Hexane Formula
Introduction
Hexane is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H14. It is a hydrocarbon belonging to the alkane family. The molecule consists of six carbon atoms bonded together in a straight chain, with each carbon atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms.
Hexane is a colourless liquid. It is nonpolar in nature and is insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.
Hexane is primarily derived from petroleum and is commonly used as a solvent in various industries, such as in the
- extraction of oils and fats,
- as a cleaning agent, and
- as a component in fuels.
Its relatively low toxicity and favorable physical properties make it a versatile compound in many applications.
Structural Formula of Hexane
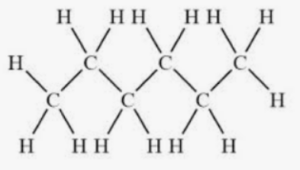
Each line represents a bond between carbon (C) atoms, and each carbon atom is attached to two hydrogen (H) atoms, except for the end carbon atoms, which are attached to three hydrogen atoms.
Uses of Hexane
- Solvent: Hexane is widely used as a non-polar solvent in various industrial processes, including the extraction of vegetable oils, cleaning of machinery and equipment, and as a solvent in the production of adhesives, paints, and coatings.
- Industrial and Laboratory Applications: Hexane is used as a solvent in the formulation of industrial chemicals, such as rubber cement, shoe polish, and industrial cleaning agents. It is also used in laboratories for analytical testing, chromatography, and as a reference standard in chemical analysis.
- Food Industry: Hexane is utilized in the food industry for oil extraction from seeds and nuts. It is commonly used to extract vegetable oils from soybeans, sunflower seeds, cottonseeds, and other oil-rich crops.
- Fuel: Hexane is used as a fuel component in gasoline blends. It provides high energy content and improves combustion efficiency.
- Adhesives and Glues: Hexane is used as a solvent in the production of various adhesives and glues, including those used in the construction, automotive, and furniture industries.
- Cleaning Agent: Hexane is employed as a cleaning agent in various industries, such as electronics manufacturing, precision cleaning, and degreasing of metal parts.
- Pharmaceuticals: Hexane is utilized in the pharmaceutical industry for the extraction and purification of active compounds from natural sources, such as medicinal plants.
Physical Properties of Hexane Formula
- State: Hexane is a colourless liquid at room temperature.
- Odour: It has a mild, sweet, and somewhat gasoline-like odour.
- Density: The density of hexane is approximately 0.659 grams per milliliter.
- Boiling Point: Hexane has a relatively low boiling point of around 68.7 degrees Celsius (155.7 degrees Fahrenheit).
- Melting Point: The melting point of hexane is around -95 degrees Celsius (-139 degrees Fahrenheit).
- Solubility: Hexane is considered a nonpolar solvent and is insoluble in water. However, it is miscible with many organic solvents.
- Flammability: Hexane is highly flammable, and its vapours can form explosive mixtures with air.
- Vapour Pressure: Hexane has a relatively high vapour pressure, which means it evapourates readily at room temperature.
- Refractive Index: The refractive index of hexane is approximately 1.374.
Chemical Properties of Hexane Formula
- Combustibility: Hexane is highly combustible. It readily reacts with oxygen in the presence of a flame or spark, undergoing combustion to produce carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). It is important to handle hexane with caution to avoid fire hazards.
- Reactivity: Hexane is relatively unreactive under normal conditions. It does not undergo significant chemical reactions with most common reagents. However, it can react with certain strong oxidizing agents, halogens, or reactive metals under specific conditions.
- Hydrocarbon Solvent: Hexane is widely used as a nonpolar solvent in various industries. It can dissolve many organic compounds, including fats, oils, and waxes. Its low polarity makes it useful for extracting oils and other nonpolar substances.
- Substitution Reactions: Hexane can undergo substitution reactions, particularly when exposed to reactive halogens such as chlorine or bromine. In the presence of light or heat, these halogens can substitute hydrogen atoms in hexane, resulting in the formation of halogenated derivatives.
- Environmental Impact: Hexane is not readily biodegradable and can persist in the environment. It can contribute to air pollution if released into the atmosphere due to its high volatility.
- Chemical Stability: Hexane is generally stable under normal storage and handling conditions. It does not decompose or undergo significant chemical changes over time.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hexane (C6H14) is an organic compound that belongs to the alkane family. It is a colorless liquid with a characteristic odor. Hexane has various applications across different industries. It is commonly used as a solvent in laboratories, industrial processes, and in the production of consumer products such as adhesives, paints, and coatings. Hexane is also utilized in the extraction of oils from seeds and vegetables, as well as in the pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries. Additionally, it serves as a fuel component and is used in some automotive fuels. However, it’s important to note that hexane can be flammable and should be handled with caution. Overall, hexane’s low toxicity and excellent solvent properties make it a valuable compound in various industrial and commercial applications.
Solved Examples on Hexane Formula
Example 1: What is the molecular weight of hexane?
Solution:
To calculate the molecular weight of hexane (C6H14), we need to sum up the atomic weights of all the atoms in the molecule.
Molecular weight = (6 * Atomic weight of Carbon) + (14 * Atomic weight of Hydrogen) = (6 * 12.01) + (14 * 1.01)
= 72.06 + 14.14 = 86.20 g/mol
Therefore, the molecular weight of hexane is approximately 86.20 g/mol.
Example 2: Balance the following chemical equation representing the combustion of hexane: C6H14 + O2 -> CO2 + H2O
Solution:
The balanced equation for the combustion of hexane is:
2C6H14 + 19O2 -> 12CO2 + 14H2O
By balancing the equation, we ensure that the number of atoms of each element is equal on both sides of the equation.
Frequently Asked Questions on Hexane Formula
1: What type of formula is hexane?
Answer: Hexane is an empirical formula for a straight-chain alkane hydrocarbon. It represents the simplest and most common structure of hexane. The structural formula of hexane is
H3C-(CH2)4-CH3, which shows the arrangement of carbon and hydrogen atoms in the molecule. The empirical formula, C6H14, provides the simplest ratio of carbon and hydrogen atoms in hexane.
2: What type of solvent is hexane?
Answer: Hexane is a non-polar solvent. It is widely used as a non-polar organic solvent due to its low polarity and excellent ability to dissolve non-polar compounds. Hexane is immiscible with water, but it readily dissolves non-polar substances such as fats, oils, waxes, and many organic compounds. Its non-polar nature makes it suitable for various applications, including extraction, chromatography, and industrial processes that require the dissolution or separation of non-polar compounds.
3: What are the unique properties of hexane?
Answer: Hexane exhibits several unique properties that make it a valuable solvent in various applications. Firstly, it is a non-polar compound, which means it has a low dielectric constant and low polarity. This property allows it to dissolve non-polar substances efficiently, including oils, fats, and hydrocarbons. Hexane is also a clear, colourless liquid with a relatively low boiling point, making it easy to handle and evaporate when necessary. It has a low viscosity and low surface tension, enabling it to spread easily and penetrate materials. Additionally, hexane is relatively inert and non-reactive, which makes it suitable for use in chemical reactions or extractions where maintaining the integrity of the compounds being worked with is important. However, it is important to note that hexane is highly flammable and poses health risks if inhaled or ingested in large quantities, so proper safety precautions should be taken when handling it.
4: Is hexane flammable?
Answer: Yes, hexane is highly flammable and should be handled with caution.
5: Is hexane toxic?
Answer: Prolonged exposure to hexane vapour or ingestion of large amounts can be harmful to human health. It may cause irritation, dizziness, and can affect the nervous system.
6: What is hexane used for?
Answer: Hexane (C6H14) is a widely used organic compound with various applications. It is primarily used as a solvent in laboratories, industrial processes, and in the production of consumer products. Hexane’s excellent solvent properties make it suitable for dissolving and extracting various substances, such as oils, fats, and waxes. It is commonly used in the extraction of vegetable oils, such as soybean oil and canola oil, as well as in the production of adhesives, paints, and
7: Is hexane a gas?
Answer: No, hexane is not a gas at room temperature. It is a volatile liquid with a low boiling point of around 69 degrees Celsius (156 degrees Fahrenheit). However, it can evaporate quickly and release vapors that are flammable. Therefore, it is important to handle hexane in well-ventilated areas and avoid ignition sources.
8: What is the cost of hexane?
Answer: The cost of hexane can vary depending on factors such as the supplier, location, quantity, and purity. As of my knowledge cutoff in September 2021, the price of hexane ranged from approximately $2 to $5 per liter. However, it’s important to note that prices may fluctuate over time, so it’s advisable to check with chemical suppliers or market sources for the most up-to-date pricing information.




