Table of Contents
Ammonium Hydroxide Formula: Ammonium hydroxide, also known as ammonia water or aqueous ammonia, is a solution of ammonia gas (NH3) dissolved in water. It is a colorless liquid with a pungent odor. Ammonium hydroxide is a common and versatile chemical compound used in various industrial, commercial, and household applications.
It is produced by dissolving ammonia gas in water, and the concentration of ammonium hydroxide can vary depending on the desired application. The solution is alkaline in nature, meaning it has a high pH value. Ammonium hydroxide readily releases ammonia gas when heated or exposed to air.
It’s important to handle ammonium hydroxide with caution and follow proper safety guidelines as it is a corrosive substance. Protective equipment and adequate ventilation should be used when working with or around ammonium hydroxide to ensure safety. It can also cause irritation or burns when in contact with the skin or eyes.
Ammonium Hydroxide
Ammonium hydroxide is a widely used chemical compound, often recognized for its versatile applications in various industries. Commonly referred to as aqueous ammonia, it is formed by dissolving ammonia gas in water, creating a weak base. The molecular formula of ammonium chloride (NH₄Cl) and ammonium hydroxide formula (NH₄OH) are closely related, as they both involve the ammonium ion (NH₄⁺). While ammonium chloride is a salt, ammonium hydroxide serves as an essential ingredient in cleaning agents, fertilizers, and laboratory solutions. Despite its mild alkalinity, ammonium hydroxide is highly effective in neutralizing acids and is valued for its role in chemical reactions and manufacturing processes.
Ammonium Hydroxide Uses
Ammonium hydroxide, also known as ammonia water, is a solution of ammonia in water. It has several uses in various industries and applications. Here are some common uses of ammonium hydroxide:
- Cleaning and Household Products: Ammonium hydroxide is commonly used in cleaning products such as window cleaners, floor cleaners, and bathroom cleaners. It helps to remove dirt, grime, and stains effectively.
- pH Adjustment: Ammonium hydroxide is used as a pH adjuster in various industries, including water treatment, agriculture, and manufacturing. It can be used to increase the alkalinity of acidic solutions.
- Fertilizer Production: Ammonium hydroxide is a source of ammonia, which is an essential nutrient for plants. It is used in the production of fertilizers to provide nitrogen to the soil and promote plant growth.
- Metal Cleaning and Etching: Ammonium hydroxide is used in metal cleaning and etching processes. It can help remove oxide layers, oils, and other contaminants from metal surfaces.
- Textile Industry: Ammonium hydroxide is used in the textile industry for dyeing and printing fabrics. It helps to fix dyes to the fabric and improve color fastness.
- Analytical Chemistry: Ammonium hydroxide is used in laboratory settings for various analytical techniques. It can be used as a reagent or solvent in chemical reactions and as a pH buffer in analytical procedures.
Structural Formula of Ammonium Hydroxide
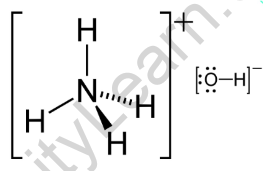
Ammonium hydroxide, with the chemical formula NH4OH, is a compound formed by combining ammonia (NH3) and water (H2O). It is also known as aqueous ammonia or ammonia solution. In the formula, NH4 represents the ammonium ion, which consists of one nitrogen atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms. The hydroxide ion (OH-) is formed by the dissociation of water. When ammonia is dissolved in water, it forms ammonium hydroxide due to the reaction between ammonia and water molecules.
Physical Properties of Ammonium Hydroxide Formula
- Appearance: Ammonium hydroxide is a clear and transparent liquid. It is soluble in water, meaning it readily dissolves in water to form a homogeneous solution.
- Odour: It has a distinctive, strong, and pungent odor, similar to that of ammonia.
- Density: The density of ammonium hydroxide is around 0.9 g/cm³, which means it is slightly less dense than water.
- Boiling Point: Ammonium hydroxide has a relatively low boiling point of approximately 38oC (100oF). This low boiling point allows it to evaporate easily.
- pH: Ammonium hydroxide is a weak base and has a pH of around 11-12 when it is in an aqueous solution. This pH indicates its basic nature.
- Volatility: Ammonium hydroxide is a volatile substance, meaning it can evaporate into the air relatively easily at room temperature. This contributes to its strong odour.
Chemical Properties of Ammonium Hydroxide Formula
- Ionization: Ammonium hydroxide readily ionizes in water to release ammonium ions (NH4+) and hydroxide ions (OH-). The dissociation of ammonium hydroxide is reversible, and the concentration of ammonium and hydroxide ions in solution depends on the pH and temperature.
- cid-Base PropertiesA: Ammonium hydroxide is a weak base. It can accept protons (H+) from other substances and act as a base in acid-base reactions. The basic nature of ammonium hydroxide is due to the presence of hydroxide ions in the solution.
- Reactivity with Acids: Ammonium hydroxide can react with acids to form ammonium salts. In these reactions, the hydroxide ion from ammonium hydroxide reacts with the hydrogen ion from the acid, forming water. For example, ammonium hydroxide reacts with hydrochloric acid (HCl) to form ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) and water (H2O).
2NH4OH+H2SO4 → (NH4)2S44+2H2O
Complex Formation: Ammonium hydroxide can form complexes with various metal ions. These complexes are formed through coordination bonding, where the metal ion acts as a Lewis acid and the hydroxide ion from ammonium hydroxide acts as a Lewis base. The resulting complex compounds often have different chemical and physical properties compared to the individual components.
Decomposition: Ammonium hydroxide is unstable at high temperatures and can decompose to release ammonia gas (NH3) and water vapor (H2O). This decomposition reaction occurs when ammonium hydroxide is heated or exposed to elevated temperatures.
NH4OH → NH3 + H2O
Solved Examples of Ammonium Hydroxide Formula
Example 1: Calculate the molarity of ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH) in a solution prepared by dissolving 25 grams of NH4OH in enough water to make 500 mL of solution.
Solution: First, calculate the number of moles of NH4OH:
Molar mass of NH4OH = 14.01 g/mol (N) + 1.01 g/mol (H) + 16.00 g/mol (O) + 1.01 g/mol (H)
= 35.03 g/mol
Number of moles = mass / molar mass = 25 g / 35.03 g/mol ≈ 0.713 mol
Next, convert the volume of the solution to liters:
500 mL = 500 mL * (1 L / 1000 mL)
= 0.5 L
Finally, calculate the molarity:
Molarity = moles / volume
= 0.713 mol / 0.5 L
= 1.426 M
Therefore, the molarity of the ammonium hydroxide solution is 1.426 M.
Example 2: A 100 mL solution of ammonium hydroxide with a molarity of 0.5 M is diluted with water to a final volume of 500 mL. What is the new molarity of the diluted solution?
Solution: The initial solution has a volume of 100 mL and a molarity of 0.5 M. To find the new molarity after dilution, we need to consider the dilution factor.
Dilution factor = final volume / initial volume
= 500 mL / 100 mL = 5
The moles of ammonium hydroxide remain the same before and after dilution, so the new moles of ammonium hydroxide in the diluted solution are the same as the initial moles.
New volume = initial volume * dilution factor
= 100 mL * 5 = 500 mL
New molarity = moles / new volume = (initial moles) / (new volume)
= (0.5 M) / (500 mL / 1000 mL/L) = 0.1 M
Therefore, the new molarity of the diluted solution is 0.1 M.
Frequently Asked Questions on Ammonium Hydroxide Formula
Ammonium hydroxide NH4OH is often referred to as ammonia water or aqueous ammonia. It is unusual in the sense that it is not a pure compound but rather a solution of ammonia NH3 gas dissolved in water. Unlike typical hydroxide compounds, such as sodium hydroxide NaOH or potassium hydroxide KOH, ammonium hydroxide does not exist as a stable compound on its own. Instead, it readily dissociates into ammonia and water molecules. Therefore, ammonium hydroxide is considered a misnomer and is more accurately described as an ammonia solution.
Another common name for ammonium hydroxide is aqueous ammonia or simply ammonia solution. These terms are used interchangeably to refer to the same compound, which is a solution of ammonia gas NH3 dissolved in water.
It's an ionic compound composed of covalently bound, polyatomic ions.
The chemical formula of ammonium hydroxide is NH4OH. What is unusual about ammonium hydroxide
What is another name for ammonium hydroxide?
What type of bond is NH4OH?
What is the chemical formula of ammonium hydroxide?









