Table of Contents
- Solid Shapes
- What’s Next?
In the first segment of the lesson Surface areas and Volumes, we will learn about solid shapes formed by combining two or more different 3-dimensional shapes.
What shapes can be formed by combining 2 or more 3-D objects?
We have studied how to find the surface areas and volumes of the three-dimensional shapes such as sphere, right circular cylinder, cuboid, cone, and hemisphere.
We will now look at some 3-D shapes that are formed by combining two or more of these objects and in the upcoming segments, we will understand how to find the surface area and volumes of these combined objects.
Let us look at some such shapes.
| Example 1
Two hemispheres attached to the plane surfaces of a right circular cylinder gives a container. hemisphere + cylinder + hemisphere |
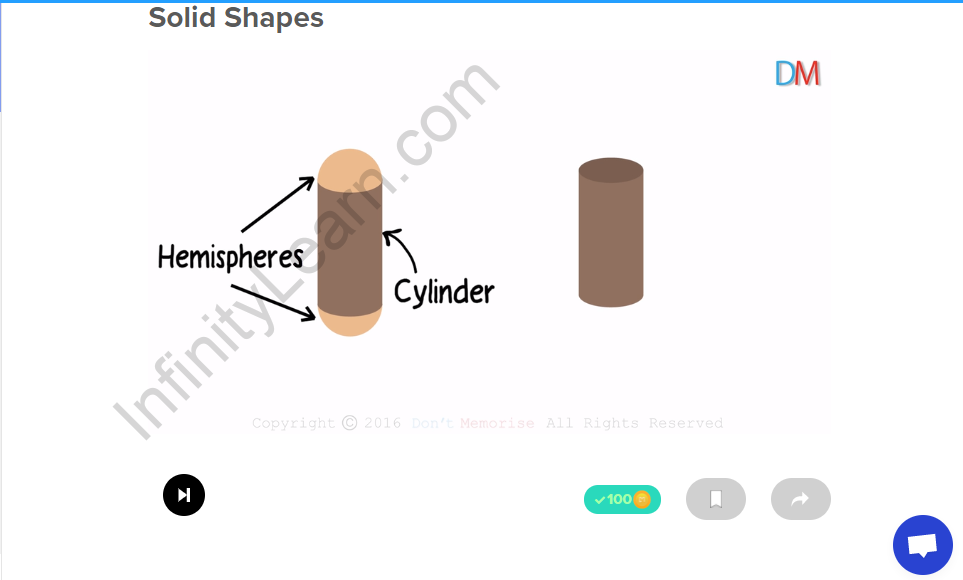 |
| Example 2
A hemisphere attached to the plane surface of the right circular cylinder gives us a test tube shape. cylinder + hemisphere |
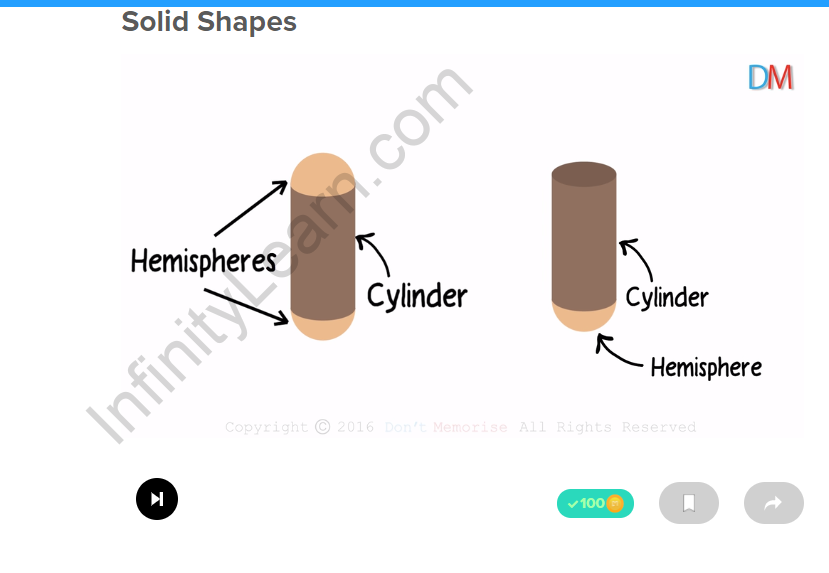 |
| Example 3
A cone with a hemisphere on its plane surface gives an ice-cream cone or a playing top type of shape hemisphere + cone |
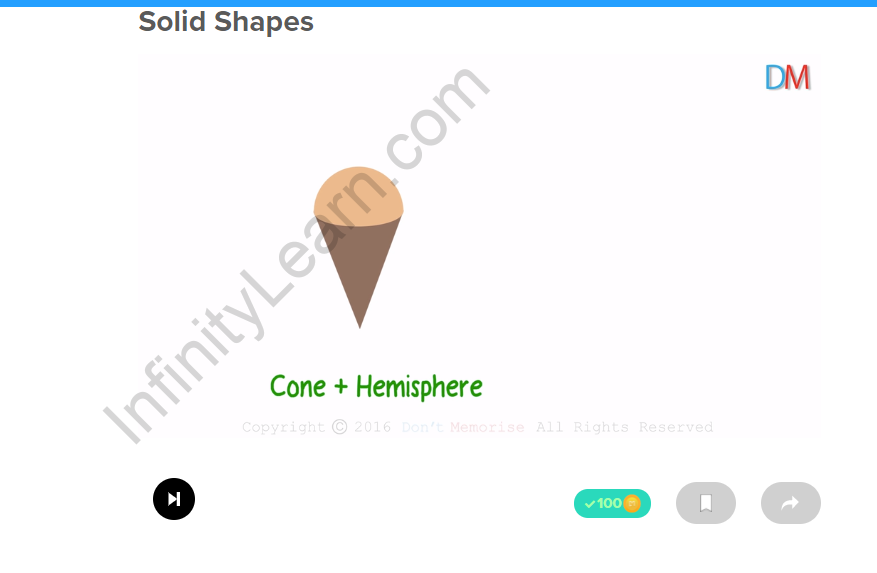
Hemisphere Cone |
| Example 4
A cylinder attached to a right circular cone gives this shape which resembles a rocket cone + cylinder |
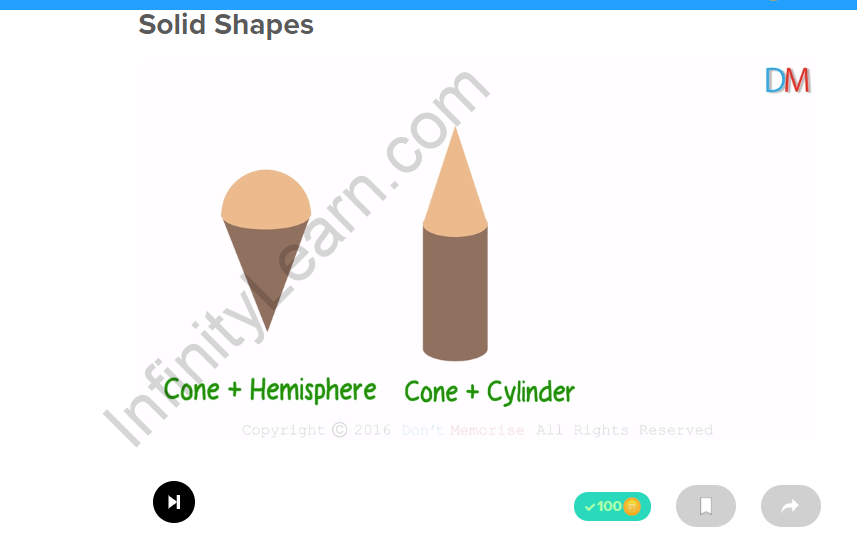 Cylinder Cone |
| Example 5
The combination of a cuboid and half a cylinder forms a shape like a safe. The half-cylinder is formed by cutting a right cylinder along its axis. half-cylinder + cuboid |
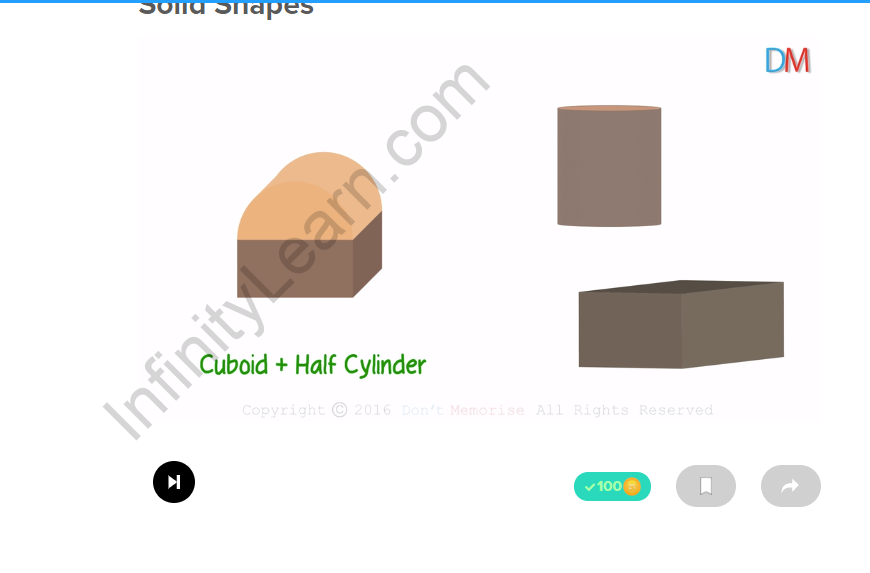
Half-cylinder Cuboid |
What’s next?
In the next segment of Class 10 Maths, we will learn about the surface area of a playing top.



