Nitride Formula
Introduction
The term “nitride” refers to a compound that contains nitrogen (N) and another element. Nitrides can have different formulas depending on the specific element they combine with. Here are a few examples of nitride formulas:
- Aluminum Nitride: AlN
- Silicon Nitride: Si3N4
- Boron Nitride: BN
- Gallium Nitride: GaN
- Titanium Nitride: TiN
These are just a few examples, and there are many more nitrides with different elements. Each nitride compound has its own unique properties and applications based on the combination of elements involved.
Chemical Formula of Nitride
The formula for nitride Ion is N-3. Nitride is an anion (negatively charged ion) consisting of nitrogen (N) with a charge of -3. When combined with different elements, it forms various nitride compounds.
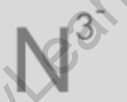
Uses of Nitride
- Ceramics and Refractory Materials: Nitrides such as silicon nitride (Si3N4) and aluminum nitride (AlN) are used in the production of advanced ceramics and refractory materials. These materials exhibit excellent thermal and mechanical properties, making them suitable for high-temperature applications, electrical insulators, cutting tools, and wear-resistant coatings.
- Semiconductor Industry: Gallium nitride (GaN) and silicon nitride (Si3N4) are widely used in the semiconductor industry. GaN is a crucial material for the production of light-emitting diodes (LEDs), laser diodes, and power electronic devices. Si3N4 is used as an insulating material and passivation layer in integrated circuits.
- Catalysts: Certain nitrides, such as titanium nitride (TiN) and vanadium nitride (VN), exhibit catalytic properties. They are used as catalysts in various chemical reactions, including ammonia synthesis, hydrogenation, and dehydrogenation processes.
- Coatings and Thin Films: Nitrides are used as protective coatings and thin films to enhance the properties of various materials. For example, titanium nitride (TiN) is commonly used as a hard coating for cutting tools, molds, and decorative purposes. Aluminum nitride (AlN) is used as a thermal interface material to improve heat dissipation in electronic devices.
- Fertilizers: Certain nitrides, such as calcium nitride (Ca3N2), are used as fertilizers in agriculture. They release nitrogen slowly into the soil, providing a long-term nutrient source for plants.
- Lubricants: Boron nitride (BN) is a lubricious material that exhibits low friction properties. It is used as a lubricant in high-temperature and high-vacuum applications where traditional oils and greases may not be suitable.
- Cutting and Grinding Tools: Cubic boron nitride (CBN) is a synthetic material that is second only to diamond in terms of hardness. It is used in the production of cutting tools, grinding wheels, and abrasive materials for precision machining applications.
Also Check: Zinc Nitrate Formula
Physical Properties of Nitride
- State: Nitrides can exist in various states, including solids, liquids, or gases, depending on the specific compound and conditions.
- Melting and Boiling Points: The melting and boiling points of nitrides vary widely depending on the elements involved. Some nitrides have high melting and boiling points, while others may be relatively low.
- Density: Nitrides generally have high densities, which means they are often heavy and compact substances.
- Hardness: Many nitrides are hard and have high hardness values. For example, cubic boron nitride (c-BN) is one of the hardest known materials.
- Electrical Conductivity: Nitrides can exhibit a range of electrical conductivity properties, from insulating to semiconducting to metallic, depending on the specific compound.
- Color: The color of nitrides can vary. For example, some nitrides may be black, gray, or even colorful, depending on their composition.
Chemical Properties of Nitride
- Reactivity with Oxygen: Nitrides generally have a strong affinity for oxygen and can readily react with it to form oxides. This reaction is often exothermic and can occur at high temperatures.
- Reactivity with Acids: Some nitrides can react with acids, such as hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid, to produce ammonia gas and corresponding salts.
- Stability: Nitrides can exhibit varying degrees of stability depending on their composition. Some nitrides, such as aluminum nitride (AlN) or silicon nitride (Si3N4), are highly stable and resistant to chemical reactions.
- Reactivity with Water: Some nitrides can react with water to produce ammonia gas and the corresponding metal hydroxide or metal oxide. This reaction is often highly exothermic and can release heat.
- Reducing Properties: Many nitrides are good reducing agents, meaning they can donate electrons in chemical reactions. They can react with oxidizing agents, such as halogens or metal oxides, to reduce them.
- Reactivity with Halogens: Some nitrides can react with halogens, such as chlorine or bromine, to form halides.
Conclusion
In conclusion, nitrides are compounds that contain nitrogen combined with other elements. They have a wide range of applications across various industries, including ceramics, semiconductors, catalysts, coatings, fertilizers, lubricants, and cutting tools. Nitrides exhibit desirable properties such as high hardness, thermal stability, electrical conductivity, and chemical reactivity, which make them valuable in different industrial processes. The specific use of a nitride compound depends on its chemical formula and the properties it possesses.
Solved Examples on Nitride Formula
Example 1: Reaction of Aluminum Nitride (AlN) with Water
Solution:
Aluminum nitride (AlN) reacts with water to produce ammonia gas (NH3) and aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH)3).
The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is:
2AlN + 6H2O -> 2NH3 + Al(OH)3
In this reaction, aluminum nitride reacts with water to form ammonia gas and aluminum hydroxide. This reaction is highly exothermic and releases heat.
Example 2: Reaction of Lithium Nitride (Li3N) with Water
Solution:
Lithium nitride (Li3N) reacts with water to produce ammonia gas (NH3) and lithium hydroxide (LiOH).
The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is: Li3N + 3H2O -> 3NH3 + LiOH
In this reaction, lithium nitride reacts with water to form ammonia gas and lithium hydroxide. The reaction takes place when lithium nitride comes into contact with water, releasing ammonia gas as a product.
To solve this example, you would calculate the number of moles of lithium nitride and water used, determine the stoichiometric ratio between the reactants and products, and calculate the resulting moles of ammonia gas and lithium hydroxide produced.
Frequently Asked Questions on Nitride Formula
1: What is the general formula for nitride?
Answer: The formula for nitride Ion is N3-. Some metal nitrates are very unstable.
2: What is the most common nitride?
Answer: Titanium nitride (TiN) film was the earliest studied film material and is the most widely used. Ti and N can form interstitial solid solutions or interstitial phases. The two common Ti-N interstitial phases are Ti2N and TiN.
3: What are the different types of nitrides?
Answer: There are several different types of nitrides, categorized based on their composition and structure. Here are some common types of nitrides:
- Metal Nitrides: These are nitrides formed by metals bonding with nitrogen. Examples include aluminum nitride (AlN), titanium nitride (TiN), and silicon nitride (Si3N4). Metal nitrides are often used in applications such as electronics, ceramics, and coatings.
- Interstitial Nitrides: These nitrides are formed when nitrogen atoms occupy interstitial positions within a crystal lattice of a host material. Examples include iron nitride (Fe3N) and tungsten nitride (WN). Interstitial nitrides often exhibit high hardness and are used in cutting tools and wear-resistant coatings.
- Covalent Nitrides: These nitrides are formed by the bonding of nitrogen with other non-metallic elements, typically through covalent bonds. Examples include boron nitride (BN) and carbon nitride (CNx). Covalent nitrides can have properties similar to those of ceramics and are used in high-temperature applications and as lubricants.
4: Is nitride a base or acid?
Answer: The nitride ion (N3-) can exhibit basic properties in certain reactions. While nitrides are not commonly used in protic solutions due to their reactivity, they can react with protic acids to form ammonia gas (NH3) or ammonium salts. In these reactions, the nitride ion acts as a base by accepting a proton (H+) from the acid. Therefore, in the context of these reactions, the nitride ion can be considered basic.
5: Why does nitride have 3?
Answer: The number 3 in “nitride” refers to the charge of the nitride ion (N3-). The nitride ion is formed when nitrogen (N) gains three electrons to achieve a full outer electron shell. This results in a net charge of -3 for the nitride ion, indicating its three-unit negative charge.
6: What is an example of a nitride?
Answer: One example of a nitride is silicon nitride (Si3N4). Silicon nitride is a ceramic material that is known for its excellent mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties. It is used in various applications such as cutting tools, bearings, turbine blades, and high-temperature components. Silicon nitride’s combination of high strength, hardness, and resistance to wear and thermal shock makes it a valuable material in demanding industrial environments.
7: What is the use of nitride?
Answer: Nitrides have various uses across different industries. One of the primary applications of nitrides is in the field of semiconductors. For instance, gallium nitride (GaN) is used in the production of high-performance electronic devices, including light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and power electronics. Nitrides also find application in ceramics, where materials like silicon nitride (Si3N4) are used for their excellent mechanical properties, such as high strength and resistance to wear. Additionally, nitrides are employed as coatings for cutting tools and other high-wear applications to enhance their hardness and durability. Nitrides are also used in the manufacturing of refractory materials, specialty glasses, and as catalysts in chemical reactions. Their unique properties make them valuable in a range of industries, contributing to advancements in electronics, engineering, and materials science.
8: Is nitrogen a nitride?
Answer: No, nitrogen itself is not a nitride. Nitrogen is an element, represented by the symbol N on the periodic table. Nitrides, on the other hand, are compounds that contain nitrogen chemically combined with other elements. Nitrogen can form nitrides with various elements, such as silicon nitride (Si3N4) or aluminum nitride (AlN), but nitrogen alone is not considered a nitride.




