Table of Contents
Introduction to Ascorbic Acid Formula
Ascorbic acid, also known as Vitamin C, has the chemical formula C₆H₈O₆. It is an organic compound and is classified as a water-soluble vitamin. Ascorbic acid plays a crucial role in various biological processes and is essential for the proper functioning of the human body.
Vitamin C is an antioxidant, meaning it helps protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. It is involved in collagen synthesis, which is important for the health of connective tissues, skin, and blood vessels. Ascorbic acid also plays a role in immune function, iron absorption, and the synthesis of certain neurotransmitters.
The formula C₆H₈O₆ represents the molecular composition of ascorbic acid indicating that it contains:
- six carbon atoms,
- eight hydrogen atoms
- six oxygen atoms.
The arrangement of these atoms in the molecule gives rise to its unique chemical and biological properties.
Structural Formula of Ascorbic Acid
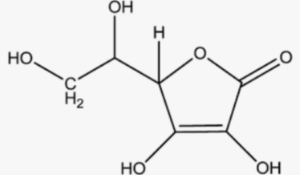
In this structural formula, the six carbon atoms are represented by the line segments, and the hydrogen (H) and hydroxyl (OH) groups are shown attached to the carbon atoms. The two hydroxyl groups (-OH) are located at the third and fourth carbon atoms from the left side of the molecule.
Uses of Ascorbic Acid
- Dietary Supplement: Ascorbic acid is a vital nutrient for the human body and is commonly used as a dietary supplement to ensure adequate intake of vitamin C.
- Antioxidant: Ascorbic acid is a powerful antioxidant that helps protect the body against damage caused by free radicals. It helps to neutralize harmful molecules and supports overall health.
- Immune Support: Ascorbic acid plays a crucial role in supporting the immune system. It helps boost the production of white blood cells and antibodies, which are essential for fighting off infections and diseases.
- Collagen Production: Ascorbic acid is involved in the synthesis of collagen, a protein that is vital for the health and strength of connective tissues, skin, and blood vessels. It promotes wound healing and supports healthy skin.
- Food Preservation: Ascorbic acid is used as a food preservative due to its antioxidant properties. It helps prevent the oxidation of food, extending its shelf life and maintaining its color and flavor.
- Antimicrobial Agent: Ascorbic acid has antimicrobial properties and is used in certain food and beverage products to inhibit the growth of bacteria and other microorganisms.
- Oxidation Reactions: Ascorbic acid is used in various chemical and industrial processes as a reducing agent and catalyst for oxidation-reduction reactions.
Physical Properties of Ascorbic Acid Formula
- Melting Point: The melting point of ascorbic acid is around 190-192 °C (374-378 °F).
- Solubility: Ascorbic acid is highly soluble in water. It is also soluble in alcohol and slightly soluble in ether.
- Odor: Ascorbic acid is odorless.
- Taste: It has a sour taste.
- Density: The density of ascorbic acid is approximately 1.65 g/cm³.
- pH: Ascorbic acid is acidic in nature and has a pH value below 7.
- Stability: Ascorbic acid is relatively unstable in air and can undergo oxidation when exposed to oxygen, heat, or light.
- Hygroscopicity: Ascorbic acid has hygroscopic properties, meaning it can absorb moisture from the surrounding environment.
Chemical Properties of Ascorbic Acid Formula
- Redox Properties: Ascorbic acid acts as a reducing agent and can undergo oxidation-reduction reactions. It readily donates electrons to other molecules, thereby acting as an antioxidant.
- Acid-Base Properties: Ascorbic acid is a weak acid and can donate a proton (H+) to form its conjugate base, ascorbate ion.
- Reactivity with Oxygen: Ascorbic acid is highly reactive with oxygen and can undergo oxidation in the presence of air or other oxidizing agents. This property allows it to act as a reducing agent and scavenge free radicals.
- Reactivity with Metals: Ascorbic acid can form complexes with certain metal ions, such as iron and copper. It can act as a chelating agent, binding to the metal ions and affecting their reactivity.
- Sensitivity to pH and Temperature: The chemical properties of ascorbic acid can be influenced by pH and temperature. It is more stable in acidic conditions and can undergo degradation and loss of activity under alkaline or high-temperature conditions.
- Reaction with Aldehydes and Ketones: Ascorbic acid can react with aldehydes and ketones, acting as a mild reducing agent in various chemical reactions.
- Reaction with Nitrites: Ascorbic acid can react with nitrites to form nitrosating agents, which can potentially lead to the formation of nitrosamines, some of which are considered carcinogenic.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ascorbic acid, with the chemical formula C6H8O6, is a versatile compound known as vitamin C. It is essential for various biological processes in the human body and has numerous applications. Ascorbic acid serves as a dietary supplement, antioxidant, immune supporter, collagen producer, food preservative, antimicrobial agent, and catalyst in oxidation reactions. Its importance in maintaining overall health, preventing diseases, and promoting proper bodily functions make it a valuable compound in various industries and fields.
Solved Examples on Ascorbic Acid Formula
Example 1: Calculate the molecular weight of ascorbic acid (C6H8O6).
Solution: The molecular weight is calculated by summing the atomic weights of all the atoms in the molecule.
C (Carbon) = 12.01 g/mol
H (Hydrogen) = 1.01 g/mol
O (Oxygen) = 16.00 g/mol
Molecular weight of ascorbic acid = (6 * 12.01) + (8 * 1.01) + (6 * 16.00)
= 72.06 + 8.08 + 96.00
= 176.14 g/mol
Therefore, the molecular weight of ascorbic acid is 176.14 g/mol.
Example 2: How many moles of ascorbic acid are present in 250 grams of ascorbic acid (C6H8O6)?
Solution: First, we need to calculate the molar mass of ascorbic acid:
C (Carbon) = 12.01 g/mol
H (Hydrogen) = 1.01 g/mol
O (Oxygen) = 16.00 g/mol
Molar mass of ascorbic acid = (6 * 12.01) + (8 * 1.01) + (6 * 16.00)
= 72.06 + 8.08 + 96.00
= 176.14 g/mol
Now, we can use the formula: Moles = Mass / Molar mass
Moles of ascorbic acid = 250 g / 176.14 g/mol ≈ 1.42 moles
Therefore, there are approximately 1.42 moles of ascorbic acid in 250 grams of ascorbic acid.
Frequently Asked Questions on Ascorbic Acid Formula
What is the other name of ascorbic acid formula?
Ascorbic Acid is also known as Vitamin C or L- ascorbic acid.
What is the ingredient formula for ascorbic acid?
The chemical formula for ascorbic acid, also known as vitamin C, is C6H8O6. It consists of six carbon atoms (C6), eight hydrogen atoms (H8), and six oxygen atoms (O6).
What type of bond is ascorbic acid?
Ascorbic acid contains covalent bonds. Covalent bonds are formed when two or more atoms share electrons in order to achieve a stable electron configuration. In the case of ascorbic acid, the carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms share electrons to form the covalent bonds within the molecule.
Why is vitamin called ascorbic acid?
Vitamin C is commonly known as ascorbic acid because it was initially isolated from citrus fruits, which contain high levels of this compound. The term ascorbic comes from the Latin word ascorbāre, which means to prevent scurvy. Scurvy is a disease caused by vitamin C deficiency, and ascorbic acid was discovered to be the compound responsible for preventing and treating this condition. Therefore, the name ascorbic acid reflects its role in preventing scurvy.
Why is ascorbic acid soluble in water?
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) is soluble in water primarily because of its polar nature. It contains hydrophilic functional groups, such as hydroxyl (-OH) groups, which can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. These hydrogen bonds allow ascorbic acid molecules to effectively mix and dissolve in water. The small size of the molecule allows for efficient interaction with water molecules and facilitates its dissolution.
What is ascorbic acid used for?
Ascorbic acid, also known as vitamin C, has a wide range of uses. It is commonly used as a dietary supplement to meet the body's vitamin C needs and support overall health. As an antioxidant, it helps protect the body against harmful free radicals and oxidative stress. Ascorbic acid is essential for collagen production, promoting healthy skin, joints, and connective tissues. It boosts the immune system, aids in wound healing, and supports the body's natural defense against infections. Ascorbic acid is also used in skincare products, food preservation, and as an antioxidant in cosmetics. Its versatile properties make it a valuable compound for various applications.
Is ascorbic acid same as vitamin C?
Yes, ascorbic acid is the chemical name for vitamin C. They refer to the same compound. Ascorbic acid is the pure form of vitamin C, while vitamin C can also refer to the compound found naturally in various fruits and vegetables.
What are ascorbic acid tablets benefits?
Ascorbic acid tablets, which contain vitamin C, offer several benefits to the body. Some of the key benefits include: Immune System Support: Vitamin C is known for its immune-boosting properties. Ascorbic acid tablets can help strengthen the immune system, reducing the risk of infections and supporting overall health. Antioxidant Protection: Ascorbic acid is a potent antioxidant that helps neutralize harmful free radicals in the body. This antioxidant activity helps protect cells from damage and may contribute to reducing the risk of chronic diseases. Collagen Synthesis: Vitamin C plays a crucial role in collagen synthesis, which is essential for healthy skin, bones, and connective tissues. Ascorbic acid tablets can support the production of collagen, promoting skin health and wound healing. Iron Absorption: Vitamin C enhances the absorption of non-heme iron from plant-based food sources. Taking ascorbic acid tablets with meals can improve iron absorption and help prevent iron deficiency anemia. Antiviral and Antihistamine Effects: Ascorbic acid has been studied for its antiviral properties and its ability to reduce the severity and duration of common cold symptoms. It may also have antihistamine effects, providing relief from allergies and respiratory conditions.








