Table of Contents
Living things stay alive by doing certain activities that keep them going. These activities help them control what they do every day. One of these activities is called excretion. Inside the cells of living things, a process called metabolism happens. This process produces both helpful and harmful substances. If harmful substances build up, they can hurt the living thing. So, living things get rid of these waste products from their bodies, and this is called excretion. Different living things get rid of waste in different ways. Now, let’s look at how plants get rid of waste and how it’s different from animals.
Also Check: CBSE Syllabus for Class 10
Excretion in Plants
When plants get rid of harmful and waste substances from their bodies, it’s called excretion. Unlike animals, plants don’t have a fancy system just for excretion. They don’t have special organs dedicated to it. So, excretion in plants isn’t as complicated as in animals.
Excretion in Plants Diagram
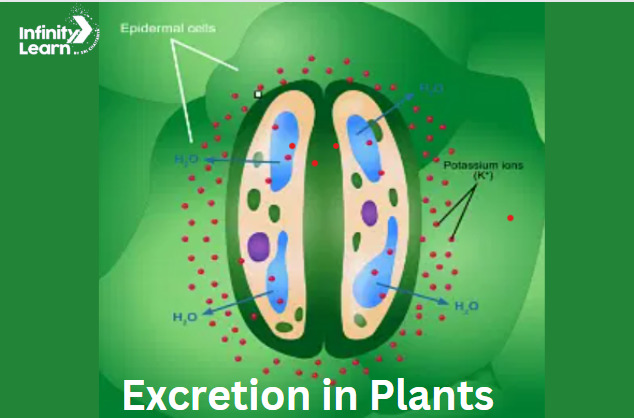
Different Types of Excretion in Plants
Transpiration: Transpiration is when a plant loses water vapor from its surface, mainly from its leaves. This loss of water helps to move water up through the plant’s xylem. Plants can lose quite a bit of water through transpiration.
Also Check: Anaerobic Respiration
Guttation: Guttation is when a plant loses water in the form of droplets from its hydathodes. Droplets of water come out from the edges of leaves of certain plants. This happens when there’s strong pressure in the roots but low transpiration.
Minerals, acids, sugars, and other substances can be found in these droplets. Plants like garden nasturtium, grasses, tomatoes, potatoes, and colocasia can exhibit guttation.
Bleeding: Bleeding is when sap flows out from injured parts of a plant. This happens because of pressure in the roots, causing sap to flow out of cuts made in the stem, especially when the soil is moist.
Respiration: Plants use carbon dioxide, water, sunlight, and chlorophyll to make food in a process called photosynthesis. Oxygen is produced as a result. This oxygen is released as waste through a process called diffusion.
Also Check: Life Process
Excretion is carried out in the plants in the following ways:
- Plants get rid of their waste gases like oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water vapor through tiny openings called stomata on their leaves and lenticels on their stems.
- Some waste collects in leaves and bark. When leaves and bark fall off, the waste goes away too.
- Other waste turns into harmless solids and stays in the plant. Things like raphides, tannins, resins, gum, rubber, and essential oils are examples of this.
- For instance, the oil from oranges, eucalyptus, and jasmine, latex from rubber trees, papaya trees, and gums from acacia, are all forms of stored waste products. Sometimes, these products even get released into the soil.
Also Check: CBSE Class 10 Science Syllabus
Plant Excretory Product
- Plants mainly get rid of carbon dioxide, extra water from breathing, and nitrogen compounds from breaking down proteins. They release two gases: oxygen when they make food and carbon dioxide when they breathe out.
- When animals breathe, they release a gas called carbon dioxide. Plants use this carbon dioxide, along with sunlight, to create their food in a process known as photosynthesis. As a result, plants release oxygen into the air, which is crucial for all living beings.
- Plants absorb water from the soil through their roots. Sometimes, they take in more water than they need. To get rid of this excess water, plants release it through small pores on their leaves called stomata. This process is called transpiration.
- In some cases, the water or soil where plants grow may contain too much salt. When plants absorb this excess salt, they must eliminate it from their systems. They do so by depositing the salts in their tissues, forming crystals.
- As animals and plants go about their daily activities, they produce waste substances. One type of waste is called nitrogenous waste, which includes compounds like urea. These wastes are expelled from the body through processes like diffusion.
- During their metabolic processes, plants produce organic acids. Some of these acids, like oxalic acid, can accumulate in plants and cause harm if not properly managed.
- Plants also produce chemicals called tannins, which act as a defense mechanism against pests. These tannins give certain plants a bitter taste and help protect them from being eaten by animals.
- Certain plants, like rubber trees, produce a milky white fluid called latex. This latex serves to seal wounds in the plant and provides protection against insects and diseases.
- Another protective substance produced by plants is resin, which is a thick liquid with a strong aroma. Resins help shield plants from damage caused by insects and fungi.
- Plants also generate gums, which are sticky substances that help seal wounds and protect against infections. These gums play a crucial role in maintaining the health of the plant.
Also Check: Organisms Reproduce Class 10
Plants Organs involved in Excretion
- Old Leaves: When leaves get old, they store waste and then fall off the tree.
- Old Xylem: Waste like resins and tannins builds up in the old xylem, making it stop working.
- Bark: Dead cells in bark collect impurities like tannins, which are used for making dyes and inks.
- Central Vacuole: Waste mostly stays in the central vacuole of a plant’s cell, but it doesn’t affect the cell’s work because of a special membrane.
- Root Excretion: Plants push some waste out through their roots.
- Detoxification: Harmful acids are turned into harmless crystals by plants.
- Salt Glands: Plants also get rid of extra salt through special glands.
Also Check: Duodenum
Plant Excretory FAQs
What is excretion?
Excretion is the process of removing waste products or harmful substances from the body or from biological systems.
What are the four types of excretion?
The four types of excretion are: sweat (perspiration), urine, carbon dioxide (from respiration), and feces.
What is the excretory organ of a plant?
Plants do not have specific excretory organs like animals. Instead, they use structures like stomata, roots, and specialized cells to excrete waste.
What are examples of plant waste?
Examples of plant waste include oxygen released during photosynthesis, excess salts, and organic compounds like tannins and alkaloids.
Is there an excretory system in plants?
No, plants do not have a dedicated excretory system like animals. They use various structures and processes to eliminate waste products and maintain balance within their cells and environment.








