Political Science Class 12 Important Questions Chapter 4 Alternative Centres of Power
1 Mark Questions
Question 1.
Why was ASEAN established? (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
ASEAN was established to accelerate economic growth and through that social progress and cultural development.
Question 2.
What does the logo on the ASEAN flag symbolise? (All India 2016)
Answer:
On the ASEAN logo, the ten stalks of paddy (Rice) represent the ten South East Asian countries bound together in friendship and solidarity. The circle symbolises the unity of ASEAN.
Question 3.
Under which plan did the USA extend financial support for reviving Europe’s economy after the Second World War? (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
The USA extended massive financial help for reviving Europe’s economy under the plan named ‘Marshall Plan’.
Question 4.
Name any two members of the EU, who are permanent members of the UN Security Council. (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
The two member states of EU, who are permanent members of the UN Security Council are :
- Britain
- France
Question 5.
Trace the evolution process of the European Union, (All indin 2014)
Answer:
The EU has gradually evolved from an economic union to a political union. It became more a nation-state. It does not have its Constitution.
Question 6.
What was the objective of founding the European Union? (All indin 2013)
Answer:
The general objectives of the founding the European Union were
- To have an area of freedom, security and justice without internal frontier.
- Promotion of scientific and technological advance.
Question 7.
What is meant by ASEAN way? (All India 2012)
Answer:
It is a kind of interaction which is informal, unofficial, non-confrontationist and cooperative.
Question 8.
What is meant by the ‘Maastricht Treaty’? (All India 2009)
Answer:
‘The Treaty of Maastricht’ was signed on 7th February 1992, establishing the European Union (EU) and laid the foundation for common foreign and security policy, cooperation and justice, home affairs and the creation of a single currency.
Question 9.
In 1992 which regional organisation was formed? (All India 2009)
Answer:
The regional organisation formed in 1992 was the European Union.
Question 10.
What do ASEAN and FTA stand for? (Delhi 2008)
Answer:
ASEAN stands for Association of South East Asian Nations and FTA stands for Free Trade Area.
Question 11.
Mention the full form of the following (Delhi (C) 2008)
(i) CTBT
(ii) ASEAN
Answer:
(i) CTBT—Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty
(ii) ASEAN—Association of South East Nations
2 Marks Questions
Question 1.
State any two features of the European Union that make it an influential organisation. (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
Two features of the European Union that make it an influential organisation are :
- EU has evolved over time from an economic union to political union. It has its own flag, anthem, founding date and currency.
- EU’s share of world trade is three times larger than that of the US.
Question 2.
When was the ASEAN regional forum established? What were its main objectives? (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
The ASEAN regional forum was established in 1994. The main objectives of ASEAN were :
- To accelerate economic growth and through that social progress and cultural development.
- To promote regional peace and stability based on the rule of law and the principles of the United Nations Charter.
Question 3.
In the European Union Flag, what does the symbol of ‘twelve gold stars in a circle’ signify? (Delhi 2012, 2011)
OR
What does the circle with golden stars on the European Union flag stand for? (Delhi 2010)
Answer:
The circle stands for solidarity and peace among the people of Europe. It contains twelve stars which symbolise perfection, completeness and unity.
Question 4.
Explain India’s improving relationship with China. (Delhi 2011)
Answer:
After the end of the Cold War, significant changes have been seen in the relationship between India and China. Rajiv Gandhi’s visit in December 1988 then both governments have taken measures to contain conflict and maintain ‘peace and tranquillity’ on the border.
Cultural exchanges and cooperation agreements are signed by both. Increased transportation and communication established more sound relationship.
Question 5.
What is the meaning of Panchsheel? (All India 2011)
OR
What does Panchsheel imply? (All India 2009)
Answer:
The five principles of peaceful coexistence are known Panchsheel which formed the bedrock of Indo-China relationship. Their first formal codification in treaty form took place in 1954 when an agreement between India and China was signed. Panchsheel act as guiding principle for Indo-China relation.
Question 6.
Mention any two steps taken by China to improve its economy. (Delhi 2010)
Answer:
Two steps taken by China to improve its economy are:
- Deng Xiaoping in 1978, announced ‘Open Door Policy’. This aimed at the generation of high productivity by investments of capital and technology from abroad.
- Privatisation of agriculture and privatisation of industry was done.
Question 7.
What led to the formation of the European Union? (Delhi 2009)
Answer:
European Union was formed after the end of the Cold War. After the disintegration of USSR, the European Union was formed to consolidate the process of reviving the shattered economies of European countries and to get massive US financial help under the Marshall Plan.
Question 8.
What was the Marshall Plan? How did it pave the way for the formation of OEEC (Organisation of European Economic Cooperation)? (All India 2008: Delhi (C) 2008)
Answer:
Marshall Plan was a plan under Mr George C Marshall, US Secretary. America extended huge financial help for reviving Europe’s economy. New collective security structure was created under NATO. Under the Marshall Plan, OEEC was created in 1948, to help West European states. It acted as a platform where the West European states began to cooperate on trade and economic issues.
Question 9.
When was the European Union established? Mention any two kinds of influence that were exercised by the European Union, (All India to 2008)
Answer:
European Union was established on 7th February 1992 after signing the Treaty of Maastricht. Influences that were exercised by the EU are :
- Economic influence
- Political and diplomatic influence
4 Marks Questions
Question 1.
Describe India-China relations from 1947 to 1962. (All India, 2017,2016)
OR
Evaluate the causes of the strained relations between India and China. (All India 2015)
OR
Describe India’s relations with China from independence to 1962. (All India 2013)
Answer:
The India-China relations examined are as below: Friendly relations
- After the Chinese Revolution in 1949, India was one of the first countries to recognise the communist government.
- Prime Minister Nehru and Chinese Premier Zhou Enlai adopted Panchsheel, the Five Principles of Peaceful Co-existence on 29 April 1954.
The Chinese invasion and strained relationship
- China annexed Tibet in 1950 and thus removed a historical buffer between the two countries.
- Tibetan spiritual leader Dalai Lama had sought asylum in India in 1959. China alleged that India was allowing anti-China activities in India.
- Boundary disputes arose between the two countries over Aksai-China area in the Ladakh region and NEFA in the Eastern region.
- The boundary disputes led to a massive Chinese invasion in October 1962. Finally, China declared a unilateral ceasefire but relations between the two countries remained strained.
Question 2.
What were the two major policy decisions taken by the Chinese leadership in the 1970s? All India 2016
OR
Describe any four new economic policies of China to make it grow at a faster rate. Delhi 2013
OR
Explain the new economic policies of China since 1978. (All India 2013)
Answer:
China’s economic success has been linked to its rise as a great power :
The major policy decisions new economic policies of China were :
- China ended its political and economic isolation with the establishments of relations with the United States in 1972.
- Four modernisations (agriculture, industry, science and technology and military) were proposed by Premier Zhou Enlai in 1973.
- Den Xiaoping declared the ‘Open Door Policy’ and rapid economic reforms in China. It was meant to generate higher productivity by investments of capital and technology from other countries.
- The privatisation of agriculture in 1982 was followed by the privatisation of industry in 1998.
- The trade barriers were eliminated only in Special Economic Zones (SEZs) where foreign investors could set up enterprises.
Question 3.
In which four ways did the new economic policy of China benefit its economy? (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
The four ways by which the new economic policy of China benefitted its economy are :
- Privatisation of agriculture led to a remarkable rise in agriculture production and rural incomes.
- The rural industry too grew due to high personal savings in the rural economy.
- The SEZs led to a phenomenal rise in foreign trade. It made China the most important destination for foreign direct investment (FDI) anywhere in the world.
- It helped in strengthening its relations with WTO in 2001 and plans to deepen its integration into the world economy.
Question 4.
Mention any four significant changes in Indo-China relations that have taken place after the Cold War. (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
End of the Cold War marked various changes in the relationship between India and China. Four significant changes in Indo-China relations took place after the Cold war was:
- Both India and China consider themselves as rising powers in international politics. After the visit of Rajiv Gandhi in 1988, both governments tried to maintain ‘peace and silence’ on the border.
- Agreements regarding cultural exchanges and cooperation were signed. Four border posts were also opened.
- Trade between India and China grew at 30 per cent per year since 1999.
- An increase in bilateral trade from $338 million in 1992 to more than $ 18 billion in 2006 was seen. India and China are following the same policies in international economic institutions like the World Trade Organisation.
- Leaders from both countries frequently visit each other’s nation and this way they get familiar with each other. Through an increase in transportation and communication links and working on common economic interests development of sound economic relationship has been taking place.
Question 5.
In spite of the improvement in the Chinese economy, there have been negative consequences affecting the people of China. Mention any four such consequences. (Delhi 2016, All India 2016)
OR
Highlight any four drawbacks in the changed Chinese economic system. (Delhi (C) 2008)
Answer:
Even though the Chinese economy has improved dramatically, there have been negative consequences affecting the people of China.
The four negative consequences or drawbacks in the changed Chinese Economic System were :
- The benefits of the reforms have not been equally received. Approximately 100 million people are still unemployed.
- Female employment and conditions of work are as bad as in Europe of the 18th and 19 th centuries.
- Corruption and environmental degradation have increased.
- There has been a rise in economic inequality between rural and urban residents and coastal and inland provinces.
Question 6.
Assess the role of ASEAN as an economic association. (All India 2016)
OR
Why does ASEAN still remain principally an economic community? (Delhi 2015)
Answer:
ASEAN was established primarily for accelerating the economic growth and through that ‘social progress and cultural development,’ It still remains principally an economic community. Though the ASEAN region as a whole is a much smaller economy compared to the US, the EU, and Japan, however, its economy is growing much faster than all these. This accounts for the growth in its influence both in the region and beyond.
The objectives of the ASEAN are to create a common market and production base within ASEAN states. ASEAN as an economic community also committed to improving the existing ASEAN. Dispute Settlement Mechanism to resolve economic disputes. ASEAN has focussed in creating a Free Trade Area (FTA) for investment, labour, and services. The US and China have already negotiated FTA with ASEAN.
The current economic strength of ASEAN particularly its economic relevance as a trading and investment partner to the growing Asian economies such as India and China makes this an attractive proposition. India signed FTA with two ASEAN members, Singapore and Thailand, and trying to sign an FTA with ASEAN itself.
ASEAN’s strength, however, lies in its policies of interaction and consultation with member states, with dialogue partners and with non-aligned organisations.
Question 7.
How has the European Union evolved over time from an economic union to an increasingly political one? (Delhi 2015)
OR
What led the evolution of the European Union from an economic union to an increasingly political one? (Delhi 2011)
Answer:
In the following ways, the European Union was evolved from economic to political union :
- Its aim was to make Europe politically, economically and culturally strong enough to face powers like the USA, Russia.
- In order to send grievances of European countries to the UN, two countries i.e. Great Britain and France are members of the Security Council of UNO.
- Due to the presence of some non-permanent members of the UN Security Council, the EU was able to influence US policies.
- It has its own flag, anthem, currency, founding date.
Question 8.
Explain the economic and military influence of the European Union. (Delhi 2015)
Answer:
Economic influence EU with more than $12 trillion (2005) is the largest economy in the world surpassing even that of the USA. Euro can cause a danger to the US hegemony of the dollar. The share of the EU is three times greater than that of the US and this makes the EU more powerful in trade disputes with the US and China. Its economy is very impressive and thus, it becomes influential to its neighbours and in Asia and Africa. It plays a significant role in the World Trade Organisation.
Military influence EU stands second in combined armed forces and on total spending on defence. Its members France and Britain have over 550 nuclear warheads and arsenals. EU is the second largest source of space and communication technology. Thus, this super national association has been able to intercede in economic, political and social areas.
But in certain cases, member states have their own foreign relations and defence policies. For example, an Iraqi invasion, where Britain and some other members of the EU joined US-led a coalition of willing, whereas France and Germany opposed the same.
Question 9.
What is meant by the ASEAN way? Mention any two of its objectives. (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
ASEAN way is a kind of interaction which is informal, unofficial, non-confrontationist and cooperative.
The two objectives of ASEAN are :
- To speed up the economic growth of member countries and through that growth, to bring social and cultural development.
- Promotion of regional peace and stability based on laws and principles of the UN Charter.
Question 10.
Explain any two causes which led to the formation of ASEAN. (All India 2013)
Answer:
The causes which led to the formation of ASEAN were :
- The South East Asian Nations suffered the economic and political consequences of repeated colonialisms before and during the Second World War.
- The end of the Second World War confronted problems of nation-building, the ravages of poverty and economic backwardness and the pressure to align with one great power or another during the Cold War.
- Hence, South East Asian countries established the Association for South East Asian Nations in order to solve the issues of South East Asian Countries.
Question 11.
What were the objectives behind the formation of the ASEAN in 1967? (All India 2011)
Answer:
Association of South East Asian (ASEAN) Nations was created in 1967 with the following objectives:
- Primary objective It was to increase economic growth, which will result in social progress and cultural development of the ASEAN. Thus, this objective was related to economic, cultural and social perspectives.
- Secondary objective Under United Nation Charter, principles and rules of law have been stated. So, the secondary objective of ASEAN nations was to promote stability and regional peace based upon those rules and principles.
Question 12.
Explain the role of emerging alternative centres of power in transforming the different countries into prosperous economies. Delhi 2010
Answer:
The end of the bipolar structure in world politics in the early 1990s interpreted that all alternative centres of economic and political power could limit the dominance by the US.
Two forces were established to compete with this factor. They were the European Union (EU) in Europe and the Association of South East Asian Nations (ASEAN) in Asia.
Both EU and ASEAN have developed alternative institutions and agreements in international law, this converted the countries into prosperous economies. Also, the economic emergence of China has made a substantial impact on world politics.
Question 13.
Why did India and China both, view themselves as rising powers in global politics in spite of the tension between them? Substantiate your answer by giving any four events that have brought cordiality in their relationship. (Delhi 2010)
Answer:
Both India and China view themselves as rising powers in global politics, as their relations now have a strategic as well as economic dimension. Both countries would like to play a major role in the Asian economy and politics.
Four events of friendship between them are:
- India’s nuclear tests sometimes justified on grounds of threat from China and did not stop their interaction.
- No issues created problems between both the countries be it Pakistan’s nuclear programme being assisted by China.
- Increasing transportation and communication link, common economic interests and global concerns establish sound relations.
- Mutual understanding of concessions’ policy to solve border problems.
Question 14.
How did the European Union exercise its political and diplomatic influence? (Delhi 2008)
Answer:
The political and diplomatic influence of the European Union has considerable significance. Its members Britain and France are permanent members of the UN Security Council. Some non-permanent members of the UNSC are also included in the EU. And this aspect has made EU impact some US policies such as present US position on Iran’s nuclear programme. EU’s usage of negotiations, diplomacy and economic investments proved more fruitful than US coercion and military force. This can be seen in dealings with China on human rights and environmental issues.
Question 15.
Mention any four common features of the European Union. Delhi 2008; (All India 2008)
Answer:
Features of the EU are as follows:
- EU’s share of world trade is three times larger than that of the US allowing it to be more assertive in trade disputes with the US and China.
- It has evolved from an economic union to a political one. It has its own flag, anthem, founding date and currency.
- Its economic power gives it influence over its closest neighbours and on Asia and Africa. It also functions as an important bloc in an international economic organisation such as WTO.
- EU has political, economic, diplomatic and military influence. GDP of the EU is slightly larger than that of the US.
Question 16.
How can the Euro pass a danger to the US Dollar? (Delhi 2008)
Answer:
European Union has a great economic influence in the world market including the market of the United States. Euro is the currency of the EU.
Euro can pass a danger to the US dollar through:
- The EU is the world biggest economy with a GDP of more than $ 12 trillion in 2005 and this was slightly larger than the US.
- Share of EU in world trade is three times larger than that of the US and this is the reason why the EU can be more assertive in trade disputes with the US and China.
- The economic power of the EU provides great influence over Asia, Africa and its close neighbours.
- Many countries have joined the EU who are directly linked with the US and carry dollar as their currency. These countries can take economic programmes which are against the interest of the US.
Question 17.
Describe any two aspects each of cordiality and tension in the relationship between India and China. (Delhi to 2008)
Answer:
Two aspects of cordiality in the relationship between India and China are :
- Bilateral trade between India and China has increased from $ 338 million in 1992 to more than $ 18 billion in 2006.
- Lately, both countries have agreed upon to cooperate with each other in areas that could otherwise create conflict between both nations.
Two aspects of tension in the relationship between India and China are :
- When China attacked Tibet in 1950-51, Dalai Lama, a political and religious leader of Tibet took shelter in India. As a result relation between the two countries became bitter.
- Controversy over MacMohan line, the borderline between India and China and border conflict in 1962, over competing for territorial claims in Arunachal Pradesh and in the Aksai Chin region of Ladakh.
Question 18.
Describe any two similarities and two differences between the USA and the EU. (All India (C) 2008)
Answer:
EU and USA carry similarities as well as differences between them.
Similarities between them are :
- Both have a democratic form of governments.
- Both the USA and the EU are federal structures. USA states whereas the EU is a combination of different states of regional blocs.
Differences between them are :
- USA is a country with the US dollar as its currency, whereas the EU has Euro as its currency.
- Basis of unity in the USA is political and military and EU has econ = nic cooperation as its basis r>l unity.
Question 19.
Give any two reasons why regionally and globally China has become an economic power to reckon with. (All India (C) 2008)
Answer:
Regionally and globally China has become an economic power to reckon to believe with as:
- The integration of China’s economy has considerable influence on trade partners.
- Adjustments through economic considerations have been made with Japan, the US, ASEAN and Russia. Its investments and help in American, African and Latin states have helped it to project itself a major global player for developing states.
6 Marks Questions
Question 1.
Evaluate any three major factors responsible for making the European Union a political force from economic forces. (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
The European Union has gradually evolved from an economic union into a political union. It has become more a nation-state. Though it does not have Constitution, it has its own flag, anthem, founding date and currency. It has a common foreign and security policy in its dealings with other states.
The areas of cooperation have been expanded by the European Union through admitting new members from the former Soviet bloc. This shifting of power of the EU from economic to political force has not been easy as people were not very enthusiastic. There are also reservations about including some new countries within the European Union.
A major factor behind this is
- Its aim was to make Europe politically, economically and culturally strong enough to face powers like the USA, Russia.
- In order to send grievances of European countries to the UN, two countries i.e. Great Britain and France are members of the Security Council of UNO.
- Due to the presence of some non-permanent members of the UN Security Council, the EU will be able to influence US policies.
Question 2.
Analyse any two factors responsible for the European Union to be a highly influential regional organisation. (All India 2015)
OR
Evaluate the role of the European Union as a supranational organisation. (All India 2011, 2009)
OR
How has the European Union risen to be a super-national organisation? What are its limitations? (All India 2008)
Answer:
European Union is considered highly influential.
For types of influences
Economic influence EU with more than $12 trillion (2005) is the largest economy in the world surpassing even that of the USA. Euro can cause a danger to the US hegemony of the dollar. The share of the EU is three times greater than that of the US and this makes the EU more powerful in trade disputes with the US and China. Its economy is very impressive and thus, it becomes influential to its neighbours and in Asia and Africa. It plays a significant role in the World Trade Organisation.
Military influence EU stands second in combined armed forces and on total spending on defence. Its members France and Britain have over 550 nuclear warheads and arsenals. EU is the second largest source of space and communication technology. Thus, this super national association has been able to intercede in economic, political and social areas. But in certain cases, member states have their own foreign relations and defence policies.
For example, in the Iraqi invasion, where Britain and some other members of the EU joined a US-led coalition of willing, whereas France and Germany opposed the same.
Limitations of the European Union European Union as a supranational association has been able to intercede in economic, political and social areas. But there are certain limitations :
- Member states of EU have their own foreign relation and defence policies, that often odds with each other.
- Presence of deep-seated ‘Euro-skepticism’ in some parts of Europe about the EU’s integrationist agenda.
Question 3.
Explain the factors responsible for the rise of the Chinese economy. (Delhi 2009)
Answer:
China is the third major alternative centre of power. It is the fastest growing economy. China at one time was based on the Soviet model and at that time, it broke all the links with the capitalist world. Following are the factors responsible for the rising of the Chinese economy :
- Use of Soviet Model China accepted the Soviet model and relied on its resources. China decided to substitute imports by domestic goods and create state-owned heavy industries from capital produced by agriculture.
- Development of Industrial Economy China used all its resources to develop an industrial economy. All citizens were provided with education and health programmes.
- Relationship with USA China established a relationship with the USA in 1972.
- Modernisation Modernisations in the field of agriculture, industry, military, science and technology were proposed.
- Major Policies Announced Open Door Policy was announced by Deng Xiaoping in 1978, which aimed at a generation of high productivity by investments in capital and technology from abroad.
- The era of Privatisation Privatisation of agriculture in 1982 and privatisation of industry in 1998 was done.
- Establishment of SEZ’s Special Economic Zones was set up. The state had a centralised role in setting up of China’s economy.
Question 4.
Explain the vision of the ASEAN for 2020. (Delhi 2009)
Answer:
ASEAN was established in 1967 with the objective to accelerate economic growth and through that ‘social progress and cultural development’.
ASEAN is rapidly growing into a very important regional organisation. It has a certain vision for 2020. The features of the ASEAN vision 2020 are as follows :
- Its vision 2020 has defined as an outward-looking role for ASEAN in the international community.
- This builds on the existing ASEAN policy to encourage negotiations over conflicts in the region. Thus, ASEAN has mediated the end of the Cambodian conflict, the East Timor Crisis and meets annually to discuss East Asian cooperation.
- ASEAN’s strength, lies in its policies of interaction and consultation with member states, with dialogue partners and with other non-regional organisations.
- It is the only regional association in Asia that provides a political forum where Asian countries and the major powers can discuss political and security concerns.
Question 5.
Examine the changing Indo-China relations. (All India 2009)
Answer:
For India-China relationship
The India-China relations examined are as below: Friendly relations
- After the Chinese Revolution in 1949, India was one of the first countries to recognise the communist government.
- Prime Minister Nehru and Chinese Premier Zhou Enlai adopted Panchsheel, the Five Principles of Peaceful Co-existence on 29 April 1954.
The Chinese invasion and strained relationship
- China annexed Tibet in 1950 and thus removed a historical buffer between the two countries.
- Tibetan spiritual leader Dalai Lama had sought asylum in India in 1959. China alleged that India was allowing anti-China activities in India.
- Boundary disputes arose between the two countries over Aksai-China area in the Ladakh region and NEFA in the Eastern region.
- The boundary disputes led to a massive Chinese invasion in October 1962. Finally, China declared a unilateral ceasefire but relations between the two countries remained strained.
Conflict of 1962 and Post-Cold Era marked a major change in Indo-China relations. Indo-China Conflict of 1962 In 1962, border dispute regarding territorial claims in Arunachal Pradesh and in Aksai Chin made India suffer military reverses. This had an impact on relations between both of them.
Till 1976, no progress was seen in the betterment of their relations, but after that, they improved slowly. The change in China’s leadership allowed both countries to improve their relations. Border issues resolution was also started in 1981.
Indo-China Relation After Cold War End of the Cold War marked various changes in the relationship between India and China. Both India and China consider themselves as rising powers in international politics.
After the visit of Rajiv Gandhi in 1988, both governments tried to maintain ‘peace and silence’ on the border.
Agreements regarding cultural exchange and cooperation were signed. Four border posts were also opened. Trade between India and China grew at 30 per cent per year since 1999. An increase in bilateral trade from $ 338 million in 1992 to more than $ 18 billion in 2006 was seen. India and China are following the same policies in international economic institutions like the World Trade Organisation.
The nuclear tests by India in 1998 created tension between the two, but the process of normalisation was continued. No issues created problems between both the countries, be it Pakistan’s nuclear programme being assisted by China.
Leaders from both countries frequently visit each other’s nation and this way, they are becoming familiar with each other. Through an increase in transportation and communication links and working on common economic interests development of sound relationship has been taking place.
Question 6.
Analyse the basis of the projection of China to overtake the US as the world’s largest economy by 2040. (Delhi 2008)
Answer:
China is viewed to dominate the US by the year 2040. The basis of the projection are :
- China is considered as the driver of East Asian growth because of the economic integration into regions.
- China is considered to be very powerful and factors such as population, land mass, resources, regional location and political influence add to its strength.
- China announced ‘Open Door Policy’ in 1978 which aimed at a generation of high productivity by investments in capital and technology from abroad.
- In the economic sector various steps were taken to encourage investment by Western entrepreneurs for modernisation of:
- Industry
- Science and technology
- Agriculture
- Military
- In 1980, China became a member of the World Bank and International Monetary Fund.
- Privatisation of agriculture and industry helped in growing economy rapidly.
- Foreign trade grew with the creation of SEZs and new trading plans This resulted in high foreign exchange reserves and this way China became most significant for FDI. The above points show China’s ability to overtake the US as the world’s largest economy by 2040.
Value-Based Question (VBQ)
Question 1.
The conflict of 1962, in which India suffered military reverses, had long-term implications for India-China relations. Diplomatic relations between the two countries were downgraded until 1976. Thereafter, relations bet even the two countries began to ii approve slowly. After the change in China’s political leadership from the mid to late 1970s, China’s policy became more pragmatic and less ideological. So, it was prepared to put off the settlement of contentious issues while improving relations with India. A series of talks to resolve the border issues were also initiated in 1981. (Delhi 2012 )
Study the paragraph given above carefully and answer the following questions
(i) Why did India suffer military reverses as a result of the conflict of 1962?
(ii) Why did the relation between India and China slowly improve?
(iii) What was the change in the policy of China in the seventies?
(iv) Which efforts were made to resolve the border issue between? India and China?
Answer:
(i) China launched a massive attack on Arunachal Pradesh and Aksai Chin in 1962, Indian forces blocked the Chinese on the Western front in Ladakh, they managed to nearly reach the initial point of Assam plains.
(ii) Relationship between India and China started improving from 1976 after the adoption of pragmatic policies by China.
(iii) The policies of China became more pragmatic and less ideological.
(iv) Since Rajiv Gandhi’s visit, both countries have taken measures to contain the conflict and maintain peace.
Map-Based Questions
Question 1.
In the given political outline map of Europe, four member countries of the European Union have been marked A, B, C and D. Identify them with the help of information given below and write their correct names in your answer-book along with with their respective serial number and the alphabet concerned. (Delhi 2013)
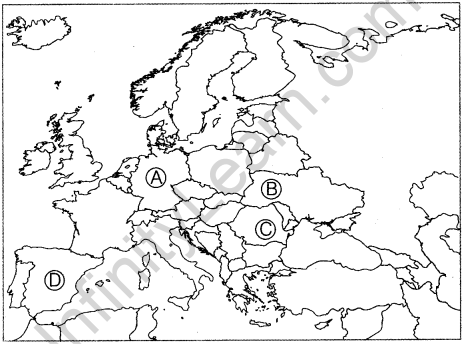
(i) An older member of the European Union located between Portugal and France.
(ii) An older member of the European Union located near Belgium and the Netherlands.
(iii) Two new members of the European Union.
Answer:
(i) Spain (A)
(ii) Luxembourg (B)
(iii) Bulgaria (C) and Romania (D)
Question 2.
In the given political outline map of the European Union, identify and write the names of four old members marked as A, B, C and D and four new members marked as P, Q, R and S in your answer-book. (All India 2010)
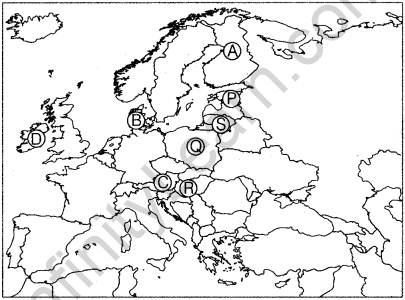
Answer:
(i) Old members of the European Union are
A-Finland
B-Denmark
C-Austria
D-Ireland
(ii) New members of the European Union
P-Estonia
Q-Poland
R-Hungary
S-Lithuania
Picture Based Question
Question 1.
Study the cartoon given below and answer the following questions (All India 2015, 2014)

(i) Which country does the given cartoon refer to?
(ii) Identify the two symbols in this cartoon which have given you the clue about the related country.
(iii) Where does the cartoon place the related country in international power politics?
Answer:
(i) The country refers to China.
(ii) The Great wall and Dragon.
(iii) The cartoon depicts the economic rise of China.
We hope the Political Science Class 12 Important Questions Chapter 4 Alternative Centres of Power help you. If you have any query regarding Political Science Class 12 Important Questions Chapter 4 Alternative Centres of Power, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.





