Table of Contents
CBSE Extra Questions – Democratic Policies
Get CBSE Extra Questions for Class 10 Democratic Policies on Infinity Learn for free.
Question and Answers
Question-1
What is Federalism?
Solution:
Federalism is the promotion of federal political regimes in which final authority is distributed among sub-units and a central authority. Unlike a unitary state, sovereignty is constitutionally divided into at least two territorial levels, with each level having final authority and acting autonomously in some areas. Citizens have political responsibility to two authorities in this situation. The division of authority between the sub-unit and the centre may be different.
As a result, the federal system has two goals: to protect and promote national unity while also accommodating regional variety.
Governments at all levels should agree on some power-sharing rules. Mutual trust and consent to live together are also characteristics of an ideal federal government.
Question-2
What makes India a Federal Country?
Solution:
India is a multilingual, multireligious, and multiregional country. After a long and bitter division, it became an independent country. Soon after independence, other princely kingdoms joined the country. The Constitution declared India to be a Union of States.
The Indian Union is based on federalist ideals. The Union Government (Central Government), which represents the Union of India, and the State governments were previously established under the Constitution. As a third layer of federalism, Panchayats and Municipalities were added later. All of these diverse types of government have their own legal jurisdiction.
Question-3
Write a brief note on the language policy adopted in India.
Solution:
The second test for the Indian federation was the ‘Language policy.’ Our Constitution does not recognize any language as a national language. The official language has been determined to be Hindi. However, only over 40% of Indians speak Hindi as their first language. As a result, the Constitution recognizes 21 other languages as Scheduled Languages in addition to Hindi. In an examination for employment in the Central Government, a candidate may choose to take the exam in either of these languages.
States, like other countries, have their own official languages. The official language of the concerned state is used for a large portion of government activities.
Our country was able to avert a language clash thanks to the flexibility exhibited by Indian political leaders.
Question-4
Write a brief note on village councils.
Solution:
Village councils were in charge of the village’s affairs, possessed police and judicial powers, and were the villages’ main point of contact with higher authorities on issues that affected them. They were raised to a hallowed position of authority by custom and religion.
These Councils served as the administrative centre, the hub of social life, and, most importantly, a focal point for communal cooperation.
Question-5
What are the dual objectives of Federalism?
Solution:
Federalism has two goals: to preserve and promote the country’s unity while also accommodating regional variety.
Question-6
What are the duties of Central and State governments?
Solution:
The Union or Central Government is responsible for matters of national importance such as the country’s defense, foreign affairs, banking, communications, and currency. This is because there will be a consistent policy on these issues across the country. All laws relevant to the foregoing responsibilities must be issued by the Union Government alone.
State governments are responsible for matters of state and local concern such as law enforcement, trade, commerce, agriculture, and irrigation. All laws relevant to the following responsibilities must be issued only by state governments. The Union Government and the State Governments both share responsibilities in several areas. Education, forests, labour unions, marriage, adoption, and succession are among them. Both governments have the authority to enact legislation on these topics. If their laws clash, the law enacted by the Union Government will take precedence.
Question-7
What is the special status the state of Jammu and Kashmir enjoys?
Solution:
Jammu & Kashmir is given special treatment. It has its own set of laws. Without the consent of the State Assembly, certain provisions of the Indian Constitution are not applicable to this State. Indians who are not permanent inhabitants of the state are unable to purchase land or homes in the state. There are similar special provisions in place for a number of other Indian states.
Multiple Choice Questions
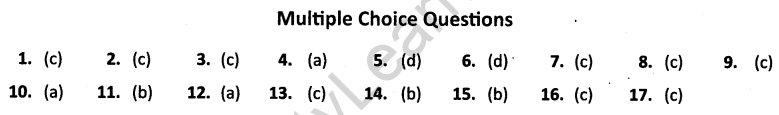
1. How many times was the constitution of Belgium amended between 1970 and 1993 ? [CBSE (CCE) 2011]
(a) Two times
(b) Three times
(c) Four times
(d) Onetime
2. Which of the following government has two or more levels ? [CBSE (CCE) 2011]
(a) Community Government
(b) Coalition Government
(c) Federal Government
(d) Unitary Government
3. Which of the following subjects falls under the concurrent list ? [CBSE (CCE) 2011]
(a) Defence
(b) Agriculture
(c) Marriage
(d) Currency
4. Which of the following countries is an example of “coming together federation” ? [CBSE (CCE) 2011]
(a) U.S.A
(b) India
(c) Spain
(d) Belgium
NCERT Questions
5. The distinguishing feature of a federal government is:
(a) National Government gives some powers to the provincial government.
(b) Power is distributed among the legislature, executive and judiciary.
(c) Elected officials exercise supreme power in the government.
(d) Governmental power is divided between different levels of government.
6. Examine the following pairs that give the level of government in India and the powers of the government at that level to make laws on the subjects mentioned against each. Which of the following pairs is not correctly matched?
| (a) State government | State List |
| (b) Central government | Union List |
| (c) Central and State governments | Concurrent List |
| (d) Local governments | Residuary powers |
7. Match List I with List II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists :
| List 1 | List II |
| (i) Union of India | A. Prime Minister |
| (ii) State | B.Sarpanch |
| (iii) Municipal Corporation | C. Governor |
| (iv) Gram Panchayat | D. Mayor |
| (i) | (ii) | (iii) | (iv) | |
| (a) | D | A | B | C |
| (b) | B | C | D | A |
| (c) | A | C | D | B |
| (d) | C | D | A | B |
8. Consider the following statements.
(i) In a federation the powers of the federal and provincial governments are clearly democrated.
(ii) India is a federation because the powers of the Union and state governments are specified in the Constitution and they have exclusive jurisdiction on their respective subjects.
(iii) Sri Lanka is a federation because the country is divided into provinces.
(iv) India is no longer a federation because some powers of the States have been devolved to the local government bodies.
Which of the statements given above are correct ?
(a) (i), (ii), (iii)
(b) (i), (iii), (iv)
(c) (i), (ii) only
(d) (ii), (iii) only
Additional Questions
9. Consider the statement:
“Coming together federation” involves:
(i) the central government to become more powerful.
(ii) Independent states coming together on their own to form bigger unit.
(iii) Constituent units have unequal powers.
(iv) Constituent states have equal powers.
Which of the statements given above are correct
(a) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(b) (i), (iii) only
(c) (ii) and (iv) only
(d) (i), (iii) and (iv).
10. The Constitution of India
(a) divided powers between centre and states in three lists.
(b) divided powers between centre and states in two lists.
(c) listed the powers of the states and left the undefined powers to the state.
(d) Specified the powers of the states and left the residuary powers with the centre.
11. In case of a clash between the laws made by the centre and a state on a subject in the concurrent list:
(a) the state law prevails.
(b) the central law prevails.
(c) both the laws prevail within their respective jurisdictions.
(d) the Supreme Court has to intervene to decide.
12. The System of Panchayati Raj involves
(a) The village, block and district levels.
(b) The village, and state levels.
(c) The village district and state levels.
(d) The village, state and Union levels.
13. The concept of decentralisation signifies
(a) The three tier government at the urban level.
(b) The two tier government at only rural level
(c) Power taken away from central and state government and given to local government at both the urban and rural levels.
(d) Autonomy given to the state government.
14. In India’s federal system, the state governments have the power to legislate on all those subjects which are included in the :
(a) Union list
(b) State list
(c) Concurrent list
(d) Residuary subjects
15. Which of the following subjects is not included in the state list ?
(a) Law and order
(b) National defence
(c) Education
(d) Agriculture
16. The highest institution of Panchayati Raj in rural area is:
(a) Gram Sabha
(b) Gram Panchayat
(c) Zila Parishad
(d) Gram Samiti
17. Match the following :
| Column 1 | Column II | |
| A. | Union Territory | (i) Decision-making body for the entire village |
| B. | Local self government | (ii) An alliance of more than two parties |
| C. | Coalition | (iii) Representatives government body at the district level |
| D. | Zila Parishad | (iv) Area which is run by the Union / Central government |
(a) A – (ii), B – (iii), C – (iv) and D – (i)
(b) A – (iv), B – (i), C – (iii) and D – (ii)
(c) A – (iv), B – (i), C – (ii) and D – (iii)
(d) A – (iv), B – (iii), C – (ii) and D – (I)
18. State True or False :
(a) The official languages are included in the 10th schedule of our constitution and are therefore called schedule languages.
(b) Education falls under the state subject.
(c) The head of the municipal corporation is called the Mayor.
(d) 1/10th seats are reserved in all local government bodies for women candidates.
19. The distinguishing feature of a federal system is:
(a) National Government gives some powers to the provincial government.
(b) Power is distributed among the legislature, executive and judiciary.
(c) Elected officials exercise Supreme Power in the government.
(d) Governmental power is divided between different levels of government.
20. A few subjects in various lists of the Indian Constitution are given here. Group them under the Union, State and Concurrent Lists as provided in the table below :
(i) Defence
(ii) Police
(iii) Agriculture
(iv) Education
(v) Banking
(vi) Forests
(vii) Communications
(viii) Trade
(ix) Marriages
Which option is correct:
(a) Union list (i), (viii) and (ix)
State list (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Concurrent list (v), (vi) and (vii)
(b) Union list (i), (v) and (vii)
State list (ii), (iii) and (viii)
Concurrent list (iv), (ix) and (vi)
(c) Union list (v), (vi) and (vii)
State list (iii), (vii) and (ix)
Concurrent list (i), (ii) and (iv)
(d) Union list (iii), (vi) and (vii)
State list (v), (viii) and (ix)
Concurrent list (iv), (ii) and (I)
21. Give answer in one word :
(a) Independent states come together on their own to form a bigger unit. Block Samiti / coming together federalism.
(b) A large country decides to divide its power between the constituent states and the national government. Holding together federalism/shortening power.
(c) The area over which someone has legal authority. Specified jurisdiction / Linguistic state.
(d) A government formed by the coming together of more than two political parties. Local government/ coalition government.
22. Fill in the blanks :
Since the United States is a ………… type of federalism, all the constituent States have equal powers and states are ……….. vis-a-vis the federal government. But India is a ………… type of federation and some states have more powers than others. In India, the ……….. has more powers.
(a) Coming together /democratic
(b) Weak/strong
(c) Holding together / coming together
(d) State government / Central government
23. What was the key change made in the constitution of Belgium?
(i) Increase the power of the central government.
(ii) Transfer of powers to the regional government.
(iii) Reduce the power of the central government
(iv) Reduce the power of the regional government.
Choose the appropriate option :
(a) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(b) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
24. In what way changes can be made in the federal constitution:
(a) Change can be unilateral
(b) Changes require the consent of both the levels of government
(c) Changes can be through the judiciary
(d) Changes require only the consent of the people
25. Why have the subjects like defense, foreign affairs, banking, etc., been included in the Union list?
(i) These subjects are of local importance.
(ii) Require a uniform policy for the execution.
(iii) These subjects are of national importance.
(iv) Require a separate policy for each subject.
(a) (iii) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (i) and (iv)
26. What is the basic idea behind the power sharing of Indian federalism ?
(a) Centralisation of Power
(b) Division of Subjects
(c) Decentralisation of Power
(d) Distribution of Power
27. The concept of linguistic states of India signifies :
(a) creation of states on the basis of religion
(b) creation of states on the basis of different culture
(c) creation of states on the basis of language
(d) creation of states on the basis of Topography
28. Which judgment of the Supreme Court made Indian federal power sharing more effective?
(a) Central government can dismiss the state government easily.
(b) Central government can dismiss the state government with the consent of judiciary.
(c) Central government can not dismiss the state government.
(d) Central government cannot dismiss the state government in an arbitrary manner.
29. What is the basic idea behind ‘decentralization of power? Consider the following statement:
(i) To take away power from local level.
(ii) To introduce democracy at grassroot level.
(iii) To centralise power at union level.
(iv) To empower the local government.
(a) (i), (ii), and (iii)
(b) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iv) only
(d) only (iv)
30. Select the countries that follow coming together federal system:
(a) The USA, China, Australia
(b) India, Spain, Belgium, Canada
(c) The USA, Switzerland, Australia
(d) China and India
31. Which of the following countries follow holding together style of federation:
(a) China, Canada, Australia and India
(b) The USA, Australia, Belgium, Canada
(c) India, Belgium, Sweden and China
(d) India, Spain, and Belgium
32. List the countries which do not follow federalism :
(a) Spain, Sweden, Britain
(b) India, Belgium, Canada and Australia
(c) The USA, Spain, Holland
(d) China, Sri Lanka, France, United Kingdom, Japan, Italy, and North Korea
33. Which Indian states have been given special status ?
(a) Punjab, Haryana, U.P.
(b) Jammu & Kashmir
(c) Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Madras
(d) Jammu & Kashmir, Assam, Meghalaya and Delhi
34. In what ways powers are shared between the state government and the central government in India :
(a) List system
(b) Decentralisation
(c) Holding Together
(d) Coming Together
35. Whose laws prevail if there is conflict between the state government and central government on the subject of concurrent list:
(a) The laws made by the state government.
(b) The laws made by both State and Union Government.
(c) The laws made by the Union Government.
(d) The laws would be canceled.
36. How many languages are spoken in India and what is the ratio of Hindi speaking people in India?
(a) 114 languages spoken and 40 percent people speak Hindi
(b) 22 languages spoken and 60 percent of people speak Hindi
(c) 21 languages spoken and 54 percent people speak Hindi
(d) 114 languages spoken and 60 percent people speak Hindi
37. Select the two bases on which new states of India have been created :
(a) Religion and geography
(b) Language and regional
(c) Culture and religion
(d) Geography and language
38. Which two Constitutional Amendments of 1992 deal with local self-government?
(a) 72nd and 73rd Amendments regarding Rural and Urban
(b) 73rd and 74th Amendments regarding Rural and Urban government.
(c) 71st and 74th Amendments regarding Urban and Rural government.
(d) 71st and 72nd Amendments regarding Rural and Urban government.
39. Who is the political head of the Municipality and Gram Panchyat ?
(a) Mayor and Sarpanch
(b) Deputy Collector and Mayor
(c) Sarpanch and Deputy Collector
(d) Mayor and Chief Minister