Table of Contents
Cellular respiration is something that happens inside cells where energy is released when glucose molecules break down. We can divide this process into two types depending on whether oxygen is used or not: aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Also Check: Organisms Reproduce Class 10
What is Anaerobic Respiration?
Let’s talk about cellular respiration – it’s a fascinating process! There are two main types: aerobic and anaerobic. Aerobic basically means ‘with air’. So, aerobic respiration is when cells use oxygen to convert food into energy. It’s pretty common in most living things, like plants, animals, and even us humans.
Now, think about when we breathe. We breathe in air, right? And that air has oxygen. When we breathe out, we release carbon dioxide. So, the oxygen we breathe in goes all over our body, reaching every single cell. Inside these cells, oxygen helps break down the food we eat, like glucose, into carbon dioxide and water. And guess what? This breakdown releases energy, which is super important for growth and keeping us going!
Also Check: Life Process
To put it simply, here’s a little equation to illustrate the process:
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy
Also Check: CBSE Syllabus for Class 10
And this aerobic respiration? It’s not a one-time thing. It’s happening constantly inside the cells of both animals and plants. Pretty cool, right?
Anaerobic Respiration in Humans: Anaerobic respiration occurs in human muscles when we do a lot of physical work and not enough oxygen reaches the muscles. This causes lactic acid to form.
Anaerobic Respiration in Animals: Anaerobic breathing in animals doesn’t need oxygen and makes lactic acid. Aerobic breathing gives much more energy for the same sugar. Anaerobic breathing isn’t very good at making energy and causes cramps. During aerobic breathing, gases are swapped.
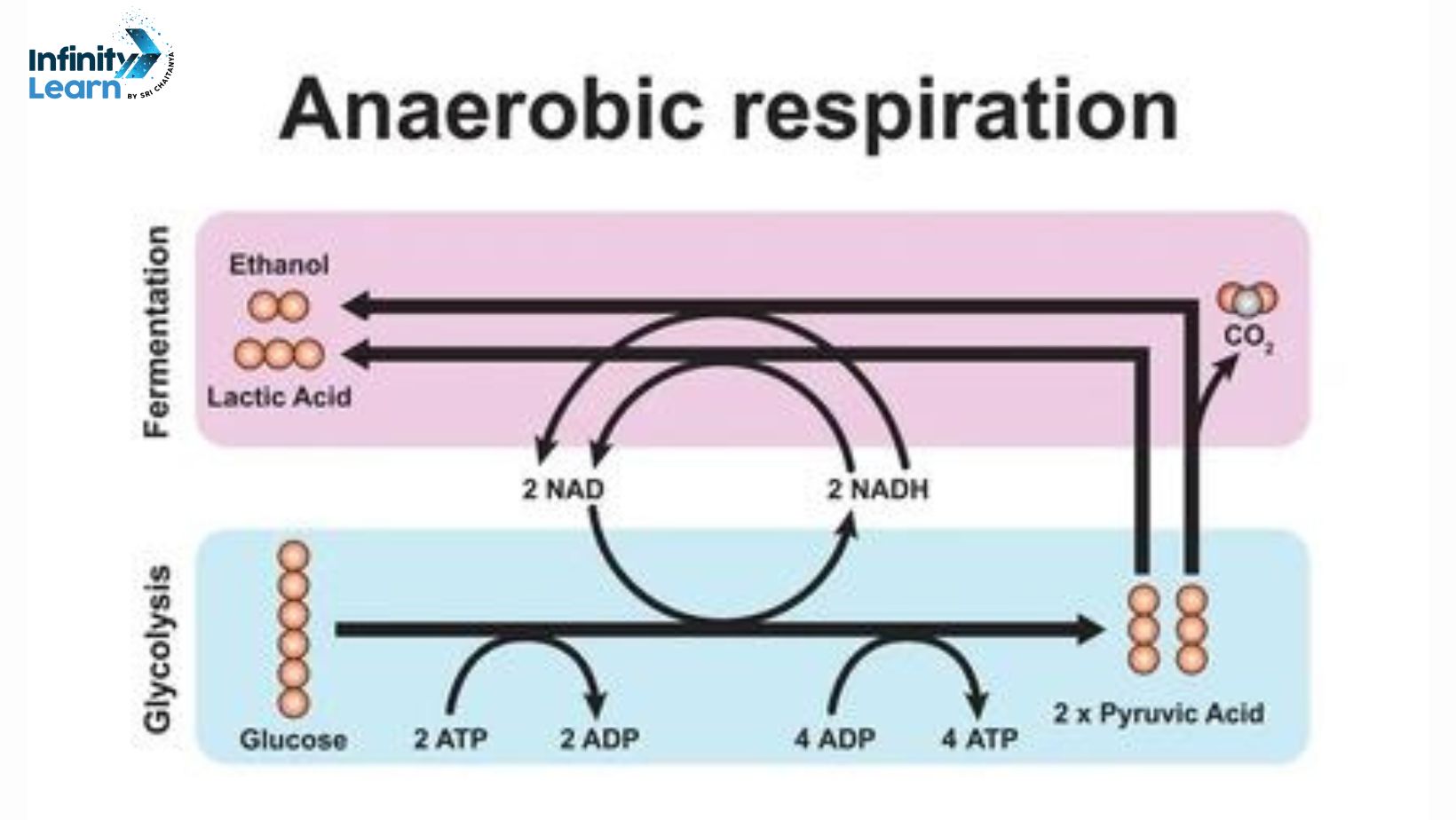
Anaerobic Respiration in Plants: In plants, when oxygen is scarce, they resort to a process known as anaerobic respiration. In this process, glucose is converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide through what’s called alcoholic fermentation. Initially, glucose undergoes glycolysis to become pyruvate, which is then further transformed into ethanol and carbon dioxide.
Also Check: CBSE Class 10 Science Syllabus
Anaerobic Respiration in Yeast: Yeast breathe with or without oxygen. When they breathe without oxygen, they make alcohol. Sugar is changed into alcohol and carbon dioxide, and this gives them energy. Muscles make lactic acid when they breathe without oxygen.
Advantages in Anaerobic Respiration
- When athletes push themselves too much during exercise, their muscles don’t get enough oxygen, leading to anaerobic respiration.
- This means that when glucose breaks down, it produces lactic acid.
- This happens quickly.
- The production of energy (ATP) happens rapidly.
- Anaerobic respiration is faster than aerobic respiration and doesn’t need oxygen to convert energy.
- In muscles, when there isn’t enough oxygen, pyruvic acid changes into lactic acid to provide energy during intense activity.
Disadvantages in Anaerobic Respiration
One drawback is that it’s not as good at making energy as aerobic respiration. It doesn’t produce as much energy from the same stuff and only makes 2 ATP from one glucose molecule. Another downside is that it creates lactic acid. Too much lactic acid can cause muscle cramps and lower blood pH. After intense exercise, muscles and the liver have to change lactic acid back into pyruvic acid.
How to Produce Anaerobic Bacteria
Two great ways to grow bacteria that don’t need oxygen are the glove box system and the roll-streak tube system. In these methods, special media called prereduced anaerobically sterilized (PRAS) media are used. This is suggested by the VPI anaerobe laboratory.
Process of Anaerobic Respiration
When oxygen is lacking, a vital process known as the electron transport chain can’t function because it lacks a necessary component. This means the body can’t produce its usual energy molecules, called ATP. When this process stalls, other important reactions in the body, like the TCA cycle and glycolysis, slow down too.
In the absence of oxygen, the body switches to an alternative pathway that utilizes pyruvate, a substance produced during glycolysis.
Without the electron transport chain working as it should, there’s an excess of two substances: NADH and pyruvate. NADH helps convert pyruvate into lactate, also known as lactic acid, and this conversion process helps recycle NAD+. By recycling NAD+, glycolysis can continue because it receives the necessary boost. Glycolysis generates a modest amount of energy called ATP, which is essential for various bodily functions.
Anaerobic Respiration FAQs
What is anaerobic respiration?
Anaerobic respiration is a process where organisms produce energy without using oxygen.
What are three examples of anaerobic respiration?
Examples include fermentation in yeast (producing alcohol), lactic acid fermentation in muscles during exercise, and bacteria breaking down organic matter in oxygen-deprived environments.
What is the anaerobic mode of respiration?
Anaerobic respiration is a mode of respiration that occurs in the absence of oxygen.
What is the primary problem with anaerobic respiration?
The main issue with anaerobic respiration is that it produces less energy compared to aerobic respiration and can lead to the buildup of waste products like lactic acid.
What is the importance of anaerobic respiration?
Anaerobic respiration allows organisms to generate energy in environments with low oxygen levels, helping them survive in various conditions.
What is an example of an anaerobic process?
An example of an anaerobic process is the fermentation of sugars to produce alcohol by yeast.









