Table of Contents
In the previous segment, we learnt how to find the surface area of a playing top. In this segment, we will learn about the surface area of a rocket-like solid.
How to find the surface area of a rocket-like shape?
The rocket-like shape is obtained by combining a cone and a cylinder. The cone of the top has a slighter larger base than the cylinder.
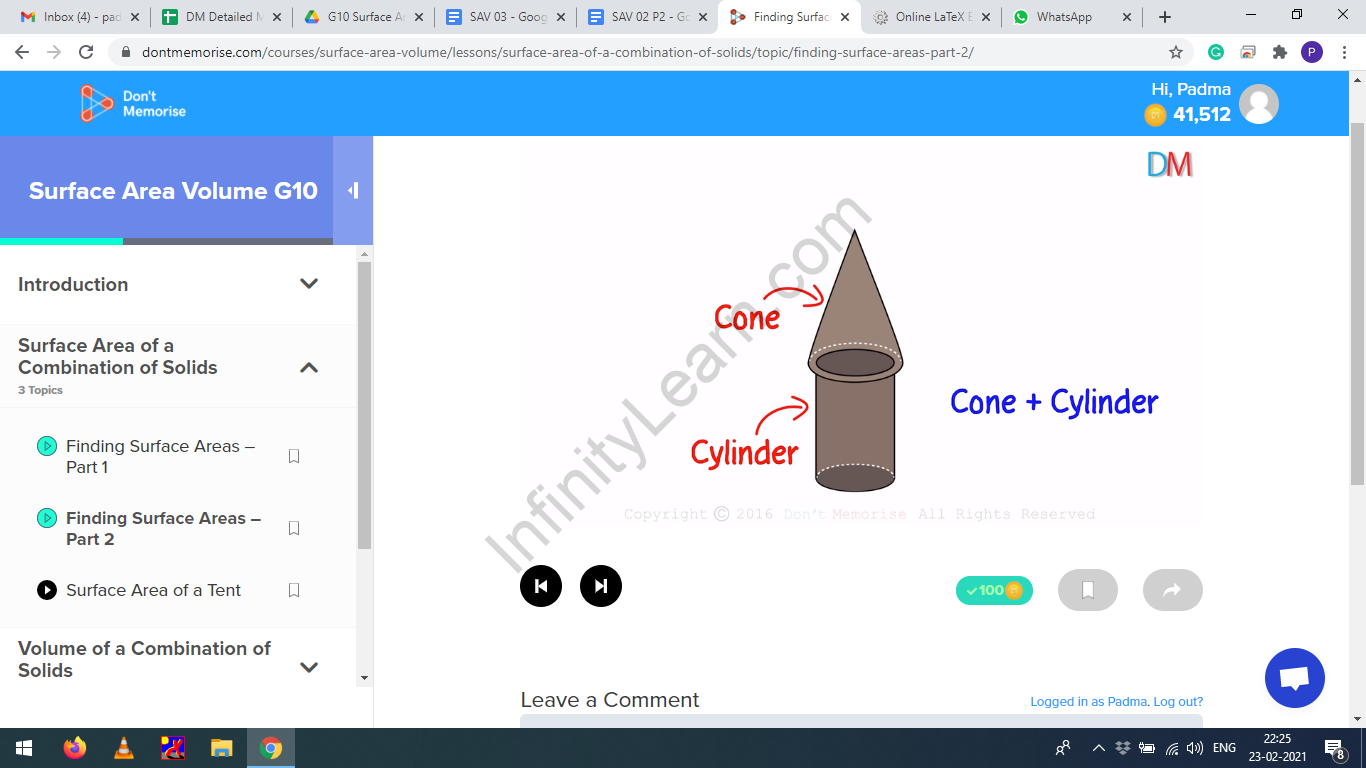
Figure 1
The surfaces that we can see in this solid shape are
- Curved surface of the cone
- Curved surface of the cylinder
- One of the bases of the cylinder
- Region formed in between the bases of the cone and cylinder
Let the parameters of the rocket-like shape be as follows:
- Radius of the cone =
- Slant height of the cone =
- Radius of the cylinder =
- Height of the cylinder =
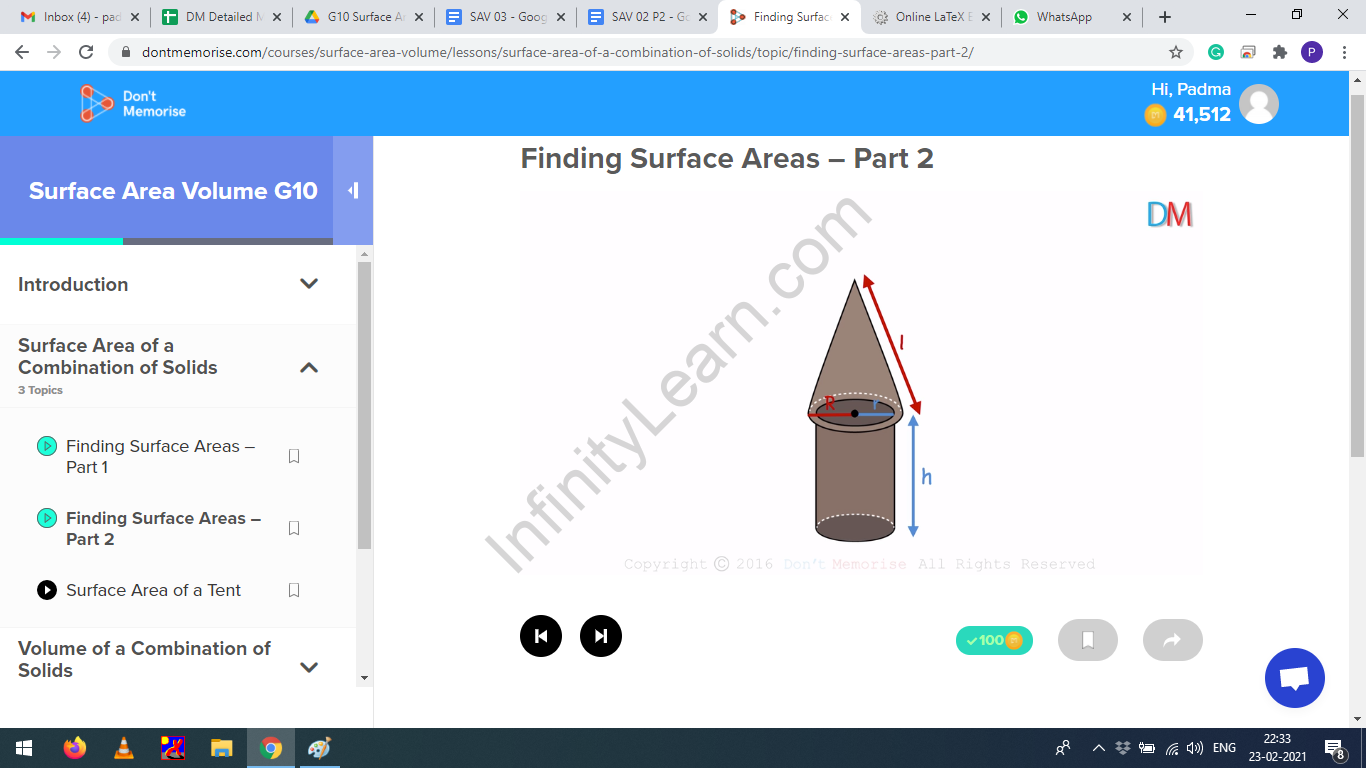
Figure 3
| Total surface area | = | CSA of cone | + | CSA of cylinder | + | Area of base of the cylinder | + | Shaded region between the cone and the cylinder |
| = | CSA of cone | + | CSA of cylinder | + | Area of base of the cylinder | + | (Area of base of the cone – Area of base of the cylinder) | |
| = | ||||||||
What’s next?
In the next segment of Class 10 Maths, we will solve an example of the surface area of combined shapes.



