Table of Contents
Benzene Formula
Benzene, with the chemical formula C6H6, is a colourless, volatile liquid that is highly important in organic chemistry. It is a cyclic hydrocarbon compound and exhibits unique properties due to its aromatic structure.
Benzene Formula and Structure of Benzene
The chemical formula of benzene is C6H6, which means it consists of six carbon (C) atoms and six hydrogen (H) atoms.
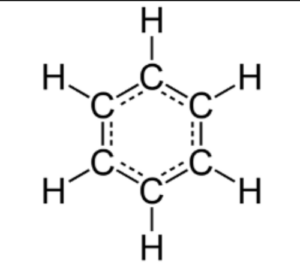
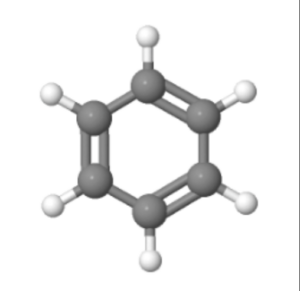
The structure of benzene is represented as a hexagonal ring of carbon atoms, with alternating single and double bonds. Each carbon atom is bonded to one hydrogen atom.
Benzene Physical Properties
- State: Benzene is a colourless liquid at room temperature. It can also be found as a gas at higher temperatures.
- Odour: It has a characteristic sweet, pleasant odour.
- Boiling Point: The boiling point of benzene is approximately 80.1 degrees Celsius (176.2 degrees Fahrenheit).
- Melting Point: Benzene has a melting point of around 5.5 degrees Celsius (41.9 degrees Fahrenheit).
- Density: The density of benzene is about 0.88 g/cm³.
- Solubility: Benzene is sparingly soluble in water but highly soluble in organic solvents like alcohol, ether, and acetone.
Benzene Chemical Properties
- Aromaticity: Benzene is an aromatic compound, meaning it possesses a stable, delocalized pi-electron system above and below the plane of the carbon ring. This property gives benzene its characteristic stability and reactivity.
- Combustibility: Benzene is highly flammable and can burn in the presence of oxygen, releasing carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O).
- Substitution Reactions: Benzene readily undergoes substitution reactions where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by other functional groups. Common substitution reactions include halogenation, nitration, sulfonation, and alkylation.
- Polymerization: Benzene can undergo polymerization reactions to form larger aromatic compounds, leading to the production of polymers like polystyrene and polyethylene.
- Toxicity: Benzene is toxic and poses health risks, including carcinogenic properties. Prolonged exposure to benzene should be avoided.
Applications of Benzene
- Industrial Solvent: Benzene is widely used as a solvent for various organic compounds, particularly in the manufacturing of chemicals, plastics, and synthetic fibers.
- Petrochemical Industry: Benzene is a crucial starting material in the production of numerous chemicals, including styrene, phenol, and nylon.
- Aromatic Compound: Due to its aromatic nature, benzene is an important building block in the synthesis of many aromatic compounds used in pharmaceuticals, dyes, perfumes, and flavorings.
Solved Examples on benzene
Example 1: Calculate the molar mass of benzene.
Solution: To determine the molar mass of benzene, we need to calculate the sum of the atomic weights of its constituent elements.
The atomic weights are as follows:
C (carbon) = 12.01 g/mol
H (hydrogen) = 1.008 g/mol
Now, let’s calculate the molar mass:
Molar mass of benzene (C6H6) = (6 * C) + (6 * H)
= (6 * 12.01) + (6 * 1.008)
= 78.11 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of benzene (C6H6) is 78.11 g/mol.
Example 2: What is the hybridization of carbon atoms in benzene?
Solution: In benzene, each carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms and one hydrogen atom. The carbon-carbon bonds in benzene are represented as a combination of sigma (σ) bonds and pi (π) bonds.
The hybridization of carbon atoms in benzene is sp2. Each carbon atom undergoes hybridization by mixing one s orbital and two p orbitals to form three sp2 hybrid orbitals. These orbitals arrange themselves in a trigonal planar geometry, with an angle of approximately 120 degrees between them. The remaining p orbital on each carbon atom forms a pi (π) bond with the adjacent carbon atoms, creating the aromatic ring structure.
The sp2 hybridization in benzene allows for the delocalization of π electrons above and below the plane of the carbon ring, giving benzene its aromaticity and unique stability.
FAQs on Benzene Formula
What is the molecular formula of benzene?
The molecular formula of benzene is C6H6.
What type of compound is benzene?
Benzene is an aromatic hydrocarbon, specifically a cyclic compound with a hexagonal ring structure.
How many pi bonds are present in the benzene molecule?
Benzene contains three pi bonds, which are formed by the overlapping of p orbitals above and below the plane of the carbon ring.
Is benzene a polar molecule?
No, benzene is a nonpolar molecule. The symmetrical arrangement of carbon and hydrogen atoms in the benzene ring results in a cancellation of dipole moments, making it nonpolar.
What is the structural formula of benzene?
The structural formula of benzene is represented as a hexagon, with alternating single and double bonds between the carbon atoms. Each carbon atom is bonded to one hydrogen atom.








