Table of Contents
Table of Contents
- Different Structures of Alkenes
- Straight Chain Structure
- Branched Chain Structure
- Ring Structure
- Different Structures of Alkynes
- Straight Chain Structure
- Branched Chain Structure
- Ring Structure
- Summary
- Did You Know?
- What’s Next?
In the previous segment, we learnt about the Branched and ring structure of Alkanes. In this segment, we will learn about the Branched and ring structure of alkenes and alkynes.
What are the Different structures of alkenes?
There are three major structures of alkenes: straight chain structure, branched chain structure and ring structure.
Straight chain structure
Straight chain structure of alkenes is One Long Straight Chain of all the carbon atoms.
For example, the arrangement for six carbon atoms in alkene, called Hexene, is shown below:
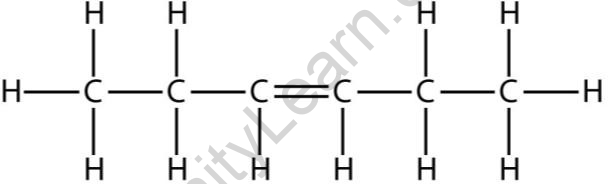
Straight chain structure
Branched chain structure
Branched chain structure of alkenes is a structure where the carbon atoms get attached as the
Side Chain to the other carbon atoms.
For example, the arrangement for six carbon atoms in alkene, called Hexene, is shown below:
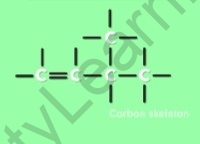
Branched-chain structure
Ring structure
The ring structure of Alkenes has carbon atoms that are arranged in the form of Rings. These structures are formed by complex compounds.
They are also known as Cyclic Alkenes.
For example, the arrangement for six carbon atoms in alkene, called Hexene, is shown below:
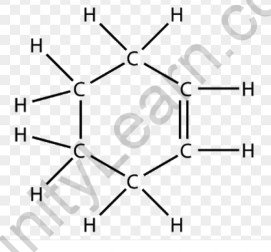
Ring structure
What are the Different structures of alkynes?
There are three major structures of alkenes: straight chain structure, branched chain structure and ring structure.
(I) Straight chain structure
Straight chain structure of alkynes is One Long Straight Chain of all the carbon atoms.
For example, the arrangement for six carbon atoms in alkyne, called Hexyne, is shown below:





