Table of Contents
Law of Segregation and the Law of Dominance are two key biological principles. They explain how we acquire features such as eye color, hair color, and even height. Have you ever observed why we might match our mom’s eyes or dad’s hair? Or why a child is tall like his or her grandfather even though their parent is not? All this is due to genetics.
Law of Segregation and the Law of Dominance were discovered by a scientist Gregor Mendel over 150 years ago. To figure out how offspring get the traits from their parents, he experimented with pea plants. Mendel’s research helped scientists understand how all living things, including humans, get features from their parents.
What is Inheritance?
Definition of Inheritance: Inheritance is defined as the process by which traits or characteristics are passed from parents to their children. Traits like eye color, hair color, or height, are determined by genes.
What are Genes?
Genes are defined as the instructions inside living things that command their bodies how to develop. Mendel’s three inheritance rules are the Law of Dominance, the Law of Segregation, and the Law of Independent Assortment. These laws were developed by tests on pea plants with various characteristics. Mendel began his studies with monohybrid crosses.
Mendel noticed that features lacking in the first generation reappeared in the second generation. These observations triggered the emergence of the Law of Dominance and the Law of Segregation.
What is the Law of Dominance?
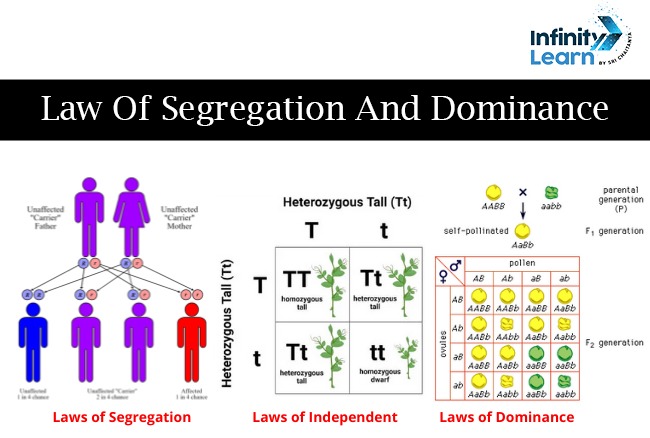
This law explains how some traits are expressed over others in genetics. Mendels says- “When parents with pure, opposing qualities are crossed, only one type of trait comes up in the next generation. The hybrid progeny will only show the dominant characteristic in the phenotypic.”
The law of dominance is the first law of inheritance. In this law, each character is monitored by units known as factors, which appear in pairs. If the pairs are heterozygous, one will always dominate the other.
What are Dominant and Recessive Traits?
Each trait has two alleles that are dominant and recessive. The dominant allele is stronger and will show its characteristic even if only one copy is present. The recessive allele is weaker and only exhibits its characteristic when both alleles are recessive.
Steps Involved in the Law of Dominance
A monohybrid cross combines the two monohybrid characteristics (TT and tt). Plants with the same characteristics but differing in only one are crossed. Similarly, take the example of purple flowers, which are dominant over white flowers.
- A plant possessing one or two purple flower alleles will produce purple flowers.
- The recessive characteristic is only present when both alleles are recessive.
- As a result, if a plant possesses two recessive flower color alleles, it will only give white flowers.
What is the Law of Segregation?
According to Mendel, during gamete production, each gene separates from the others, resulting in only one allele for each gene. The law of segregation is the second law of inheritance. The law states that the pair of alleles separate from each other during the process called meiosis. Post this, only one allele is present in each gamete.
Steps Involved in the Law of Segregation
A monohybrid cross expresses both alleles in the F2 generation without any blending. Thus, the law of segregation depends on the fact that each gamete only has one allele.
- Any living thing carries two copies of each gene, one from each parent. These two copies are known as alleles.
- For example, a plant may contain one allele for purple flowers and one for white flowers.
- When an organism produces offspring, it only passes down one of these two alleles to each offspring.
- This means that each parent imparts only one allele for each attribute to the next generation.
- Because this is a random process, the resultant flower could inherit either the purple or white alleles.
What are Phenotypes and Genotypes?
The two terms phenotypes and genotypes are two concepts of genetics. Here is the brief of both the terms explained below.
Genotype
Genotype refers to the accurate combination of alleles that an organism inherited from its parents. These alleles may be dominant or recessive.
- For example, in the case of flower colour, a plant’s genotype may be PP (where P represents the dominant allele for purple flowers).
- It can also be pp (where p represents the recessive gene for white flowers).
- The genotype is simply the genetic code that determines what qualities an organism may have.
Phenotype
Phenotype refers to an organism’s physical appearance or observable traits as a result of the interplay between its genotype and the environment. It is what you observe or measure.
- In the flower color example, if a plant has the genotype PP or Pp, the phenotype will be purple flowers.
- This is because the dominant allele determines the trait’s appearance.
- If the plant has the genotype pp, the phenotype will be white blooms.
- The reason is, that there are no dominant alleles that cover up the recessive characteristic.
So, phenotype is an observable trait of an organism that arises from the combined effects of its genotype and environment.
FAQs on Law of Segregation and Law of Dominance
What is the Law of Segregation?
According to the Law of Segregation, every organism carries two alleles for each trait. These alleles split during the development of gametes. Each gamete has only one allele per trait. When gametes unite during fertilization, the offspring receives one allele from each parent. According to Mendel, during gamete development, each gene separates from the others, resulting in only one allele for each gene.
What is the Law of Dominance?
It is the first law of inheritance. The Law of Dominance states that some alleles are dominant over others. According to Mendel, when parents with pure, opposing qualities are crossed. In this way, only one type of trait comes up in the next generation. The hybrid progeny will only show the dominant characteristic in the phenotypic.
How does the Law of Segregation and the Law of Dominance work together?
The Law of Segregation explains how alleles separate into gametes. Whereas the Law of Dominance, explains how dominant alleles specify visible features. It occurs when both dominant and recessive alleles are present.
What is an allele?
An allele is an extra copy of a gene. Genes are the instructions contained within the human body that determine factors like eye color, hair color, and height. For each feature, there are two versions of the gene, one from our mother and the other from our father. These variations are called alleles.
Why are Mendel's laws important in genetics?
Mendel’s laws are the law of dominance and the law of inheritance which are the main laws of inheritance. They play a very important role in explaining how traits are inherited and how genetic variation occurs.