Table of Contents
Magnesium Carbonate Formula
Introduction
Magnesium carbonate is a chemical compound with the formula MgCO3. It is a white, powdery solid that occurs naturally as the mineral magnesite.
Magnesium carbonate is widely used in various industries and applications due to its unique properties. It is commonly utilized as an antacid to relieve symptoms of acid indigestion and heartburn. In addition, it is employed as a dietary supplement to provide magnesium to the body. Magnesium carbonate is also used in the production of ceramics, cosmetics, fire retardants, and as a drying agent in some pharmaceutical formulations.
Structural Formula of Magnesium Carbonate Formula
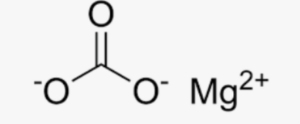
The structural formula of magnesium carbonate (MgCO3) represents the arrangement of atoms in the compound. It consists of one magnesium ion (Mg2+) bonded to one carbonate ion (CO32-). The carbonate ion is composed of one carbon atom bonded to three oxygen atoms. The magnesium ion is surrounded by six oxygen atoms, forming a polyhedral structure. The structural formula provides a visual representation of the bonding and arrangement of atoms in the compound.
Uses of Magnesium Carbonate
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Magnesium carbonate is used in the pharmaceutical industry as an antacid and laxative. It helps in neutralizing excess stomach acid and relieving symptoms of indigestion, heartburn, and upset stomach. It can also be used as a component in medications for treating constipation.
- Personal Care Products: Magnesium carbonate is used in personal care products, such as cosmetics and skincare formulations. It is commonly used as an absorbent and bulking agent in face powders, talcum powders, body powders, and deodorants. It helps in absorbing excess moisture and oil from the skin, providing a dry and smooth feel.
- Sports and Fitness: Magnesium carbonate is used in the sports and fitness industry as a gripping agent for sports equipment like climbing chalk and gymnastics chalk. It helps to improve grip and prevent slipping by reducing moisture and sweat on the hands.
- Food Industry: Magnesium carbonate can be used as a food additive and dietary supplement. It may be added to certain food products as an anticaking agent or as a source of magnesium, an essential mineral for various bodily functions.
- Industrial Applications: Magnesium carbonate finds applications in various industrial processes. It is used in the production of ceramics, glass, and refractory materials. It can also be used as a component in fireproof materials and insulation products.
- Agriculture and Horticulture: Magnesium carbonate can be used as a soil amendment in agriculture and horticulture. It helps in correcting magnesium deficiencies in the soil, which is essential for plant growth and development.
Physical Properties of Magnesium Carbonate Formula
- Appearance: Magnesium carbonate is a white solid in its pure form. It can occur as a powder or in crystalline form.
- Density: The density of magnesium carbonate varies depending on the form and degree of hydration. In its anhydrous form, it has a density of about 2.96 g/cm3.
- Melting Point: The melting point of magnesium carbonate is relatively high, around 350-400°C (662-752°F). However, it can decompose before reaching its melting point.
- Solubility: Magnesium carbonate is sparingly soluble in water. It has a low solubility, and its solubility decreases with increasing temperature. It is more soluble in acidic solutions.
- pH: When dissolved in water, magnesium carbonate can slightly increase the pH, making the solution slightly basic.
- Hygroscopicity: Magnesium carbonate has some hygroscopic properties, meaning it can absorb moisture from the surrounding environment.
- Stability: Magnesium carbonate is stable under normal conditions. However, it can undergo thermal decomposition at high temperatures, releasing carbon dioxide and leaving behind magnesium oxide.
Chemical Properties of Magnesium Carbonate Formula
- Reaction with Acids: Magnesium carbonate reacts with acids, such as hydrochloric acid (HCl), to produce carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and a soluble magnesium salt. The reaction can be represented as follows: MgCO3 + 2HCl → MgCl2 + CO2 + H2O
- Thermal Decomposition: Magnesium carbonate undergoes thermal decomposition when heated to high temperatures. It breaks down into magnesium oxide (MgO) and carbon dioxide. The reaction can be represented as: MgCO3 → MgO + CO2
- pH Regulation: Magnesium carbonate can act as a pH buffer or pH regulator due to its weak basic nature. It can neutralize excess acid and help maintain a desired pH level.
- Reactivity with Metal Ions: Magnesium carbonate can react with certain metal ions, such as copper (Cu2+), to form insoluble precipitates. This property can be utilized in various chemical processes and water treatment applications.
- Complex Formation: Magnesium carbonate can form complexes with other compounds or metal ions, leading to the formation of coordination complexes. These complexes can exhibit unique chemical and physical properties.
Conclusion
In conclusion, magnesium carbonate (MgCO3) is a compound with a wide range of applications and uses. Its chemical formula represents its composition, consisting of magnesium ions (Mg2+) and carbonate ions (CO32-) bonded together. Magnesium carbonate is commonly used as an ingredient in antacid medications to alleviate symptoms of heartburn, acid indigestion, and upset stomach. It works by neutralizing excess stomach acid and providing relief to the digestive system. Additionally, it is utilized as a food additive in the form of an acidity regulator, anticaking agent, and firming agent. In sports and fitness, magnesium carbonate is employed as a drying agent for the hands in activities such as rock climbing, weightlifting, and gymnastics, enhancing grip and reducing sweat. It also finds application as a component in cosmetics and personal care products due to its absorbent properties. Moreover, magnesium carbonate is utilized in the production of ceramics, paints, and coatings as a filler and pigment, contributing to improved strength and coloration. Its versatility and beneficial properties make magnesium carbonate a valuable compound in various industries and everyday applications.
Solved Examples on Magnesium Carbonate Formula
Example 1: Calculate the molar mass of magnesium carbonate (MgCO3).
Solution: Molar mass of Mg = 24.31 g/mol
Molar mass of C = 12.01 g/mol Molar mass of O = 16.00 g/mol
Molar mass of MgCO3 = (1 × molar mass of Mg) + (1 × molar mass of C) + (3 × molar mass of O) = (1 × 24.31) + (1 × 12.01) + (3 × 16.00)
= 24.31 + 12.01 + 48.00
= 84.32 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of magnesium carbonate is 84.32 g/mol.
Example 2: How many moles of carbon dioxide (CO2) are produced when 5 moles of magnesium carbonate react?
Solution: From the balanced chemical equation of the decomposition of magnesium carbonate: MgCO3 → MgO + CO2
The stoichiometric ratio between magnesium carbonate and carbon dioxide is 1:1. This means that for every 1 mole of magnesium carbonate, 1 mole of carbon dioxide is produced.
Given that 5 moles of magnesium carbonate react, the number of moles of carbon dioxide produced is also 5 moles.
Therefore, when 5 moles of magnesium carbonate react, 5 moles of carbon dioxide are produced.
Frequently Asked Questions on Magnesium Carbonate Formula
1: What is the use of magnesium carbonate in formulation?
Answer: One of the primary uses of magnesium carbonate is in the production of magnesium oxide through a process called calcination. Calcination involves heating magnesium carbonate at high temperatures, typically around 700-900 degrees Celsius. During this process, magnesium carbonate decomposes, releasing carbon dioxide (CO2) and leaving behind magnesium oxide (MgO).
Magnesium oxide, also known as magnesia, is a white, odorless powder that has various applications across different industries.
2: What is the best chemical formula for magnesium carbonate?
Answer: The best chemical formula for magnesium carbonate is MgCO3. This formula represents the compound magnesium carbonate, which consists of one magnesium ion (Mg2+) and one carbonate ion (CO32-). It is important to note that there can be different forms or hydrates of magnesium carbonate, which can vary in their crystal structures and water content. However, the chemical formula MgCO3 represents the basic composition of magnesium carbonate.
3: What is another name for magnesium carbonate?
Answer: Another name for magnesium carbonate is magnesite. It is a common over the counter remedy for heartburn and upset stomach caused by overproduction of acid in the stomach.
4: Why is magnesium carbonate used in talcum powder?
Answer: Magnesium carbonate is used in talcum powder for its ability to absorb moisture and reduce friction. It helps to keep the skin dry and prevent chafing. Additionally, magnesium carbonate has a soft and silky texture, which contributes to the smooth and luxurious feel of talcum powder when applied to the skin.
5: What colour is magnesium carbonate?
Answer: Magnesium carbonate is typically a white, odorless powder. It is insoluble in water and has a slightly basic taste. The white color of magnesium carbonate is a result of its chemical composition and crystal structure. However, it is worth noting that impurities or variations in manufacturing processes can sometimes result in slight color variations, ranging from off-white to light gray.
6: Is MgCO3 strong or weak base?
Answer: Magnesium carbonate (MgCO3) is considered a weak base. In water, it undergoes a limited dissociation to release hydroxide ions (OH–), which are responsible for the basic properties. However, compared to strong bases like sodium hydroxide (NaOH), magnesium carbonate has a lower affinity for releasing hydroxide ions and does not completely dissociate. Therefore, it exhibits weaker alkaline properties.
7: What is the difference between CaCO3 and MgCO3?
Answer: The main difference between calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and magnesium carbonate (MgCO3) lies in the composition of the metal cation. In calcium carbonate, the metal cation is calcium (Ca2+), while in magnesium carbonate, it is magnesium (Mg2+). This difference in cation affects various properties of the compounds.
- Chemical Composition: Both compounds contain the carbonate anion (CO32-), but the cationic component differs. CaCO3 consists of one calcium ion and one carbonate ion, while MgCO3 contains one magnesium ion and one carbonate ion.
- Solubility: Calcium carbonate is less soluble in water compared to magnesium carbonate. Calcium carbonate has lower solubility, and its solubility decreases with increasing temperature. On the other hand, magnesium carbonate is slightly more soluble in water than calcium carbonate.
- Alkalinity: Both compounds are considered bases, but calcium carbonate has stronger alkaline properties compared to magnesium carbonate. This is because calcium ions have a higher charge density than magnesium ions, resulting in a greater ability to release hydroxide ions and neutralize acids.
- Occurrence: Calcium carbonate is more abundant and commonly found in nature, particularly in rocks, shells, and minerals like limestone and chalk. Magnesium carbonate, though less abundant, can also occur naturally in some minerals and deposits.
8: Is MgCO3 a limestone?
Answer: Magnesium carbonate (MgCO3) is not typically referred to as limestone. Limestone is primarily composed of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and is a sedimentary rock that forms from the accumulation of calcium carbonate-rich materials over time. It is commonly found in marine environments and can be used as a building material, in the production of cement, and as a raw material for various industrial applications.
While magnesium carbonate can occur naturally and is sometimes associated with limestone formations, it is not the primary component of limestone. Magnesium carbonate is more commonly found in minerals such as magnesite and dolomite. These minerals contain varying proportions of magnesium carbonate along with other minerals.





