Table of Contents
Sodium Thiosulphate Formula
Sodium thiosulphate is a chemical compound with the formula Na2S2O3. It is also known as sodium thiosulphate or sodium hyposulfite. The compound consists of two sodium ions (Na+) and the thiosulphate anion (S2O32-).
Structural Formula of Sodium Thiosulphate Formula
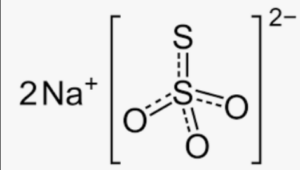
The structural formula of sodium thiosulphate consists of two sodium ions (Na+) and a thiosulphate ion (S2O32-). The thiosulphate ion is composed of a central sulfur atom bonded to three oxygen atoms and one sulfur atom. In this structure, the sodium ions are positively charged and are associated with the negatively charged thiosulphate ion through ionic bonds.
Uses of Sodium Thiosulphate
- Photography: Sodium thiosulfate is used in photographic processing as a fixing agent. It helps remove unexposed and undeveloped silver halide crystals from photographic films and papers, preventing further light-sensitive reactions and stabilizing the final image.
- Water Treatment: Sodium thiosulfate is utilized in water treatment processes, particularly for the removal of chlorine. It acts as a dechlorinating agent, neutralizing chlorine and chloramine residues in tap water or swimming pools, making the water safe for various applications.
- Medical Applications: Sodium thiosulfate is employed in certain medical treatments. It is used as an antidote for cyanide poisoning, as it forms a complex with cyanide ions, facilitating their elimination from the body. Additionally, sodium thiosulfate can be used in dermatological treatments for conditions like fungal infections or as a neutralizing agent for certain chemical burns.
- Analytical Chemistry: Sodium thiosulfate is commonly used in chemical analysis and titration procedures. It is employed as a reducing agent to react with excess iodine in iodometric titrations, allowing the determination of analyte concentrations.
- Industrial Applications: Sodium thiosulfate finds application in various industrial processes. It can be used as a bleaching agent in textile and paper industries, as a component in gold extraction processes, and as a source of sulfur in the production of chemicals like sodium sulfite or sodium bisulfite.
Physical Properties of Sodium Thiosulphate Formula
- Appearance: Sodium thiosulphate is a white crystalline solid.
- Molecular Weight: The molecular weight of sodium thiosulphate is 158.11 grams per mole.
- Solubility: It is highly soluble in water, with a solubility of about 70 grams per 100 milliliters of water at room temperature.
- Density: The density of solid sodium thiosulphate is approximately 1.67 grams per cubic centimeter.
- Melting Point: Sodium thiosulphate has a relatively high melting point of around 48.3 degrees Celsius.
- Boiling Point: When heated, sodium thiosulphate decomposes rather than boiling.
- Odour: It is odourless.
- pH: Aqueous solutions of sodium thiosulphate are usually slightly alkaline with a pH ranging from 8 to 9.
- Hygroscopicity: Sodium thiosulphate has hygroscopic properties, meaning it can absorb moisture from the surrounding environment.
Chemical Properties of Sodium Thiosulphate Formula
- Reducing Agent: Sodium thiosulphate is a strong reducing agent. It can undergo oxidation-reduction reactions and is commonly used as a reducing agent in various chemical processes.
- Reaction with Acid: Sodium thiosulphate reacts with acids, such as hydrochloric acid (HCl), to produce sulfur dioxide (SO2), water (H2O), and sodium chloride (NaCl). This reaction is often used to neutralize excess acid in various chemical reactions.
- Reaction with Iodine: Sodium thiosulphate can react with iodine (I2) to form sodium iodide (NaI) and sodium tetrathionate (Na2S4O6). This reaction is often used in iodometric titrations to determine the concentration of iodine or other oxidizing agents.
- Complex Formation: Sodium thiosulphate can form complexes with various metal ions. For example, it can form a complex with silver ions (Ag+) to produce a stable complex known as sodium silver thiosulphate, which is used in photography for fixing developed images.
- Decomposition: At high temperatures, sodium thiosulphate can undergo decomposition, releasing sulfur dioxide gas (SO2), sulfur, and oxygen. This decomposition reaction is often used in pyrotechnics and fireworks.
- Solubility: Sodium thiosulphate is highly soluble in water, forming clear and colourless solutions. This property makes it suitable for various applications in solution-based chemistry and analytical techniques.
Conclusion
Sodium thiosulfate, with its versatile properties, finds application in various industries and fields. It is commonly used as a fixing agent in photography, a dechlorinating agent in water treatment, and an antidote for cyanide poisoning in medical treatments. In analytical chemistry, it serves as a reducing agent in titrations, while in industrial settings, it has applications in bleaching, gold extraction, and chemical production. The wide range of uses for sodium thiosulfate highlights its importance and utility across different sectors. Its ability to address specific needs in various processes and treatments makes it a valuable compound in the field of chemistry and beyond.
Solved Examples on Sodium Thiosulphate Formula
Example 1: Calculate the mass of sodium thiosulphate required to prepare 500 mL of a 0.2 M solution.
Solution:
Step 1: Calculate the number of moles of sodium thiosulphate needed.
Moles = concentration (M) × volume (L)
Moles = 0.2 M × 0.5 L = 0.1 moles
Step 2: Calculate the molar mass of sodium thiosulphate.
Na2S2O3 = 2 × (22.99 g/mol) + 32.07 g/mol + 3 × (16.00 g/mol) Na2S2O3
= 158.11 g/mol
Step 3: Calculate the mass of sodium thiosulphate.
Mass = moles × molar mass
Mass = 0.1 moles × 158.11 g/mol = 15.811 g
Therefore, 15.811 grams of sodium thiosulphate are required to prepare 500 mL of a 0.2 M solution.
Example 2: A 100 mL solution contains 0.25 moles of sodium thiosulphate. What is the molarity of the solution?
Solution:
Step 1: Calculate the volume of the solution in liters.
Volume = 100 mL
= 100/1000 L = 0.1 L
Step 2: Calculate the molarity of the solution.
Molarity = moles/volume
Molarity = 0.25 moles/0.1 L = 2.5 M
Therefore, the molarity of the solution is 2.5 M.
Frequently Asked Questions on Sodium Thiosulphate Formula
1: What is sodium thiosulphate also known as?
Answer: Sodium thiosulphate is also known as sodium thiosulphate or sodium hyposulfite. It is commonly referred to by its chemical formula Na2S2O3.
2: Why is Na2S2O3 called hypo solution?
Answer: Na2S2O3, which is the chemical formula for sodium thiosulphate, is commonly called “hypo solution” due to its use as a photographic fixer. In photography, sodium thiosulphate is used to remove unexposed or undeveloped silver halide crystals from photographic film or paper. The term “hypo” is derived from the Greek word “hupó,” meaning “under,” which refers to its ability to fix or remove the “underexposed” silver halide. Therefore, sodium thiosulphate became widely known as hypo solution in the context of photography.
3: Is sodium thiosulphate a reducing or oxidizing agent?
Answer: Sodium thiosulphate (Na2S2O3) is a reducing agent. It can undergo oxidation itself while reducing another substance in a chemical reaction. In particular, sodium thiosulphate is commonly used as a reducing agent in various applications, such as in photographic processes, analytical chemistry, and water treatment. It is capable of reducing certain metals, halogens, and other oxidizing agents by donating electrons and undergoing oxidation itself.
4: What are the uses of sodium thiosulphate in industry?
Answer: The uses of sodium thiosulphate in industry are:
- Photography: Sodium thiosulphate is used in photographic processing as a fixing agent. It is used to remove unexposed silver halide from photographic film or paper, preventing further development and stabilizing the image.
- Water treatment: Sodium thiosulphate is used in water treatment processes to remove chlorine and chloramine from tap water. It acts as a dechlorinating agent, neutralizing the disinfectant properties of chlorine and making the water safe for various applications.
- Analytical chemistry: Sodium thiosulphate is used in analytical chemistry as a reducing agent, particularly in redox titrations. It can be used to determine the concentration of various analytes, such as iodine, arsenic, and copper, by reacting with them and measuring the resulting colour change or titrating against a standardized solution.
- Gold and silver refining: Sodium thiosulphate is used in the extraction and refining of precious metals like gold and silver. It forms soluble complexes with these metals, allowing them to be separated from other impurities during the refining process.
- Industrial processes: Sodium thiosulphate finds applications in various industrial processes, including textile, pulp and paper, and leather industries. It is used as a reducing agent, bleaching agent, or stabilizer in certain chemical reactions and processes.
- Medical applications: Sodium thiosulphate is sometimes used in medical treatments, such as in the management of cyanide poisoning. It reacts with cyanide to form thiocyanate, which is less toxic and can be eliminated from the body more easily.
5: Why is it called thiosulphate?
Answer: The term “thiosulphate” is derived from the combination of two components: “thio” and “sulphate.”
- “Thio” refers to the presence of a sulfur atom in the compound. It is derived from the Greek word “thiόs,” meaning sulfur.
- “Sulphate” refers to the anion (negatively charged ion) present in the compound. Sulphate is derived from the Latin word “sulfur,” which also refers to sulfur.
Therefore, the term “thiosulphate” is used to describe a compound that contains a sulfur atom in combination with a sulphate group. In the case of sodium thiosulphate (Na2S2O3), it consists of two sulfur atoms bonded to three oxygen atoms (forming the sulphate group) and two sodium atoms.
6: Is Na2S2O3 a base or acid?
Answer: Sodium thiosulfate (Na2S2O3) is neither a base nor an acid. It is a salt composed of sodium cations (Na+) and thiosulfate anions (S2O32-). Salts like sodium thiosulfate are typically neutral compounds, meaning they do not exhibit acidic or basic properties. However, when dissolved in water, sodium thiosulfate can undergo hydrolysis and produce a slightly basic solution due to the release of hydroxide ions (OH–) from the hydrolysis of the sodium cations.
7: What is the physical appearance of sodium thiosulphate?
Answer: Sodium thiosulfate typically appears as a white crystalline solid. It is commonly found in the form of small transparent or opaque crystals or as a fine white powder. The crystals are often odorless and have a characteristic salty taste. Sodium thiosulfate is highly soluble in water, and its aqueous solutions are clear and colorless.
8: What are the uses of Sodium thiosulphate for skin?
Answer: Sodium thiosulfate has several uses for the skin due to its properties. It is commonly used in skincare products and treatments for various purposes. One of its primary uses is as an antidote for skin irritations caused by certain chemicals or substances. Sodium thiosulfate helps neutralize and remove harmful substances from the skin, providing relief from itching, burning, and inflammation. It is also used in certain skin conditions such as acne to help reduce redness and inflammation. Additionally, sodium thiosulfate is sometimes included in bath products to help soothe and soften the skin. However, it is important to note that the specific use and application of sodium thiosulfate for skin-related concerns should be under the guidance of a healthcare professional or dermatologist.





