Table of Contents
Understanding the difference between osmosis and diffusion is a fundamental concept in Biology, especially for students in Class 9. These two processes play a crucial role in various biological phenomena, from the absorption of water by plants to the functioning of our cells. By delving deeper into their distinctions, we unlock a deeper understanding of how life thrives.
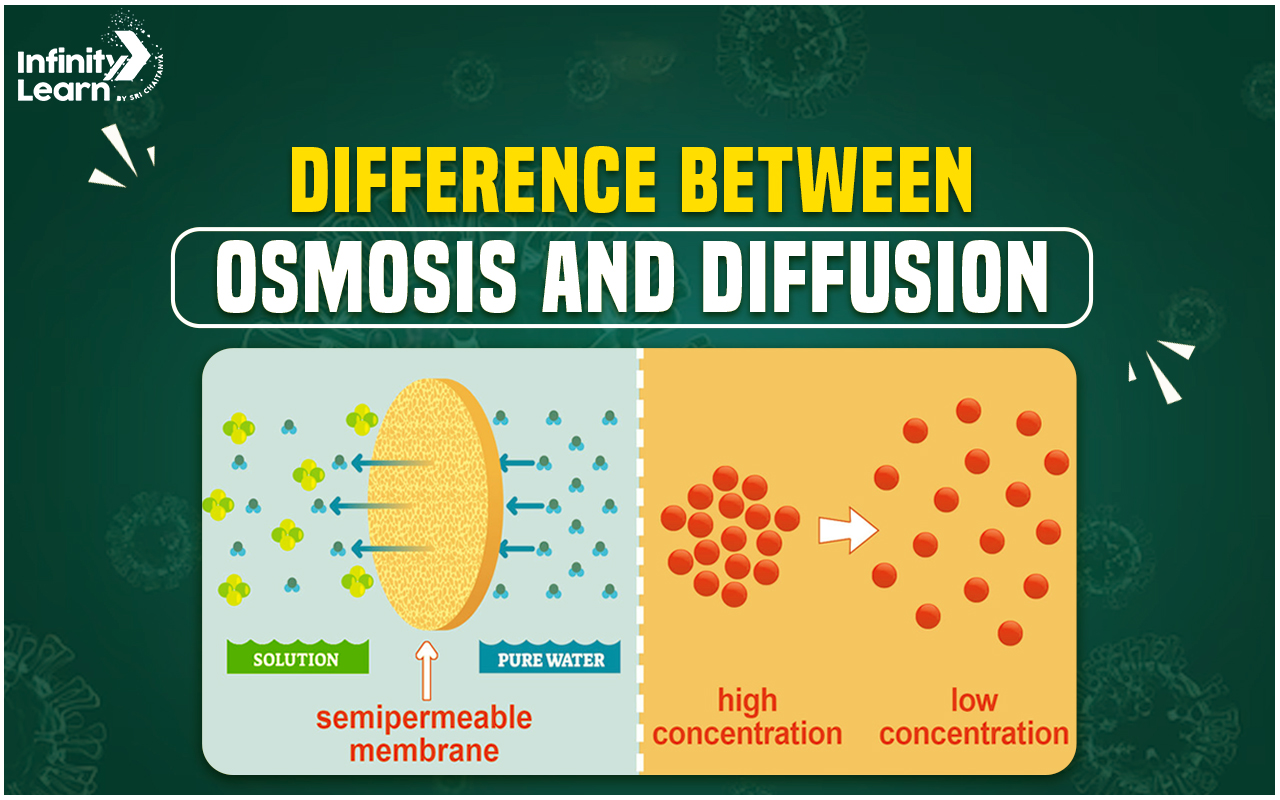
What is Osmosis?
Osmosis is a specific type of diffusion that involves the movement of solvent molecules, usually water, across a semi-permeable membrane. This membrane allows only the solvent molecules to pass through, while larger solute molecules are blocked.
Osmosis occurs in a direction that equalizes the concentration of the solvent across the membrane. For example, when a plant root is placed in water, water moves across the semi-permeable cell membrane into the plant cell until the concentration of water is balanced on both sides.
Examples of Osmosis –
- Plant cell water absorption: Root hairs have a higher concentration of solutes than the surrounding soil water. This difference in concentration creates an osmotic gradient that draws water into the plant cell, maintaining turgor pressure and allowing the plant to stand upright.
- Preserving food: Soaking food in concentrated salt or sugar solutions (hypertonic environments) draws water out of the food. This process inhibits the growth of bacteria and microorganisms, extending shelf life.
- Guttation: Excess water absorbed by plant roots is excreted through tiny pores called hydathodes on the leaf margins as water droplets. This process is known as guttation.
- Contact lenses: Soft contact lenses allow water molecules to pass through them, keeping the eye hydrated and oxygenated. However, they act as a semi-permeable membrane, preventing larger molecules from entering and protecting the eye from irritation.
- Dialysis: In this medical procedure, a semi-permeable membrane separates the patient’s blood from a dialysis solution. Waste products like urea and creatinine move from the blood into the dialysis solution due to the difference in concentration across the membrane, helping cleanse the blood in individuals with kidney failure.
What is Diffusion?
Diffusion is a broader term that refers to the movement of all particles from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. This movement occurs due to the natural tendency of particles to spread out evenly in their available space.
Diffusion can occur in any medium, including solids, liquids, and gases. It does not require a semi-permeable membrane and can involve the movement of both solvent and solute molecules.
Examples of Diffusion –
- Perfume scent: Perfume molecules diffuse into the air, filling the room with fragrance.
- Food coloring in water: When dropped into water, food coloring molecules diffuse throughout the water, creating a uniform color.
- Gas exchange in lungs: Oxygen from inhaled air diffuses across the thin membrane in the lungs into the bloodstream, while carbon dioxide diffuses from the bloodstream into the exhaled air.
- Nutrient delivery: Oxygen and nutrients dissolved in blood plasma diffuse across the cell membrane and into the cytoplasm of cells, providing them with the necessary energy and materials to function.
- Ink in water: When a drop of ink is placed on the surface of water, it spreads outward due to the diffusion of ink molecules into the surrounding water.
Difference Between Osmosis and Diffusion for Class 9
| What is Osmosis and Diffusion | |
| Osmosis | Diffusion |
| Movement of solvent (usually water) across a membrane. | Movement of particles from high to low concentration. |
| Requires a semipermeable membrane. | Does not require a membrane. |
| Driven by the solvent concentration gradient. | Driven by the concentration gradient of particles. |
| Occurs in living cells. | Occurs in both living and non-living systems. |
| Vital in regulating cell pressure and volume. | Responsible for gas exchange and scent dispersion. |
| Directly involves water as the primary solvent. | Involves all types of particles (solids, liquids, gases). |
| Rate is affected by temperature and the type of solute. | Rate influenced by temperature, pressure, and concentration. |
| No energy expenditure in passive osmosis. | Passive diffusion does not require energy. |
| Crucial for maintaining cell turgidity in plants. | Essential for the mixing of substances in solutions. |
| Osmotic pressure can be quantitatively measured. | Concentration gradient is the driving force. |
In this context, the difference between osmosis and diffusion class 9 emphasizes the distinct ways in which substances move in biological systems. What is osmosis and diffusion and the diffusion and osmosis difference are fundamental concepts in understanding cellular processes.
Importance of Learning What is Osmosis and Diffusion
Learning about diffusion and osmosis and being able to define diffusion and osmosis provides a foundation for advanced biological studies.
- Practical Applications in Everyday Life: Understanding the principles of what is osmosis and diffusion is not just academic. These processes are at play in everyday phenomena, such as the brewing of coffee (diffusion) and the preservation of food with salt or sugar (osmosis).
- Foundation for Advanced Scientific Learning: Grasping the diffusion and osmosis difference lays the groundwork for more complex topics in biology, chemistry, and environmental science. This knowledge is crucial for students aiming to pursue careers in science and medicine.
- Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Skills: Learning about diffusion and osmosis and how to define diffusion and osmosis enhances critical thinking. Students learn to apply theoretical knowledge to practical problems, a skill valuable in all areas of life.
These points highlight the broad-reaching implications and applications of understanding osmosis and diffusion. From their crucial roles in biological systems to their presence in everyday life, these processes form a foundational component of scientific education, emphasizing the relevance and necessity of understanding the difference between osmosis and diffusion.
NCERT Exam Questions on Osmosis and Diffusion
These questions encompass various aspects of osmosis and diffusion, from their basic definitions to their applications in biological systems. They are designed to test the students’ understanding of these fundamental concepts in biology, in line with the NCERT curriculum for class 9.
Long Answer Type Questions
- Describe how osmosis plays a critical role in the kidney’s function in human beings.
- Explain the process of diffusion in the alveoli during gas exchange.
- Discuss the impact of osmosis on plant cells when placed in a hypertonic solution.
- Elaborate on the role of diffusion in the distribution of nutrients and oxygen to cells in multicellular organisms.
- Analyze how osmotic pressure is established in cells and its significance in maintaining cell integrity.
Short Answer Type Questions
- Define osmosis and give an example of where it is vital in everyday life.
- How does diffusion differ in gases compared to liquids? Provide an example.
- Explain the role of a semipermeable membrane in osmosis with a suitable example.
- Describe a real-world application where diffusion is an essential process.
- What happens to a red blood cell placed in a hypotonic solution, and why? Use the concept of osmosis to explain.
| Check all the Biology Difference Between Articles | |
| Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell | Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell |
| Difference Between DNA and RNA | Difference Between Cold Blooded and Warm Blooded |
| Difference Between Flora and Fauna | Difference between mitosis and meiosis |
| Difference Between Weather and Climate | Difference Between Arteries and Veins |
| Difference Between Xylem and Phloem | Difference Between Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration |
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between osmosis and diffusion is not just a curriculum requirement but a stepping stone to understanding more complex biological and chemical phenomena. This knowledge forms the basis for advanced studies in various scientific fields.
FAQs on Difference Between Osmosis and Diffusion
What is the difference between osmosis and diffusion?
Osmosis: Movement of solvent molecules across a semi-permeable membrane from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution. Diffusion: Movement of all particles (solvent and solute) from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration.
What is the main similarity between osmosis and diffusion?
Both are driven by the tendency of particles to spread out evenly in their available space








