materials and in different shapes.
Magnetic materials
The materials attracted to the magnet are known as magnetic materials, e.g., iron, nickel, and cobalt.
Magnetic Force
- The force exerted by a magnet to attract or repel other magnetic materials.
- Strongest at the poles of the magnet.
- Chapter 1 Food: Where Does It Come From?
- Chapter 2 Components of Food
- Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric
- Chapter 4 Sorting Materials Into Groups
- Chapter 5 Separation of Substances
- Chapter 6 Changes Around Us
- Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants
- Chapter 8 Body Movements
- Chapter 9 The Living Organisms and Their Surroundings
- Chapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances
- Chapter 11 Light, Shadows, and Reflection
- Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits
- Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets
- Chapter 14 Water
- Chapter 15 Air Around Us
- Chapter 16 Garbage In, Garbage Out
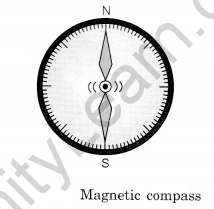
Magnetic Compass
- A device that uses a magnetized needle to indicate the North-South direction.
- The needle aligns itself with the Earth’s magnetic field.
Demagnetisation
- Process of removing magnetism from a magnet.
- Can be caused by heating, hammering, or dropping the magnet.
Magnetic and Non-magnetic Materials
- Non-magnetic materials: The materials which are not attracted to the magnet are known as non-magnetic materials, e.g., leather, plastic, cloth, and paper. Magnetic poles: Magnetic attraction is maximum near the ends of the magnet. These ends are called magnetic poles.
- Non-magnetic Materials: Materials that are not attracted by magnets (e.g., wood, plastic).

The magnet always aligns in a north-south (N-S) direction when suspended freely.
Compass
This is a small glass case containing a magnetized needle pivoted on a nail. The needle can rotate freely. Wherever it is kept, its needle always rests in a north-south direction. Normally, the needle’s north pole is painted red, or some other indication is given to identify the north and south poles. So using this needle, north and south can be identified.
Look at the pictures shown below. Put a V’ mark against the object you think would stick to a magnet and ‘an X against the objects that would not stick to a magnet.
Let us now learn more about magnets.
Answers: 1. False, 2. True, 3. True, 4. False, 5. False, 6. True.
Poles of a Magnet
North pole: When suspended freely, one magnet pole always points north. This is known as the north pole.
South pole: When suspended freely, the end of a magnet points towards the south. This is known as the south pole.
.There are two poles in every magnet, irrespective of its shape. These are, by convention, called the North Pole (N) and the South Pole (S) (Fig. 12.2). The two poles cannot exist independently. That is, they always come in pairs.
If we break a bar magnet in the middle, we will get two pieces, each with the North Pole and the South Pole. We could go on breaking the magnet into smaller pieces, and every time we would get both the poles in each piece.
Finding Directions
Today, we use magnets for various purposes. In ancient times, the primary use of a magnet was to find directions.
If a magnet can move freely, it comes to rest in a direction very close to the Earth’s North-South direction. This property of interest was used to find directions on the surface of the Earth by travelers. An instrument with a magnet used to find directions is called a magnetic compass.
It has a small magnetic needle at its centre. This needle can rotate freely and always points in the Earth’s North-South direction. Different directions (north, south, east, and west) are marked on the compass. Figure 12.3 shows how one can find directions using a magnetic compass.
Do you know why a freely suspended magnet always points in the Earth’s north-south direction? It behaves like it is under the influence of another magnet. But where is this other magnet? It is the Earth itself. This alignment happens because of the influence of the Earth, which itself acts like a giant bar magnet (Fig. 12.4). It influences all the magnets (within its region of influence) to align themselves along its North-South direction.
- CBSE Class 6 Science Syllabus
- CBSE Class 6 English Syllabus
- CBSE Class 6 Hindi Syllabus
- CBSE Class 6 Social Science Syllabus
Attraction and Repulsion between Magnets
When two magnets are brought close to each other, they are either pulled towards each other or pushed away. When the magnets are pulled towards each other, they are said to attract each other. When they have pushed away from each other, they are said to repel each other. Whether the magnets attract or repel depends on which poles of the magnets face each other.
When poles of the magnets (N-N or S-S) are brought close, they repel. This is called repulsion.
When unlike poles of the magnets (N-S or S-N) are brought close to each other, they attract. This is called attraction.
Care Of Magnets
A magnet can lose its properties due to the following activities.
- Dropping from a height
- Hitting with a hammer
- Applying heat
- Improper storage can also cause loss of magnetic properties.
We hope the given CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets Pdf free download will help you. If you have any queries regarding NCERT Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets, drop a comment below, and we will get back to you at the earliest.
| Other Resources for Class 6 | |
| NCERT Syllabus for Class 6 | NCERT Solutions Class 6 |
| Worksheet for Class 6 All subjects | CBSE Notes Class 6 |
| NCERT Books for Class 6 | Online Tuition for Class 6 |
FAQs on Class 6 Science Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets
What is a magnet Class 6 notes?
In Class 6 Science notes, a magnet is described as a material that can attract iron, nickel, and cobalt. Magnets have two poles: North and South.
What are the 4 types of magnets?
The four types of magnets are permanent magnets, temporary magnets, electromagnets, and superconductors. Each type has different properties and uses.
Who invented magnet?
Magnets were not invented but discovered. According to legend, a Greek shepherd named Magnes discovered natural magnets, known as magnetite, in ancient Greece.
How magnets work?
Magnets work by exerting a magnetic force that attracts or repels other magnetic materials. This force is strongest at the magnet's poles: North and South.
What are the 2 types of magnet?
The two main types of magnets are natural magnets, like magnetite, and artificial magnets, which are man-made from materials like iron, cobalt, or nickel.
What is the strongest magnet?
The strongest type of magnet is the neodymium magnet, a type of rare earth magnet. It is known for its exceptional magnetic strength and is used in various applications.








