Table of Contents
Welcome to the Components of Food chapter for Class 6, an essential part of the NCERT CBSE syllabus. This chapter helps students learn about different food types and where they come from, emphasizing the importance of nutrients. A key focus here is on the extra questions that help students test their understanding and deepen their knowledge. These extra questions, including multiple-choice and detailed answers, challenge students to apply what they’ve learned and improve their exam preparation. Engaging with these questions is a great way for students to reinforce the chapter’s concepts and ensure they are ready for their tests.
Components of Food Class 6 Extra Questions Science Chapter 2
What do different food items contain? – Components of Food Extra Questions
Question 1. What are nutrients?
Ans.: Nutrients are the elements in food that are essential for the growth, development, and maintenance of the body.
Question 2. Which nutrients are essential for our body?
Ans.: Essential nutrients for our body include carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, dietary fiber, and water.
Question 3. What is nutrition?
Ans.: Nutrition is the process by which our body absorbs and utilizes the nutrients from our food to support its growth, development, and to generate energy
Question 4. What are the functions of food?
Ans.: The functions of food include:
- Providing essential nutrients for growth and bodily functions.
- Offering protection against diseases.
- Supplying energy needed for physical activities.
Question 5. Why does our body need nutritious food?
Ans.: Nutritious food is crucial as it fuels growth, provides energy for daily activities, and helps in disease prevention. It includes vital components like carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, fiber, and water. These nutrients perform specific functions and work synergistically to maintain health and support life.
Question 6. What are the different food groups?
Ans.: Food is commonly divided into three main groups:
- Energy-giving foods, such as carbohydrates and fats.
- Body-building foods, such as proteins.
- Protective foods, such as vitamins and minerals.
Question 7. How will you test for starch in a food sample?
Ans.: To test for starch, apply 2-3 drops of iodine solution on a small amount of the food sample. The presence of starch is indicated by a blue-black color change.
Question 8. How will you test for protein in a food sample?
Ans.: For a protein test, place a small sample of food in a test tube, add 10 drops of water and shake well. Then, add two drops of copper sulfate solution and ten drops of caustic soda. A violet color indicates the presence of protein.
Question 9. How will you test for fat in a food sample?
Ans. To test for fat, press a piece of food onto a piece of paper and crush it. If the paper becomes translucent and greasy at that spot, it indicates the presence of fat.
Question 10. What are the main carbohydrates found in our food?
Ans.: The primary carbohydrates in our food include starches and sugars.
Question 11. Name two energy-producing nutrients.
Ans.: The two energy-producing nutrients are carbohydrates and fats.
Question 12. Name two nutrients which protect the body from diseases.
Ans.: Vitamins and minerals are two nutrients that help protect the body from diseases.
Question 13. Name two food items which provide fats.
Ans.:
- Oil
- Ghee.
What do various nutrients do for our body? – Components of Food Extra Questions
Question 1: Name the food each rich in:
- dietary fibre
- sugar
- protein
- starch
- fat and oil
Ans.:
- Dietary fibre: Spinach, cabbage, okra.
- Sugar: Milk, bananas, sugarcane.
- Protein: Milk, meat, fish, eggs.
- Starch: Rice, wheat, pearl millet.
- Fat and oil: Butter, ghee, cheese, peanuts.
Question 2: Name the food needed:
- for strong bones and teeth
- to prevent scurvy
- to avoid constipation
- for warmth
- for growth
Ans.:
- For strong bones and teeth, sources of calcium include milk, buttermilk, cheese, green leafy vegetables, and ragi, while sources of phosphorus include cereals, pulses, fish, and meat.
- To prevent scurvy, which requires vitamin C, consume citrus fruits, green and red peppers.
- To avoid constipation, include roughage in your diet, primarily from plant-based foods containing cellulose, such as vegetables, fruits, and whole grains.
- For warmth, consume ghee, butter, meat, and fish.
- For growth, incorporate milk and green leafy vegetables.
Question 3: What are the roles of:
(a) carbohydrates,
(b) fats,
(c) vitamins, and
(d) minerals.
Ans.:
- Carbohydrates provide energy.
- Fats also serve as a source of energy.
- Vitamins:
- Essential for various physiological functions.
- Maintain health and protect against diseases.
- Necessary for proper organ function.
- Minerals:
- Strengthen bones and teeth.
- Contribute to blood production.
Question 4: What do you mean by staple food?
Ans.: Staple food refers to the primary food consumed to meet energy needs. Common examples in our diet include rice, chapati, and bread.
Question 5: What is the function of vitamins?
Ans.: Vitamins facilitate the proper utilization of other nutrients like carbohydrates and fats, often acting as co-enzymes in enzymatic reactions
Question 6: Name any two sources of Vitamin B.
Ans.:
- Milk
- Soybeans
Question 7: Name the vitamin present in orange.
Ans.: Vitamin C.
Question 8: What is the role of Vitamin C?
Ans.: Vitamin C supports growth, maintains healthy teeth, gums, and joints, and enhances the body’s disease-fighting capabilities.
Question 9: Write the names of fat-soluble vitamins.
Ans.: Vitamins A and D.
Question 10: Write the names of any two water-soluble vitamins.
Ans.:
- Vitamin B
- Vitamin C
Question 11: Write the sources of fat.
Ans.:Sources include vegetable oil, ghee, butter, milk, cheese, meat, fish, and cod-liver oil.
Question 12: What are the sources of carbohydrates?
Ans.: Sources include rice, wheat, maize, potatoes, sugar, and jaggery.
Question 13: What is roughage? Why its presence in our food is important?
Ans.: Roughage, mainly cellulose, is the fibrous part of plant foods. It is crucial for aiding bowel movement and preventing constipation. It is abundantly found in green vegetables like spinach, cabbage, okra, and beans.
Question 14: Name the main constituent of roughage.
Ans.: Cellulose.
Question 15: Which among the following provides maximum roughage to the diet if taken in equal amounts? Egg, cucumber, grapes, cabbage.
Ans.: Cabbage.
Question 16: Name the minerals which make our teeth and bones.
Ans.: Calcium and Phosphorus.
Question 17: What are various functions of proteins?
Ans.:
- Proteins are essential building materials of the body.
- They are integral to enzymes.
- They form muscles, skin, hair, and nails.
- They produce hemoglobin, which transports oxygen.
- They aid in blood clotting.
- They repair and replace damaged or dead cells.
- They enhance the body’s resistance to infections.
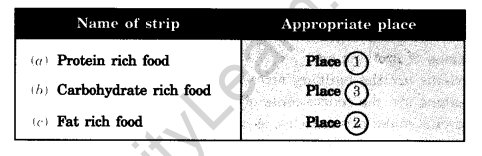
Question 18: Here are three strips. You have to paste them in figure at three places 1, 2, and 3. At which place will you paste each strip?
- Protein-rich food
- Carbohydrate-rich food
- Fat-rich food.
Ans.: (Place the appropriate labels on the figure as directed.)
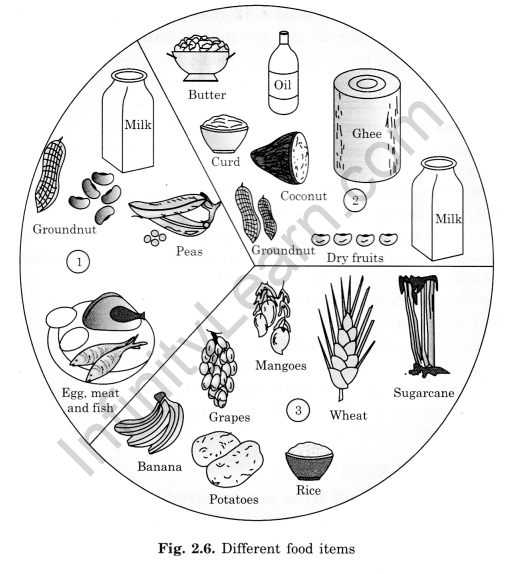 Answer:
Answer:
Names of strips and their appropriate places are:
Question 19: How are vitamins classified?
Ans.: Vitamins are divided into two groups:
- Water-soluble vitamins, such as vitamins B and C.
- Fat-soluble vitamins, including vitamins A, D, E, and K.
Balanced Diet – Components of Food Extra Questions
Question 1: What is a balanced diet?
Ans.: A balanced diet includes all essential food components (carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, water, and roughage) in appropriate proportions to maintain health.
Question 2: How many calories does a 12-year-old boy or girl need each day? How can the boy or girl get this in his/her diet?
Ans.: A 12-year-old boy or girl requires 2000-2200 calories daily. They can achieve this through a diet comprising dal, rice, roti, green vegetables, ghee, and a bit of jaggery.
Question 3: Why does a growing child need more minerals?
Ans.: Growing children require additional minerals like calcium and phosphorus to aid in the development and strengthening of bones.
Question 4: Write three important properties of a balanced diet.
Ans.: Three key properties of a balanced diet are:
- It’s rich in essential nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, and certain amino acids.
- It supplies sufficient material for growth, repair, and renewal of cells, tissues, and organs.
- It provides the necessary energy for bodily functions.
Question 5: What is obesity?
Ans.: Obesity is a condition resulting from excessive intake of fatty foods leading to fat accumulation in the body.
Question 6: Explain why people who eat seafood do not suffer from goitre.
Ans.: Goitre is typically caused by iodine deficiency. Seafood is high in iodine, helping prevent goitre in individuals who regularly consume it.
Deficiency diseases – Components of Food Extra Questions
Write the sources and deficiency diseases of the vitamins ‘A’, ‘B’ complex, C, D, E and K.
Answer:
| Vitamins | Sources | Deficiency diseases |
| 1. Vitamin A | Milk, butter, yellow fruits and vegetables, egg yolk, liver oil of fish. | Xerophthalmia, Night blindness, anaemia |
| 2. Vitamin B complex | Milk, egg, green vegetables, cheese, meat, germinating seeds, yeast and unpolished rice. | Beriberi |
| 3. Vitamin C | Citrus fruits, green and red peppers. | Scurvy |
| 4. Vitamin D | Milk, egg, fish, liver oil, sunlight. | Rickets |
| 5. Vitamin E | Vegetable seeds, eggs, sweet potatoes, oil, meat, sprouted grains. | Sterility |
| 6. Vitamin K | Egg yolk, liver, cheese, tomato, cabbage, soybean, cauliflower. | Improper coagulation of blood |
Question 5: What is anaemia? What are the symptoms of anaemia?
Ans.: Anaemia is a condition caused by iron deficiency. Symptoms include a pale appearance, easy fatigue, weight loss, and white nails.
Question 6: Why is it advised to take iodised salt?
Ans.: Iodised salt is recommended because it helps prevent iodine deficiency, which can cause thyroid gland enlargement, stunted growth, and mental impairment. Iodised salt assists in maintaining adequate iodine levels in the body.
Objective Type Questions – Components of Food Extra Questions
Question 1. Match the following items given in Column A with that in Column B:
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) Energy giving food | (i) Vitamins and minerals |
| (b) Body building food | (ii) Iodine |
| (c) Protective food | (iii) Fats, carbohydrates |
| (d) Test for fat | (iv) Copper sulphate and caustic soda |
| (e) Test for starch | (v) Oily patch on paper sheet |
| (f) Test for protein | (vi) Proteins |
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) Energy giving food | (iii) Fats, carbohydrates |
| (b) Body building food | (vi) Proteins |
| (c) Protective food | (i) Vitamins and minerals |
| (d) Test for fat | (v) Oily patch on paper sheet |
| (e) Test for starch | (ii) Iodine |
| (f) Test for protein | (iv) Copper sulphate and caustic soda |
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words:
- For proper ……………….. and …………………… our bodies need adequate food.
- Proteins build ………….. material.
- Non-living machines burn the fuel at ……………… temperature while living machines burn their food at ………………… temperature.
- Starch is a ……………… of sugar.
- ……………….. gives blue colour with iodine.
- Proteins are made up of …………………… .
- Skin, hair and nails are …………………… .
- Co-enzymes are nothing but …………….. .
- Vitamin C causes ……………….. when found deficient.
- Our body contains ……………………. of water.
- Most of the reactions in our body occur in ……………. solutions.
- Balanced diet is one containing all ……………….. .
- Deficiency of ……………. causes rough skin, weak eyesight and thinness of body.
- Excess intake of………………… over a large period may damage kidneys.
- Lack of ……………….. leads to lethargy, inactivity and feeling of tiredness.
- Intake of inadequate quantities of proteins may ………………….. the growth and development of children.
Answer:
Question 3. State whether the statements given below are True or False:
- Deficiency of vitamin A makes our bones weak.
- Deficiency of iron causes paleness.
- Calcium is necessary for strong bones and teeth.
- Deficiency of vitamin B helps to increase our appetite.
- Deficiency of vitamin D causes swollen and bleeding gums.
- Carbohydrates are the main source of energy in our diet.
- Expensive food is not always the best food
- Protein is a staple food.
- Haemoglobin is a carbohydrate.
- Cotton and paper are carbohydrates.
- Tomatoes contain vitamin C.
- Eating lady finger makes you good in mathematics.
Answer:
- Deficiency of vitamin A makes our bones weak. – False
- Deficiency of iron causes paleness. – True
- Calcium is necessary for strong bones and teeth. – True
- Deficiency of vitamin B helps to increase our appetite. – False
- Deficiency of vitamin D causes swollen and bleeding gums. – False
- Carbohydrates are the main source of energy in our diet. – True
- Expensive food is not always the best food – True
- Protein is a staple food. – False
- Haemoglobin is a carbohydrate. – False
- Cotton and paper are carbohydrates. – True
- Tomatoes contain vitamin C. – True
- Eating lady finger makes you good in mathematics. – False
Class 6 Components of Food MCQs Extra Questions
Choose the correct option in the following questions:
Question 1: The food components needed by our body are called
- ingredients
- nutrients
- fragments
- ornaments
Ans. b)
Question 2: Carbohydrates can be tested by using
- iodine solution
- caustic soda
- copper sulphate
- fehling solution
Ans. a)
Question 3: Which one of the following is an energy giving component?
- Protein
- Vitamins and minerals
- Roughage
- Carbohydrates and fats
Ans. d)
Question 4: Vitamins and minerals are
- protective food
- energy giving food
- body building food
- roughage
Ans. a)
Question 5: Roughage helps in
- protecting our body from diseases
- movement of bowel
- providing energy
- building and repair of various body parts
Ans. b)
Question 6: Scurvy is caused due to the deficiency of
- vitamin A
- vitamin B
- vitamin C
- vitamin D
Ans. c)
Question 7: Diseases caused due to the deficiency of vitamins are known as
- dietary diseases
- chronic diseases
- deficiency diseases
- transmitted diseases
Ans. c)
Question 8: All the deficiency diseases can be prevented by
- cleanliness
- taking medicine at proper time
- vaccination
- taking balanced diet
Ans. d)
Question 9: Which of the following food items contains carbohydrates?
- Rice
- Gram
- Cabbage
- Pulses
- Ans. a)
Question 10: Night blindness is caused due to deficiency of
- vitamin A
- vitamin B
- vitamin C
- vitamin D
Ans. a)
FAQs on Class 6 Science Chapter 2 Components of Food Extra Questions
What are the components of food class 6th chapter 2 science?
The components of food are proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, minerals, and water. These are essential for providing energy and nutrients to our bodies.
What are the components of food Class 6 short note?
In Class 6, the components of food are proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, minerals, and water. These components are crucial for maintaining health and providing energy.
Why choose Infinity Learn for components of food class 6 extra questions?
Infinity Learn offers extra questions for Class 6 components of food to enhance understanding. They cover topics like proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, minerals, and their importance in nutrition.
What are main components of food?
The main components of food are proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, minerals, and water. These elements are vital for energy production, growth, and overall health.
What are the 4 components of food?
The four main components of food are proteins, carbohydrates, fats, and water. These components provide energy, essential nutrients, and support various bodily functions.