Introduction
Sodium nitrate, with the chemical formula NaNO3, is an inorganic compound composed of sodium cations (Na+) and nitrate anions (NO3-). It is a white crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water. Sodium nitrate is commonly found in nature, particularly in mineral deposits and as a component of certain types of soil.
Uses of Sodium Nitrate
It has various applications across different industries and sectors.
In agriculture, sodium nitrate is used as a fertilizer due to its high nitrogen content. It provides plants with essential nitrogen nutrients necessary for growth and development. Additionally, sodium nitrate can be utilized as an ingredient in livestock feed to enhance protein synthesis.
The chemical industry employs sodium nitrate in the production of various compounds, such as nitric acid, which is used in the manufacture of fertilizers, explosives, and dyes. Sodium nitrate can also serve as an oxidizing agent in certain chemical reactions.
Furthermore, sodium nitrate finds applications in the food industry as a food preservative. It helps inhibit bacterial growth and prevents spoilage in cured meats, such as bacon and ham. Additionally, sodium nitrate contributes to the characteristic pink color of cured meats.
It is important to handle sodium nitrate with caution as it can be harmful if ingested or inhaled in large amounts. It is advisable to follow proper safety protocols and guidelines when working with sodium nitrate to ensure safe handling and use.
Chemical Formula of Sodium Nitrate
The chemical formula for sodium nitrate is NaNO3.
In this formula:
- Na represents the chemical symbol for sodium.
- N represents the chemical symbol for nitrogen.
- O represents the chemical symbol for oxygen.
- The subscript number 3 indicates that there are three oxygen atoms in the compound.
Sodium nitrate is a compound composed of sodium ions (Na+) and nitrate ions (NO3-). It is commonly used in fertilizers, food preservatives, and pyrotechnics.
Structural Formula of Sodium Nitrate
The structural formula of sodium nitrate (NaNO3) represents the arrangement of atoms in the compound. However, sodium nitrate does not have a complex structural formula since it is an ionic compound, consisting of sodium cations (Na+) and nitrate anions (NO3-).
In the crystal lattice structure of sodium nitrate, the sodium cations and nitrate anions are arranged in a three-dimensional network. The sodium cations are surrounded by six nitrate anions, and each nitrate anion is surrounded by six sodium cations. The arrangement forms a repeating pattern throughout the crystal lattice.
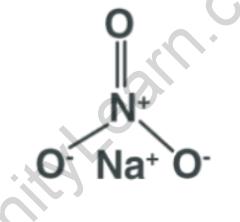
Physical Properties of Sodium Nitrate Formula
- Appearance: Sodium nitrate is a white, crystalline solid in its pure form.
- Melting Point: The melting point of sodium nitrate is approximately 308oC (586 degrees Fahrenheit). It can undergo decomposition at higher temperatures.
- Solubility: Sodium nitrate is highly soluble in water. It readily dissolves in water, resulting in a clear solution.
- Crystal Structure: Sodium nitrate crystallizes in a trigonal crystal system. It forms rhombohedral crystals with a characteristic shape.
- Odour and Taste: Sodium nitrate is odorless and has a slightly salty taste.
- Electrical Conductivity: In its solid state, sodium nitrate is a poor conductor of electricity. However, when dissolved in water, it dissociates into sodium and nitrate ions, allowing it to conduct electricity.
Chemical Properties of Sodium Nitrate Formula
- Oxidizing Agent: Sodium nitrate is a strong oxidizing agent. It has the ability to transfer oxygen to other substances, promoting oxidation reactions.
- Decomposition: When heated to high temperatures, sodium nitrate undergoes decomposition. It breaks down into sodium nitrite (NaNO2) and oxygen gas (O2).
- Reaction with Acids: Sodium nitrate reacts with acids, releasing nitric acid (HNO3). This reaction is often used in the laboratory to produce nitric acid.
- Reaction with Metals: Sodium nitrate can react with certain metals, such as magnesium, to produce metal nitrates and evolve nitrogen dioxide gas (NO2).
- Solubility: Sodium nitrate is highly soluble in water. This property allows it to readily dissolve in water, forming a solution of sodium ions (Na+) and nitrate ions (NO3-).
- Acid-Base Reactions: Sodium nitrate can undergo acid-base reactions. For example, it can react with strong bases to form corresponding salts.
- Explosive Properties: While sodium nitrate itself is not explosive, it is commonly used in combination with other substances, such as fuels or oxidizable materials, to create explosives.
Solved Examples on Sodium Nitrate Formula
Example 1: Calculate the molar mass of sodium nitrate (NaNO3).
Solution: To calculate the molar mass, we need to determine the atomic masses of each element in the formula and sum them up.
Molar mass of Na = 22.99 g/mol
Molar mass of N = 14.01 g/mol
Molar mass of O = 16.00 g/mol (multiplied by 3, since there are three oxygen atoms)
Molar mass of NaNO3 = (22.99 g/mol) + (14.01 g/mol) + (16.00 g/mol * 3)
= 85.00 g/mol
Example 2: What is the percent composition of sodium nitrate (NaNO3) by mass?
Solution: To find the percent composition, we need to determine the mass of each element in the formula and calculate its percentage in relation to the total molar mass.
Molar mass of NaNO3 = 85.00 g/mol
Mass of Na = 22.99 g/mol
Mass of N = 14.01 g/mol Mass of O = 16.00 g/mol (x3, since there are three oxygen atoms)
Total mass = (22.99 g/mol) + (14.01 g/mol) + (16.00 g/mol * 3) = 85.00 g/mol
Percent composition of Na = (22.99 g/mol / 85.00 g/mol) * 100% = 27.05%
Percent composition of N = (14.01 g/mol / 85.00 g/mol) * 100% = 16.48%
Percent composition of O = (16.00 g/mol * 3 / 85.00 g/mol) * 100% = 56.47%
Frequently Asked Questions on Sodium Nitrate Formula
1: What is the common name for the formula sodium nitrate?
Answer: The common name for the chemical formula NaNO3 is “sodium nitrate.” It is also known by other names such as Chile saltpeter, soda niter, or simply nitrate of soda. The name Chile saltpeter serves as a historical reference to the origin of sodium nitrate and its importance in various industries during the time when Chile was the primary source of this compound.
2: What is the purpose of sodium nitrate?
Answer: Sodium nitrate (NaNO3) serves various purposes across different industries and applications. Some common uses and purposes of sodium nitrate include:
- Fertilizer: Sodium nitrate is a valuable source of nitrogen, an essential nutrient for plant growth. It is commonly used as a fertilizer to provide nitrogen to crops and improve their overall health and productivity.
- Food Preservative: Sodium nitrate is used as a food preservative, primarily in cured and processed meats such as bacon, ham, and hot dogs. It helps to inhibit the growth of bacteria, prevent spoilage, and maintain the color and flavor of the meat products.
- Oxidizer: Sodium nitrate is an effective oxidizer, meaning it can provide oxygen to support combustion. It is used in various pyrotechnic compositions, fireworks, and explosives to facilitate controlled and controlled release of energy.
- Glass Production: Sodium nitrate is used in the manufacturing of glass, particularly in the production of specialty glasses, such as laboratory glassware and certain types of glass used in the automotive industry.
- Heat Transfer Fluid: Sodium nitrate is also utilized as a heat transfer fluid in certain applications, such as solar thermal power plants and heat storage systems. It has the ability to absorb and release heat efficiently, making it useful in these thermal energy applications.
- Stain Remover: Sodium nitrate is sometimes used as an ingredient in stain removers or rust removers. It can help to break down and dissolve stubborn stains or rust deposits.
3: Why is it called sodium nitrate?
Answer: The name “sodium nitrate” reflects the composition and structure of the compound. It consists of sodium (Na) and nitrate (NO3) ions.
The term “sodium” refers to the element sodium (Na), which is an alkali metal commonly found in various compounds. Sodium is highly reactive and readily forms ionic compounds, including sodium nitrate.
The term “nitrate” refers to the polyatomic ion NO3, which is composed of one nitrogen atom bonded to three oxygen atoms. The nitrate ion is negatively charged, and it combines with the positively charged sodium ion (Na+) to form the compound sodium nitrate (NaNO3).
4: What type of bond is sodium nitrate?
Answer: Sodium nitrate (NaNO3) forms an ionic bond.
In an ionic bond, electrons are transferred from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of ions. In the case of sodium nitrate, the sodium (Na) atom donates one electron to the nitrate (NO3) ion. This transfer of electrons creates a positively charged sodium ion (Na+) and a negatively charged nitrate ion (NO3-).
The strong electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions holds them together in a crystal lattice structure. This ionic bond is responsible for the solid-state properties of sodium nitrate, such as its high melting point and the ability to conduct electricity when dissolved in water.
5: What is a substitute for sodium nitrate?
Answer: There are several substitutes for sodium nitrate depending on the specific application. Here are a few alternatives commonly used:
- Potassium Nitrate: Potassium nitrate (KNO3) is a compound similar to sodium nitrate in terms of its chemical properties. It is often used as a substitute in fertilizers, food preservation, and certain pyrotechnic applications.
- Potassium Chloride: Potassium chloride (KCl) can be used as a substitute for sodium nitrate in some applications. It is commonly used as a fertilizer and has similar effects on plant growth.
- Potassium Nitrite: Potassium nitrite (KNO2) can be used as a substitute for sodium nitrate in food preservation, particularly in curing meat products. It helps inhibit bacterial growth and maintains the color and flavor of the meat.
- Calcium Nitrate: Calcium nitrate (Ca(NO3)2) is an alternative to sodium nitrate in fertilizers. It provides a source of nitrogen and calcium to promote plant growth.
- Ammonium Nitrate: Ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3) can be used as a substitute for sodium nitrate in certain applications. It is commonly used as a nitrogen fertilizer and also has uses in explosive formulations.
6: Is sodium nitrate good for humans?
Answer: Sodium nitrate, when consumed within regulatory limits, is generally considered safe for humans. It is commonly used as a food preservative in cured meats to prevent bacterial growth and extend shelf life. However, excessive consumption or the formation of nitrosamines during high-heat cooking can pose potential health risks. Adhering to recommended limits and consuming a balanced diet is important. It is advisable to consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and to follow regulatory guidelines for safe usage.
7: Why is NaNO3 called sodium nitrate?
Answer: NaNO3 is called sodium nitrate because it is composed of sodium (Na) cations and nitrate (NO3-) anions. The name “sodium” refers to the metallic element sodium, which is a component of the compound. The term “nitrate” refers to the polyatomic ion NO3-, which consists of one nitrogen atom bonded to three oxygen atoms. Thus, the compound is named sodium nitrate to indicate its composition and the elements present in it.
8: Is NaNO3 strong or weak?
Answer: Sodium nitrate (NaNO3) is considered a strong electrolyte. When dissolved in water, it dissociates completely into sodium ions (Na+) and nitrate ions (NO3-). These ions are highly reactive and contribute to the strong conductivity of the solution. As a strong electrolyte, sodium nitrate readily conducts electricity and exhibits typical properties associated with strong ionic compounds.



