Magnesium Bicarbonate Formula
Introduction
Magnesium bicarbonate is an unstable compound that readily decomposes in aqueous solutions into magnesium ions (Mg2+) and bicarbonate ions (HCO3-). Magnesium bicarbonate is not commonly encountered as a solid compound because it readily decomposes into other magnesium compounds in solution.
Magnesium bicarbonate, along with other magnesium compounds, plays a role in various biological and chemical processes. Magnesium is an essential mineral for human health, involved in enzyme activities, muscle function, and nerve transmission. The bicarbonate ion, on the other hand, contributes to the buffering capacity and regulation of pH in biological systems.
Structural Formula of Magnesium Bicarbonate
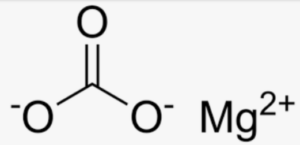
When magnesium bicarbonate is dissolved in water, it dissociates into magnesium ions (Mg2+) and bicarbonate ions (HCO3-).
Uses of Magnesium Bicarbonate
- Dietary Supplements: Magnesium is commonly used in dietary supplements to support overall health and well-being. It is essential for maintaining proper muscle function, nerve transmission, and normal heart rhythm.
- Medicine and Healthcare: Magnesium compounds, such as magnesium hydroxide and magnesium sulfate, are used in medicine as laxatives, antacids, and treatments for conditions like constipation, indigestion, and pre-eclampsia.
- Agriculture: Magnesium is an important nutrient for plant growth and development. It is used as a component of fertilizers to ensure healthy plant growth and improve crop yield.
- Water Treatment: Magnesium hydroxide is used in water treatment processes to raise the pH level and neutralize acidic water. It helps to control corrosion and maintain water quality.
- Industrial Applications: Magnesium is utilized in various industrial processes, including metal production, alloy manufacturing, and as a component in ceramics, refractories, and construction materials.
Physical Properties of Magnesium Bicarbonate Formula
The physical properties of magnesium ions (Mg2+) ions and bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) ions are as follows:
- Magnesium ions (Mg2+): Magnesium ions are colorless and typically exist as hydrated ions in solution. They have a relatively high charge density and can form coordination complexes with other molecules or ions. The hydrated magnesium ions contribute to the electrical conductivity of the solution.
- Bicarbonate ions (HCO3-): Bicarbonate ions are also colorless and contribute to the overall pH and alkalinity of the solution. They can act as a weak acid, donating a hydrogen ion (H+) to the solution, or as a weak base, accepting a hydrogen ion. Bicarbonate ions also participate in buffering systems, helping to maintain the pH stability of the solution.
Chemical Properties of Magnesium Bicarbonate Formula
Some general chemical properties associated with the constituents of magnesium bicarbonate are:
- Magnesium (Mg): Magnesium is an active alkaline earth metal. It readily reacts with water to form magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2) and hydrogen gas (H2). It also reacts with acids to produce magnesium salts and hydrogen gas. Magnesium can undergo redox reactions, commonly forming magnesium oxide (MgO) when heated in the presence of oxygen.
- Bicarbonate (HCO3-): Bicarbonate is an anion that can act as a weak acid or a weak base. In acidic conditions, bicarbonate can accept a hydrogen ion (H+) to form carbonic acid (H2CO3). In basic conditions, bicarbonate can donate a hydrogen ion to act as a weak base.
Conclusion
In conclusion, magnesium bicarbonate (Mg(HCO3)2) is a chemical compound that is not commonly found in pure form but exists in aqueous solutions. It is formed when magnesium hydroxide reacts with carbonic acid. Magnesium bicarbonate is primarily used in the field of water treatment as a source of magnesium and bicarbonate ions. It is believed to have potential health benefits and is often used in dietary supplements for magnesium supplementation. However, it is important to note that solid magnesium bicarbonate does not exist as a stable compound and decomposes readily into other magnesium salts and carbon dioxide.
Solved Examples on Magnesium Bicarbonate Formula
Example 1: A 0.1 M magnesium bicarbonate solution is prepared by dissolving magnesium bicarbonate in water. Calculate the concentration of magnesium ions (Mg2+) and bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) in the solution.
Solution:
The chemical equation for the dissociation of magnesium bicarbonate is: Mg(HCO3)2 → Mg2+ + 2HCO3-
Since the solution is 0.1 M in magnesium bicarbonate, the concentration of magnesium ions (Mg2+) will also be 0.1 M. This is because every mole of magnesium bicarbonate dissociates to produce one mole of magnesium ions.
The concentration of bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) can be determined by considering the stoichiometry of the dissociation reaction.
For every mole of magnesium bicarbonate that dissociates, two moles of bicarbonate ions are produced. Therefore, the concentration of bicarbonate ions will be twice the concentration of magnesium ions, i.e., 0.2 M.
So, in the given 0.1 M magnesium bicarbonate solution, the concentration of magnesium ions is 0.1 M, and the concentration of bicarbonate ions is 0.2 M.
Example 2: A solution contains 50 mL of a 0.2 M magnesium bicarbonate (Mg(HCO3)2 )solution. Calculate the number of moles of magnesium ions (Mg2+) and bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) present in the solution.
Solution:
To calculate the number of moles of magnesium ions (Mg2+) and bicarbonate ions (HCO3-), we need to use the given volume and concentration of the magnesium bicarbonate solution.
- Moles of magnesium ions (Mg2+):
Given volume of solution = 50 mL = 0.05 L
Concentration of magnesium bicarbonate solution = 0.2 M
Moles of Mg2+ = Concentration × Volume
Moles of Mg2+ = 0.2 M × 0.05 L
Moles of Mg2+ = 0.01 moles
Therefore, there are 0.01 moles of magnesium ions (Mg2+) present in the solution.
- Moles of bicarbonate ions (HCO3-): Since magnesium bicarbonate dissociates into two bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) for every magnesium ion, the number of moles of bicarbonate ions will be twice the number of moles of magnesium ions.
Moles of HCO3- = 2 × Moles of Mg2+
= 2 × 0.01 moles
= 0.02 moles
Therefore, there are 0.02 moles of bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) present in the solution.
In summary, the solution containing 50 mL of a 0.2 M magnesium bicarbonate solution contains 0.01 moles of magnesium ions (Mg2+) and 0.02 moles of bicarbonate ions (HCO3-).
Frequently Asked Questions on Magnesium Bicarbonate Formula
1: Which type of salt is magnesium bicarbonate ?
Answer: Magnesium bicarbonate is a type of salt known as a bicarbonate salt. Bicarbonate salts are formed by the combination of a metal cation (in this case, magnesium, Mg2+) and the bicarbonate anion (HCO3-). In the case of magnesium bicarbonate (Mg(HCO3)2), two bicarbonate ions are combined with one magnesium ion. The resulting compound, magnesium bicarbonate, is an example of a bicarbonate salt.
2: What happens when magnesium bicarbonate is heated?
Answer: When magnesium bicarbonate (Mg(HCO3)2) is heated, it undergoes thermal decomposition. This decomposition reaction results in the formation of magnesium oxide (MgO), water (H2O), and carbon dioxide (CO2).
The reaction can be represented by the following equation:
2Mg(HCO3)2(s) → 2MgO(s) + 4H2O(g) + 3CO2(g)
3: What is the source of magnesium bicarbonate?
Answer: Magnesium bicarbonate or magnesium hydrogencarbonate, Mg(HCO3)2, is the bicarbonate salt of magnesium. Magnesium bicarbonate (Mg(HCO3)2) is not naturally found as a stable compound or a mineral in significant quantities.
It can be formed through the reaction of dilute solutions of carbonic acid (such as seltzer water) and magnesium hydroxide (milk of magnesia).
4: What is the pH of magnesium bicarbonate?
Answer: Magnesium bicarbonate (Mg(HCO3)2) is an alkaline compound, and its aqueous solution has a basic pH. The exact pH of a magnesium bicarbonate solution depends on various factors such as concentration, temperature, and the presence of other substances. However, typically, a dilute solution of magnesium bicarbonate will have a pH in the range of 8 to 9, indicating its basic nature.
5: What is the other name for magnesium bicarbonate?
Answer: It has the IUPAC name as ‘Magnesium Hydrogen Carbonate. ‘ The formula of Magnesium Bicarbonate is Mg(HCO3)2.
6: What is the use of magnesium bicarbonate?
Answer: Magnesium bicarbonate is primarily used as a dietary supplement to provide magnesium and support various bodily functions. Magnesium is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in numerous enzymatic reactions, muscle and nerve function, energy production, and maintaining healthy bones and teeth. As magnesium bicarbonate is water-soluble, it can be easily consumed in liquid form, making it convenient for those who have difficulty swallowing pills. It is believed that magnesium bicarbonate may help with conditions such as magnesium deficiency, muscle cramps, migraines, and high blood pressure. However, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional before using magnesium bicarbonate as a supplement to ensure proper dosage and suitability for individual needs.
7: What is the reaction of magnesium with bicarbonate?
Answer: Magnesium does not directly react with bicarbonate (HCO3-) ions. However, magnesium bicarbonate can be formed indirectly when magnesium hydroxide reacts with carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) in the presence of dissolved bicarbonate ions. The reaction can be summarized as follows:
Mg(OH)2 + CO2 + H2O + HCO3- → Mg(HCO3)2
In this reaction, carbon dioxide reacts with water to form carbonic acid (H2CO3), which then reacts with magnesium hydroxide to produce magnesium bicarbonate. The resulting magnesium bicarbonate is a soluble compound that can be found in solution rather than as a solid.
8: What is the other name for magnesium bicarbonate?
Answer: Magnesium bicarbonate is also known as magnesium hydrogen carbonate. Both terms refer to the same compound, which is formed when magnesium hydroxide reacts with carbon dioxide and water in the presence of dissolved bicarbonate ions.





