Table of Contents
Introduction Butanoic Acid Formula
Butanoic acid, also known as butyric acid, is an organic compound with the chemical formula C4H8O2. It belongs to the carboxylic acid family and is characterized by its distinct odor, often described as rancid or resembling sweaty socks. It occurs naturally in various sources such as dairy products, butter, and certain fruits.
Applications of Butanoic Acid
Butanoic acid has several industrial applications.
- It is used as a flavoring agent in food products, giving a characteristic taste to items like cheese and butter.
- It is also employed in the production of esters, which are used in fragrances, perfumes, and artificial flavors.
- Additionally, butanoic acid is used as a precursor in the synthesis of various chemicals, including pharmaceuticals, plasticizers, and animal feed additives.
From a biological perspective, butanoic acid plays a role in metabolic processes in organisms. It is produced by bacteria in the gut during the digestion of dietary fibers and can serve as an energy source for cells. However, its odor can be off-putting in high concentrations.
Structural Formula of Butanoic Acid
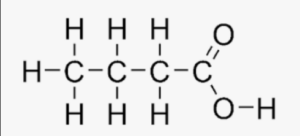
Each line represents a bond, and each carbon atom is bonded to the appropriate number of hydrogen atoms. The carbon chain consists of four carbon atoms (C4) with a carboxyl group (-COOH) attached to one end. The carboxyl group consists of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom (C=O) and single-bonded to a hydroxyl group (-OH). This structural arrangement gives butanoic acid its characteristic properties and reactivity as a carboxylic acid.
Uses of Butanoic Acid
- Flavor and Fragrance: Butanoic acid is used in the food and beverage industry as a flavoring agent, providing a distinctive odor and taste. It is commonly found in butter, cheese, and other dairy products. It is also used in the production of artificial fruit flavors.
- Pharmaceuticals: Butanoic acid is used in the production of certain pharmaceuticals, such as esters, salts, and derivatives. These compounds have various applications in the pharmaceutical industry, including as solvents, intermediates, and active ingredients in medications.
- Animal Feed: Butanoic acid is added to animal feed to improve palatability and promote healthy digestion. It is especially used in feed for pigs and poultry.
- Industrial Applications: Butanoic acid is used in the production of various industrial chemicals and materials. It is a precursor for the synthesis of esters, which are widely used as solvents, plasticizers, and flavorings in industries such as coatings, adhesives, and textiles.
- Biological Control: Butanoic acid has antimicrobial properties and is sometimes used as a natural preservative and antimicrobial agent in certain products, such as cosmetics, personal care products, and food preservation.
Physical Properties of Butanoic Acid Formula
- State: Butanoic acid is a colorless liquid at room temperature.
- Odor: It has a strong, pungent odor similar to that of rancid butter or sweaty socks.
- Density: The density of butanoic acid is approximately 0.96 grams per milliliter.
- Boiling Point: Butanoic acid has a relatively high boiling point of around 163-165 degrees Celsius (325-329 degrees Fahrenheit).
- Melting Point: The melting point of butanoic acid is around 16-18 degrees Celsius (61-64 degrees Fahrenheit).
- Solubility: Butanoic acid is soluble in water to some extent. It forms a slightly acidic solution when dissolved in water. It is more soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol and diethyl ether.
- Vapor Pressure: Butanoic acid has a moderate vapor pressure, which means it can evaporate into the air at room temperature.
- Miscibility: Butanoic acid is miscible with other organic solvents such as ethanol, acetone, and benzene.
- Appearance: Pure butanoic acid appears as a clear liquid, but it may develop a yellowish tint upon exposure to air and light.
Chemical Properties of Butanoic Acid Formula
- Acidic Nature: Butanoic acid is a carboxylic acid, which means it is acidic in nature. It has a carboxyl group (COOH) that can donate a proton (H+) in a chemical reaction, making it capable of behaving as an acid.
- Reactivity with Metals: Butanoic acid can react with certain reactive metals, such as sodium or potassium, to produce salts known as butanoates. The reaction involves the displacement of hydrogen from the carboxyl group.
- Ester Formation: Butanoic acid can undergo esterification reactions with alcohols in the presence of an acid catalyst. This reaction forms esters, which are compounds derived from the combination of an alcohol and an acid. For example, the reaction of butanoic acid with methanol (CH3OH) can form methyl butanoate.
- Oxidation: Butanoic acid can be oxidized to form carbon dioxide and water. Strong oxidizing agents, such as potassium permanganate or chromic acid, can initiate this oxidation reaction.
- Hydrolysis: Butanoic acid can undergo hydrolysis reactions, where it reacts with water to form the corresponding carboxylic acid and alcohol. The reaction is catalyzed by an acid or a base.
- Reaction with Bases: Butanoic acid can react with bases to form salts known as butanoates. The carboxyl group donates a proton to the base, resulting in the formation of the salt and water.
- Ester Hydrolysis: Butanoic acid esters can undergo hydrolysis in the presence of acid or base, resulting in the formation of butanoic acid and the corresponding alcohol.
Conclusion
In conclusion, butanoic acid, also known as butyric acid, is a carboxylic acid with the formula C4H8O2. It is a colorless liquid with a strong, unpleasant odor. Butanoic acid has several important uses in various industries. It is commonly used as a flavoring agent in the food industry, providing a distinctive, buttery taste and aroma. It is also used in the production of esters for perfumes and fragrances. Butanoic acid has applications in the manufacture of plastics, resins, and pharmaceuticals. Additionally, it is used as a precursor in the synthesis of various chemicals and as a solvent in some industrial processes. While butanoic acid is generally recognized as safe for use in food and cosmetic products, it is important to handle it with care due to its corrosive and irritating properties.
Solved Examples on Butanoic Acid Formula
Example 1: Calculate the molar mass of butanoic acid.
Solution: To calculate the molar mass of butanoic acid (C4H8O2), we need to sum up the atomic weights of all the atoms in the molecule.
Molar mass = (4 * Atomic weight of Carbon) + (8 * Atomic weight of Hydrogen) + (2 * Atomic weight of Oxygen)
= (4 * 12.01) + (8 * 1.01) + (2 * 16.00)
= 48.04 + 8.08 + 32.00 = 88.12 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of butanoic acid is approximately 88.12 g/mol.
Example 2: Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction between butanoic acid and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to form the sodium salt of butanoic acid and water.
Solution:
The balanced equation for this reaction is:
C4H8O2 + NaOH → C4H7O2Na + H2O
By balancing the equation, we ensure that the number of atoms of each element is equal on both sides of the equation.
Example 3: What is the IUPAC name of butanoic acid?
Solution: The IUPAC name of butanoic acid is “butanoic acid” itself. The prefix “but-” represents the four-carbon chain, and the suffix “-anoic acid” indicates that it is a carboxylic acid.
Frequently Asked Questions on Butanoic Acid Formula
What is the general formula of butanoic acid?
The general formula of butanoic acid is C4H8O2. It consists of four carbon atoms, eight hydrogen atoms, and two oxygen atoms arranged in a specific structure.
Why is it called butanoic acid?
It's called butanoic acid because it has a chain of four carbon atoms. The prefix butan comes from the traditional name for compounds with four carbons.
How do you write the structure of butanoic acid?
The structure of butanoic acid is written as CH3CH2CH2COOH. It has a straight chain of three carbon atoms, followed by a carboxyl group (COOH) attached to the last carbon.
What is the full name of butanoic acid?
The full name of butanoic acid is butyric acid. The name butyric
What is the common name of butanoic acid?
The common name of butanoic acid is butyric acid. This name is often used interchangeably with butanoic acid in various scientific and industrial contexts.
What are the common uses of butanoic acid?
Butanoic acid is used in making esters for flavors and fragrances, as an animal feed additive, in food processing, and as a precursor to chemicals like butyrate plastics.
Is butanoic acid a volatile compound?
Yes, butanoic acid is a volatile compound. It has a strong, unpleasant odor and can evaporate into the air at room temperature, releasing its distinct smell.








