Table of Contents
Forest Map of India: Forests are a critical part of our environment, providing numerous benefits such as oxygen production, carbon sequestration, and wildlife habitat. Forests are a valuable source of timber, fuelwood, non-timber forest products, and medicinal plants. India has a significant number of national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and protected areas that help in the conservation of its rich biodiversity.
In India, forests have been an important part of its culture and economy for centuries. The forest cover in India is spread across a vast area of land, encompassing a diverse range of ecosystems and habitats.
India has a diverse range of forest ecosystems ranging from tropical evergreen forests to temperate forests and mangroves.
To understand the distribution and extent of forests in India, a forest map is an essential tool. A forest map of India provides a comprehensive overview of the country’s forests, including details on the distribution and types of forests, protected areas, wildlife habitats, and other ecological features of the country. The forest map is based on satellite imagery and ground truthing data.
The satellite imagery captures the vegetation cover, and the ground truthing data confirms the type of vegetation that is being covered.
A map of India is a valuable tool. A forest map of India can be used for planning and management of forests. It provides valuable information for designing management plans for forest conservation, restoration, and forestry resources development. It also helps in identifying specific areas that require attention for conservation and restoration programs.
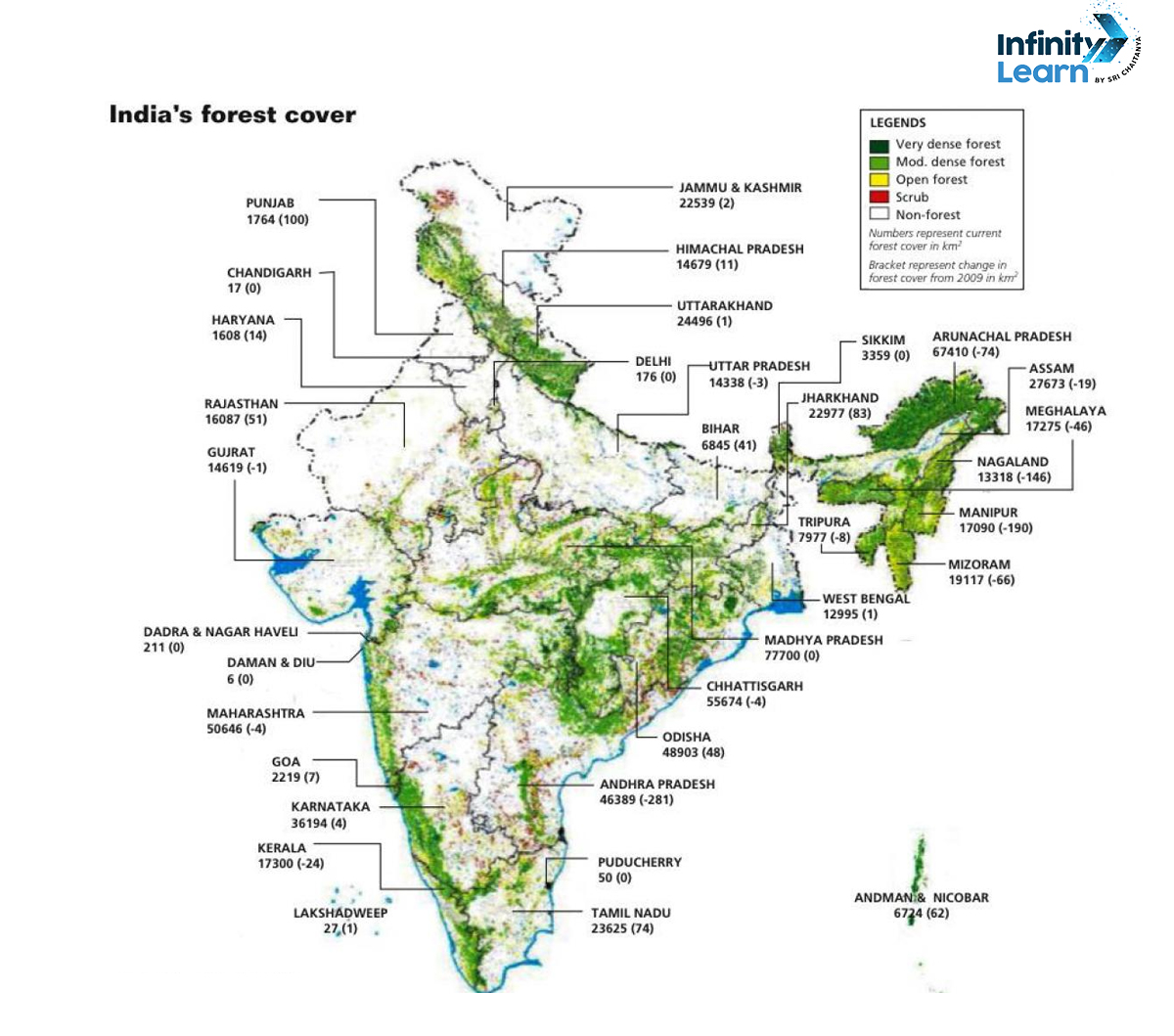
Forest cover in India
- Extent: India’s forest cover spans about 24% of its total land area, encompassing diverse ecosystems such as tropical, subtropical, montane, and deciduous forests.
- Biodiversity: These forests host a rich variety of flora and fauna, contributing significantly to India’s biodiversity.
- Threats: However, urbanization, industrialization, and agricultural expansion pose persistent threats, leading to deforestation and degradation.
- Conservation Efforts: Various initiatives by the government, NGOs, and local communities focus on conserving and expanding indian forest cover through reforestation, afforestation, and sustainable management practices.
- Importance: Recognizing their critical role, these efforts aim to mitigate climate change, protect biodiversity, and sustain the livelihoods of millions dependent on forest resources.
Types of Forests in India
India’s forest cover is diverse and spread across the country. The types of forests that are shown in a forest map of India are numerous. The Forest Survey of India categorises forests into various types, including tropical evergreen, tropical semi-evergreen, tropical deciduous, subtropical broad-leaved hill, subtropical pine, temperate broad-leaved, temperate coniferous, and alpine forests. Each of these indian forests has its unique characteristics, and they are home to a wide range of wildlife.
Here is a general distribution:
Tropical Forests
● Found in regions with high temperature and high annual precipitation.
● Includes evergreen, semi-evergreen, and deciduous forests.
● Examples: Western Ghats, Northeastern states.
Subtropical Forests
● Found in regions with a moderate climate.
● Includes broad-leaved hill forests and pine forests.
● Examples: Parts of Himalayan region.
Temperate Forests
● Found in regions with cool temperatures.
● Includes broad-leaved and coniferous forests.
● Examples: Parts of Himalayan region.
Alpine Forests
● Found in high-altitude areas with cold temperatures.
● Includes vegetation adapted to extreme conditions.
● Examples: Alpine regions in the Himalayas.
Mangrove Forests
● Found in coastal areas with brackish water.
● Examples: Sundarbans in West Bengal, Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Importance of Forest Map of India
The forest map of India is a powerful tool that supports various aspects of environmental conservation, sustainable development, and natural resource management. It serves as a foundation for informed decision-making and actions that balance ecological health with human needs. The importance of forests lies in their irreplaceable role in sustaining life, ecosystems, and economies worldwide. Below mentioned are some of the key significance of forest map of India:
● Biodiversity Conservation: Forest maps help identify areas with high biodiversity, aiding conservation efforts by highlighting regions that require special protection and management.
● Wildlife Habitat Assessment: By mapping forests, it becomes possible to assess and understand the distribution of wildlife habitats. This information is crucial for planning and implementing conservation strategies for various species.
● Resource Management: Forest maps are essential for sustainable resource management. They assist in planning the extraction of timber, non-timber forest products, and other resources without causing ecological imbalances.
● Carbon Sequestration: Forests play a vital role in carbon sequestration. Maps help estimate the carbon stock in different forested areas, contributing to climate change mitigation strategies.
● Identification of Forest Types: Forest maps classify different types of forests, such as tropical, subtropical, temperate, and alpine. This information is crucial for understanding the unique characteristics and ecological functions of each type.
● Monitoring Forest Cover Changes: Over time, forest maps enable the monitoring of changes in forest cover, including deforestation, afforestation, and forest degradation. This information guides policymakers in addressing environmental concerns.
● Water Resource Management: Forests play a role in maintaining water cycles. Forest maps assist in identifying watershed areas, which are crucial for sustainable water resource management.
● Planning Protected Areas: Forest maps aid in identifying and planning protected areas, national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and other conservation zones to ensure the preservation of critical habitats.
● Conservation Planning: Conservation planners use forest maps to prioritise areas for conservation initiatives, restoration projects, and wildlife corridors, optimising limited resources for maximum impact.
● Ecosystem Services Mapping: Forests provide numerous ecosystem services, including air and water purification, soil stabilisation, and recreational opportunities. Maps help quantify and prioritise these services for sustainable planning.
● Community Engagement: Forest maps facilitate community engagement by providing a visual representation of forest resources. Local communities can actively participate in sustainable forest management based on this information.
● Land Use Planning: Forest maps contribute to land use planning by identifying areas suitable for agriculture, urban development, or other purposes without compromising critical forest ecosystems.
● Fire Risk Assessment: Forest maps assist in assessing fire risk and planning preventive measures. They help identify areas prone to wildfires and guide strategies for fire management.
● Research and Education: Forest maps serve as valuable tools for research, education, and awareness programs. They contribute to a better understanding of forest ecosystems and their role in the environment.
● Policy Formulation: Policymakers use forest maps to formulate effective policies for sustainable forest management, conservation, and environmental protection.
| Other Topics Related to Trees and Forest | |
| Essay on Benefits of Planting Trees | Paragraph on Forest |
| Essay on Forest | Save Forest Slogans |
| Effects and Impacts of Deforestation | Catchy Slogans on Forest |
| Conservation of Forest and Wildlife | Speech on Deforestation |
| Speech on Importance of Trees in our Lives | Paragraph on Save Trees |
| 100+ Van Mahotsav Slogans | Trees Our Best Friend Essay |
| Speech on Nature | Usefulness of Trees Paragraph |
| Slogans on Deforestation | |
Government’s Initiative To Protect Forests of India
Forests are important for many reasons, including providing shelter and habitat for wildlife, preventing soil erosion, regulating the water cycle, storing carbon, and providing resources such as timber, medicine, and food. And it is important for the government to take measures to protect them. For this purpose, the government needs a forest map of india.
Effective planning and management of forests require comprehensive, accurate, and current forest maps, which are essential tools in safeguarding the country’s biological diversity, ecological services, and socio-economic development. A forest map helps in identifying the changes in forest cover over time. By comparison with previous years’ forest maps, policymakers and researchers can track changes in the forest cover, and the extent of deforestation or reforestation efforts over the years. This helps in measuring the success or failure of conservation efforts and identifying areas where new policies and conservation programs are required.
The Government of India has implemented various policies and programs such as the National Afforestation Program, Project Tiger, and the National Mission for Green India to protect and conserve forests in India.
The Indian government has taken several steps towards the conservation and management of forests. The National Forest Policy of 1988 provided a framework for sustainable forest management, conservation, and development. The Forest Conservation Act of 1980 and the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972 provided legal protection to Indian forests and wildlife and prohibited the use of forestland for non-forestry purposes.
Additionally, community involvement, education, and awareness campaigns are also used to protect and conserve forests.
Key Points
● The Forest Survey of India (FSI), an organisation under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, provides detailed forest maps. The Forest Survey of India provides maps that highlight the locations of wildlife sanctuaries and national parks across the country.
● The northeastern states, followed by the central and southern regions, including parts of Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh, often have higher forest cover compared to other regions.
● A forest map of India can be found on the website of the Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education (ICFRE), Forest Survey of India (FSI), and the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
Forest Map Of India – Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What information does a forest map of India provide?
A forest map of India provides information on the distribution and types of forests, protected areas, wildlife habitats, and other ecological features of the country.
What is the main threat to forests in India?
The main threat to forests in India is deforestation, which is largely caused by human activities such as mining, logging, agriculture, and urbanisation.
What is the total forest cover of India?
According to the India State of Forest Report 2019, the total forest cover of India is 21.67% of its geographical area.
How is forest cover assessed in India?
The Forest Survey of India conducts periodic assessments using satellite data to determine the forest cover, density, and types. These assessments help in creating detailed forest maps.






