Table of Contents
Privatization is a term implying the transformation of a public sector company into a private sector company. Also, when government regulations on a private company are lessened or removed, the company is said to have undergone “deregulation.” The term “deregulation” is also often used as a synonym for privatization. Advantages and Disadvantages of Privatization.
In other words, privatization means that the control of the government over a particular service has been shifted into private hands. Privatization had advantages and disadvantages over the economy, social welfare, and other sectors. We will further understand “Privatization” with suitable examples and its pros and cons.
Examples And Advantages and Disadvantages of Privatization
1) Privatization in Healthcare
Put, privatization in healthcare implies the involvement of private hospitals and clinics in the government’s healthcare schemes and services. It could mean the full or partial transfer of the ownership of healthcare services to private entities. A government can take such a decision if it finds it difficult to manage or provide the services independently—one finest example. Let us talk about the privatization of the healthcare system in Great Britain. Privatization of NHS means, where the health industry is rapidly growing after the government adopted a policy of sustaining old people in private hospitals, on state budget, when there is no bed available in public sector hospitals.
2) Privatization in Education
Privatization in education has been a hot topic for debates over its advantages, disadvantages, and social consequences. Still, several governments worldwide have displayed their interest in the privatization of the education sector from time to time. The ever-growing need for the education sector and the government’s commitment to providing free and compulsory education to all is ultimately getting more difficult to be managed by government authorities alone; even funding education expenses through the taxpayer’s money is no longer a feasible idea.
3) Privatization in Welfare
Privatization in welfare refers to the full or partial management of public welfare schemes by private entities. It includes water supply, skill and job training, job placements, etc. In some countries, shelter homes and community lunch centers are also managed by private players. Many countries, including India, have privatized mainly their wastewater treatment plants. Though, the privatization of public welfare should be meticulously carried out else it will only remain a method to excuse government of its prime responsibility towards its citizens.
4) Privatization of Infrastructure
Privatization of Infrastructure refers to leasing roads, bridges, and tunnels to private entities for revenue collection and maintenance. Such deals have been common in European countries, but today it’s’ gaining global popularity. The terms and conditions of such contracts are flexible. A contractor who has constructed a particular road is allowed to recover a particular amount of the company’s bill by collecting toll for the leased time duration as mutually agreed upon in the contract agreement.
Reasons of Privatization
There are several reasons for privatization, as visualized by the governments. Some of the most significant reasons are cost reduction, risk transfer, and a good source of revenue. Several other reasons, like the inefficiency of government agencies, and a willingness to improve the service level, can also be valid reasons for privatization. Below we will discuss some of the reasons for privatization briefly.
1) Reduction in Cost
Cost reduction is one of the main reasons for privatizing public sector undertakings. Private players achieved the target at a lower cost than the government. Private contractors have more flexibility in employee compensations and benefits, which hugely impacts the overall cost of a project.
2) Transfer of Risk
Risk transfer is another reason why governments prefer the privatization of several sectors. By handing over a project to the private players, the government transfers the responsibility and risk to the private player for an agreed sum of money. Now the private company has the risk of completing the project on time, paying the penalty, or bearing the losses on its own.
3) Potential Revenue Source
Privatization in some sectors can be a useful source of revenue generation by leasing public assets like roads, bridges, and tunnels to private firms. The government can draft a good lease or purchase agreement to benefit monetarily from the deal. The revenue thus generated by the government can be used for other projects or to pay debts.
4) Service Quality Improvement
One of the main reasons for privatization is that the government might be looking to improve the quality of services at a lower cost. Private sector companies/contactors can manage to improve service quality without affecting cost due to their flexible policies in management and low compensation paid to the employees.
5) Punctuality of Delivery
Another factor behind privatization is the willingness of the government to complete the project on time. Despite having the necessary skills, the government might be unable to complete the project on time due to several other restraints. On the other hand, private companies can have 24/7 dedicated resources for the project’s timely completion.
Privatization in India
Privatization in India has long been a political issue at the national level. Privatization of some sectors in the past had stirred up protests from employee unions and political parties; nevertheless, in some cases, it was imposed, while in some, the government-backed off.
In India, PSUs (Public Sector Undertakings) have contributed to the country’s economic and industrial growth, though they suffer from acute inefficiencies. Many Indian PSUs have reported losses due to factors such as overstaffing, overly compensated employees, delay in project deliverance, managerial delays, etc.
Some of the important examples of privatization in India are briefly stated below-
- Hotel Corporation of India Limited (HCL): Initially privatized, the HCL operated as an owned subsidiary of Air India (AI), India’s international airline. The government took the decision of privatization /sale of HCL properties and assets when it posted a total loss of 15 million in the financial year 2000-2001. HCL was in persistent loss, amounting to over 900 million, mainly due to mismanagement by the government and Air India.
- Videsh Sanchar Nigan Limited (VSNL): Incorporated in 1986, Videsh Sanchar Nigam Limited (VSNL) was a public sector undertaking with the main objective of catering overseas communication services. In 2002, the government of India took a decision to privatize VSNL, transferring the maximum company’s stake to the Tata Group.
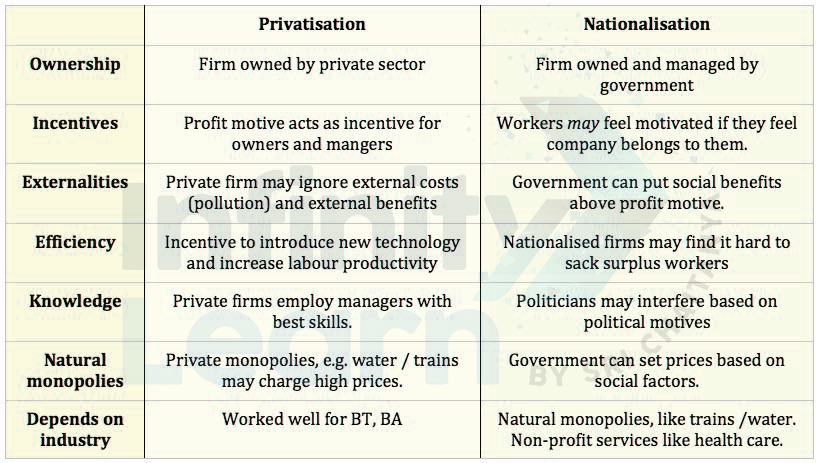
Privatization has its own set of pros (advantages) and cons (disadvantages) as discussed below-
Advantages of Privatization
1) Increased Productivity: Privatization of a Public Sector Undertaking can increase efficiency as private enterprises are more profit-oriented than the government. The management-level employees of a privately run business are more profit-oriented. British Telecom (BT) and British Airways are the two finest examples of improved efficiency after privatization.
2) No Political Intrusion: Privatizing a government-owned subsidiary removes all the political interferences, improving efficiency, and turning losses into profits. Managers in a government-run enterprise work under political pressure and thus can’t’ think rationally about making a profit. State-run companies often employ more than required persons under political pressure, ultimately compromising their profits.
3) Far Sighted Commitment: Transferring the authority of a government-run company into private hands means that more free hand is given to the management, who can now make commitments for long-term gains. A far-sightedness is lacking in the government sector, which is more concerned about the short-term electoral gains.
4) Competitive Environment: Privatization increases competition by allowing more and more private firms to try their hands in the industry. More competition among private entities naturally brings out efficiency and imposes quality restrictions on them. They become more quality and service-oriented to be number one.
5) Revenue Generation: Privatization could be an instant mode of revenue generation for the government looking for funds for investing in some project or welfare scheme. Leasing roads or bridges or selling them right away to private firms return quick monetary rewards; however, looking at the long-term benefits, it is a loss for the government in some cases, if not all.
Disadvantages of Privatization
1) Natural Monopoly: Privatization in some sectors where there is low competition may lead to the monopoly of a single private firm. Having complete monopoly over a particular sector, the firm gets a free hand to compromise its quality and fix higher price rates, etc., to churn out large profits. On the other hand, a government-run agency would have prioritized public interest over profit.
2) Decline in Public Interest: Private companies dealing mainly in public welfare sectors like health, education, and others are more profit-oriented than welfare-oriented. This dearly costs the common person in the form of excessive taxes, higher prices, and a poor state of quality and services.
3) Lack of Regulations: Privatization slips the power of financial and other managerial decisions out of the government into private hands. This means that the government has limited or no say in the company’s decisions; neither can the government impose much regulation over the functioning of the company or its policies.
4) Low Future Investment: Private firms, out of the government’s regulation and control, may look out for short-term gains, compromising the long-term future projects. This forces the companies to invest in short-term beneficial projects rather than long-term ones.
5) Fragmentation of Companies: Privatization might lead to the breaking up of one giant company into several other rather small enterprises. This fragmentation ultimately decreases the efficiency and also reduces the accountability in the management. Companies throw the responsibility for any losses onto each other and try to escape responsibility.
Conclusion
Whether privatizing a particular industry will be beneficial in the long run depends entirely on the industry. For example, let us compare the transport industry and education sector. In the transport industry, the revenue collected can be used for further improvement. Still, there is a need to regulate the fare charges as it may compromise public interest by overcharging. Switching to the education industry, the motive of profit generation becomes less significant, hence it would be an uphill task for any private firm to work for absolutely no or very low profit. Even if it does so, it’s’ more likely that public interests will be compromised in some way or the other.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Privatization in India FAQs
What are the advantages of privatization?
Privatization leads to increased efficiency due to better management practices. It also encourages innovation, competition, and investment, which can improve services and reduce costs. It can also reduce the financial burden on the government.
What are the positive impacts of privatization in India?
Privatization in India has led to improved service quality, increased foreign investment, better management of state-owned enterprises, and enhanced job opportunities. It can also contribute to faster economic growth and development.
Why does India need privatization?
India needs privatization to improve the efficiency of public enterprises, reduce the fiscal deficit, increase private sector participation, foster competition, and bring in advanced technology and global best practices.
What are the disadvantages of privatization?
Privatization can lead to job losses, widening income inequality, and reduced government control over important sectors. It may also prioritize profit over social welfare, potentially marginalizing less profitable communities or regions.
What are the disadvantages of privatization of banks in India?
Privatizing banks in India could result in higher service fees, reduced access to credit for economically weaker sections, and a focus on profitability rather than public welfare. It may also lead to job losses in the banking sector.
What are the disadvantages of privatization of education?
Privatization of education can increase educational inequality, making quality education unaffordable for lower-income families. It could lead to a focus on profit rather than student well-being and may compromise the quality of education.
Which is not a benefit of privatization?
Privatization is not always beneficial for the poor, as it can lead to reduced access to essential services like healthcare, education, and utilities for low-income communities.
What is negative about privatization?
Privatization can result in a loss of public control over vital services, increased costs, and the prioritization of profit over public welfare. It may also lead to layoffs and reduced job security for workers.
What are the disadvantages of being privately owned?
Being privately owned can limit transparency, reduce accountability to the public, and prioritize profits over public interest. It may also lead to less government intervention in case of market failures.
How does privatization affect education?
Privatization of education can lead to unequal access, with better-quality education being available to those who can afford it, while others may be left behind. It may also shift the focus from holistic education to business-driven models.
What are the advantages of privatization in education?
Privatization can lead to improved quality of education, better infrastructure, innovative teaching methods, and more diverse choices for students. It can also increase competition, driving improvements in education standards.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of going to a private school?
Advantages: Private schools often offer better facilities, smaller class sizes, personalized attention, and a more focused curriculum. Disadvantages: They can be expensive, may have limited diversity, and the quality of education can vary significantly.
What is the main advantage of privatization?
The main advantage of privatization is increased efficiency, as private entities tend to be more focused on cost-cutting, innovation, and quality service, driven by competition and profit motives.








