Table of Contents
Subject specialists have designed NCERT solutions for Science Class 7 Chapter 4 Heat which includes thorough solutions for NCERT textbook. These NCERT solutions are updated according to the latest CBSE syllabus for 2024-25 and are provided in easy language for understanding. Tips and tricks are also provided.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 4 Heat
These NCERT solutions for class 7 are provided so a student can clear his doubts and get help with deep understanding of the concept. Discover comprehensive NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 4, Heat. This chapter delves into the essential concepts of heat, its transfer, and its effects on different materials. Our solutions provide clear explanations and step-by-step answers to help students grasp the principles of thermal energy and its applications effectively. Perfect for enhancing understanding and preparing for exams, these solutions cover all the key topics and questions from the chapter. Access the full PDF and strengthen your knowledge of heat with detailed explanations and practice problems. Also you can refer them to make the class 7 science chapter 4 notes and revisions notes. You can download class 7 science chapter 4 pdf question answer from the given pdf.

NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 4 PDF Download
In below pdf we have provided NCERT class 7 science chapter 4 pdf question answer from class 7 science NCERT textbook
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 4 Questions Answers
Here are all the science chapter 4 class 7 question answer form NCERT textbook for the year 2024-25
Class 7 Science Chapter 4 Exercise Question Answer Page No. 34-35
1. State similarities and differences between the laboratory thermometer and the clinical thermometer.
Ans.
Similarities
- Both are used to measure temperature.
- They are made of long, narrow, uniform glass tubes with a bulb at one end.
- Mercury is used as the measuring fluid.
- They are marked in Celsius scale.
Differences
- Laboratory thermometer is larger and broader compared to clinical
- Laboratory thermometers are marked from -10°C to 110°C, while clinical thermometers are marked from 35°C to 42°C only.
- Laboratory thermometers are used to measure the temperature of various objects in different states.
- Clinical thermometers are specifically designed to measure human body temperature.
- There is no kink in laboratory thermometers.
- Clinical thermometers have a kink to prevent the mercury level from falling on its own.
- When noting readings with a laboratory thermometer, it has to be in contact with the object whose temperature is being measured.
- Clinical thermometer readings are observed when it is outside the body.
2. Give two examples each of conductors and insulators of heat.
Ans.
Examples of conductors: Aluminium, iron, copper, etc.
Examples of insulators: Water, air, etc.
3. Fill in the blanks :
- The hotness of an object is determined by its __________.
- Temperature of boiling water cannot be measured by a _____________ thermometer.
- Temperature is measured in degree ______________.
- No medium is required for transfer of heat by the process of __________.
- A cold steel spoon is dipped in a cup of hot milk. Heat is transferred to its other end by the process of ______________.
- Clothes of ______________ colours absorb heat better than clothes of light colours.
Ans.
- How hot an object is determined by its hotness or coldness.
- The temperature of boiling water cannot be measured by a clinical thermometer.
- Temperature is measured in degrees of hotness (or coldness).
- No medium is required for the transfer of heat by the process of radiation.
- A cold steel spoon is dipped in a cup of hot milk. It transfers heat to its other end by the process of conduction.
- Clothes of dark colors absorb heat better than clothes of light color.
| Column-I | Column-II |
| (i) Land breeze blows during | (a) summer |
| (ii) Sea breeze blows during | (b) winter |
| (iii) Dark coloured clothes are preferred during | (c) day |
| (iv) Light coloured clothes are preferred during | (d) night |
Ans.
| Column-I | Column-II |
| (i) The land breeze blows during | (d) night |
| (ii) The sea breeze blows during | (c) day |
| (iii) Dark coloured clothes are preferred during | (b) winter |
| (iv) Light coloured clothes are preferred during | (a) summer |
5. Discuss why wearing more layers of clothing during winter keeps us warmer than wearing just one thick piece of clothing.
A. Different layers of clothing trap air inside them. Air is a poor conductor of heat, so it prevents the flow of heat from the body to the cold surroundings and makes the body feel warm.
Look at the figure. Mark where the heat is being transferred by conduction, by convection, and by radiation.
6. Look at Fig. 4.13. Mark where the heat is being transferred by conduction, by convection and by radiation.
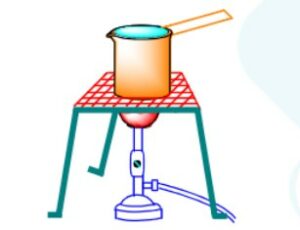
Ans.
- By conduction: Heat transfer occurs from the lower surface to the upper surface of the pan.
- By convection: Heat moves from the lower box to the upper region of pan water.
- By radiation: Heat transfers from the flame to the bottom of the pan.
7. In places of hot climate it is advised that the outer walls of houses be painted white. Explain.
Light-coloured surfaces reflect most of the heat that falls on them, resulting in the surface remaining cooler. Therefore, it is advised to paint the outer walls of houses white in places with hot climates.
8. One litre of water at 30°C is mixed with one litre of water at 50°C. The temperature of the mixture will be
- 80°C
- More than 50°C but less than 80°C
- 20°C
- Between 30°C and 50°C
Answer: d) Between 30°C and 50°C.
9. An iron ball at 40°C is dropped in a mug containing water at 40°C. The heat will
- Heat flows from the iron ball to the water.
- Heat does not flow from the iron ball to the water or from water to the iron ball.
- Heat flows from the water to the iron ball.
- The temperature of both increases.
Answer: b) Heat does not flow from the iron ball to the water or from water to the iron ball.
10. A wooden spoon is dipped in a cup of ice cream. Its other end
- Becomes cold by the process of conduction.
- Becomes cold by the process of convection.
- Becomes cold by the process of radiation.
- Does not become cold.
Answer: d) Does not become cold.
Reasons for Copper Bottoms on Stainless Steel Pans:
- Possible Reasons:
- a) Copper bottom makes the pan more durable.
- b) Such pans appear colourful.
- c) Copper is a better conductor of heat than stainless steel.
- d) Copper is easier to clean than stainless steel.
- Answer: c) Copper is a better conductor of heat than stainless steel.
- Chapter 1 Nutrition In Plants
- Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals
- Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric
- Chapter 4 Heat
- Chapter 5 Acids, Bases, and Salts
- Chapter 6 Physical and Chemical Changes
- Chapter 7 Weather, Climate, and Adaptations of Animals to Climate
- Chapter 8 Winds, Storms, and Cyclones
- Chapter 9 Soil
- Chapter 10 Respiration in Organisms
- Chapter 11 Transportation in Animals and Plants
- Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants
- Chapter 13 Motion and Time
- Chapter 14 Electric Current and Its Effects
- Chapter 15 Light
- Chapter 16 Water: A Precious Resource
- Chapter 17 Forests: Our Lifeline
- Chapter 18 Wastewater Story
Introduction to NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 4 Heat
In the chapter, students learn about how we find out whether an object is hot or cold, how to measure temperature end it talks about the kind of clothes we wear in summer and winters. Then it covers the laboratory thermometer and transfer of heat.
Important Topics covered in NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 4 Heat
- Hot and cold
- Temperature measurement
- Thermometers
- Heat transfer
- Clothes in different climatic conditions
Students can use these NCERT Solutions for quick revisions during exam preparation
About Infinite Learn Solutions
Infinite Learn mission is to create world-class learning content for students. We are focussed on raising the students learning abilities. These Solutions have been structured very carefully to give several benefits to the students that utilize these study materials. That is why, these are crafted by subject matter experts to focus on concept and its explanation.
For any type of support related to the NCERT Solutions for Class 7 given here, students can approach our support team who will help clear all their doubts. Students can also check out Infinite Learn for a more efficient learning experience.
| Other Resources for Class 7 | |
| NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 7 | NCERT Books for Class 7 |
| Class 7 Worksheets | NCERT Solutions for Class 7 |
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 4 Heat
What is heat?
Heat is the transfer of energy from a warmer object to a cooler one. In Class 7, heat is studied as the process of molecules moving from higher to lower temperatures.
What causes the heat to flow?
Heat flows due to the movement of molecules from regions of higher temperature to lower temperature. This movement is a natural process that equalizes temperatures in a system.
What will absorb heat?
In Class 7, materials like metals, water, and air can absorb heat. When these materials absorb heat, their temperature increases as they gain thermal energy.
What's the SI unit of heat?
The SI unit of heat is the Joule. It is a measure of energy transfer and is used to quantify the amount of heat transferred between objects or systems.
What are the similarities between laboratory and clinical thermometers in these NCERT Solutions?
Both the thermometers are made up of glass and have long narrow glass tubes. Both of them have a bulb at one end. Mercury is present in the bulbs of both thermometers. Both the thermometers have celsius scale.
Is NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 4 important from an exam point of view?
Yes, these NCERT Solutions deals with solutions for all questions given in NCERT Textbook Science for Class 7. The most of the questions coming in the exams are from these exercises. By studying these concepts, you can achieve good grades.
What are the topics covered in these NCERT Solutions?
The topics covered are – Hot and cold, Temperature measurement, Thermometers, Heat transfer, Clothes in different climatic conditions.









