Table of Contents
Phosphate Formula
Introduction
Phosphates are chemical compounds that contain the phosphate ion (PO43-). They are widely used in various industrial, agricultural, and biological applications. The phosphate ion consists of one phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms.
Uses of Phosphate
- Fertilizers: Phosphates, such as ammonium phosphate and triple superphosphate, are widely used in agriculture as fertilizers. They provide essential phosphorus to plants, promoting healthy root development and overall growth.
- Food and Beverage Industry: Phosphates are used as food additives in the food and beverage industry. They serve various functions, such as pH regulation, emulsification, and moisture retention. Phosphates can be found in processed meats, cheeses, baked goods, and soft drinks.
- Water Treatment: Phosphates are used in water treatment processes to prevent the formation of scale and corrosion in pipes and equipment. They help in controlling the levels of calcium, magnesium, and other minerals that can cause scaling and reduce the efficiency of water systems.
- Detergents and Cleaning Products: Phosphates are commonly found in laundry detergents and cleaning products. They enhance the cleaning power by softening water, preventing the redeposition of dirt, and improving stain removal.
- Industrial Applications: Phosphates are used in various industrial processes, including metal treatment, flame retardants, ceramics production, and as catalysts in chemical reactions.
- Pharmaceuticals: Phosphates are used in the pharmaceutical industry for various purposes, such as the formulation of medicines, buffering agents, and as excipients in drug formulations.
- Personal Care Products: Phosphates can be found in personal care products, including toothpaste, mouthwash, and cosmetics. They help in stabilizing formulations, adjusting pH levels, and enhancing product performance.
Structural Formula of Phosphate
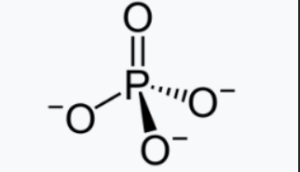
Phosphate is an inorganic chemical compound that consists of a central phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms.
The structure of phosphate can be represented using different models depending on the specific compound. However, in general, phosphate compounds contain a central phosphorus atom (P) surrounded by four oxygen atoms (O). The oxygen atoms are typically arranged in a tetrahedral shape around the phosphorus atom.
Phosphates can form different types of compounds, such as mono-, di-, and triphosphates, depending on the number of phosphate groups present. These compounds can further combine with other elements or functional groups to form various phosphates with different properties and functions.
Physical Properties of Phosphate Formula
- Solid State: Phosphate compounds can exist as solids with varying colors and crystal structures. For example, calcium phosphate is commonly found in the form of white crystalline solids.
- Solubility: The solubility of phosphate compounds in water can vary depending on the specific compound. Some phosphates, such as sodium phosphate, are highly soluble in water, while others, like calcium phosphate, have lower solubility.
- Melting and Boiling Points: The melting and boiling points of phosphate compounds can vary depending on the specific compound and its structure. Generally, phosphate compounds have relatively high melting and boiling points compared to many organic compounds.
- pH: Phosphate compounds can exhibit different pH values depending on their chemical nature. For example, sodium phosphate is alkaline and can increase the pH of a solution when dissolved in water.
- Density: The density of phosphate compounds can vary depending on their chemical composition. Generally, phosphate compounds have densities ranging from low to moderate values
Chemical Properties of Phosphate Formula
- Acid-Base Reactions: Phosphate compounds can act as both acids and bases. In acidic conditions, phosphate compounds can donate protons (H+) to react with bases. In basic conditions, phosphate compounds can accept protons to form acidic species.
- Buffering Capacity: Phosphate compounds, particularly those containing the dihydrogen phosphate (H2PO4-) or hydrogen phosphate (HPO42-) ions, have excellent buffering capacity. They can resist changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added to a solution.
- Precipitation Reactions: Phosphate compounds can participate in precipitation reactions with metal cations, forming insoluble phosphate salts. For example, when phosphate ions react with calcium ions, insoluble calcium phosphate precipitates out of the solution.
- Complex Formation: Phosphate compounds can form complexes with metal ions, particularly transition metals. These complexes exhibit unique chemical and physical properties and find applications in various fields, including catalysis and coordination chemistry.
- Hydrolysis Reactions: Phosphate compounds can undergo hydrolysis reactions, especially in the presence of water or under alkaline conditions. This can result in the release of hydroxide ions (OH–) or the formation of phosphate anions with different degrees of protonation.
- Redox Reactions: Phosphate compounds can participate in redox reactions, either as oxidizing agents or reducing agents. For example, some phosphate compounds can be oxidized to form phosphoric acid, while others can be reduced to produce phosphine gas.
Solved Examples on Phosphate Formula
Example 1: Calculating Molar Mass of Disodium Phosphate (Na2HPO4).
To calculate the molar mass of disodium phosphate, we sum up the atomic masses of all the atoms in the compound.
Disodium phosphate (Na2HPO4) consists of 2 sodium atoms (Na), 1 hydrogen atom(H), 1 phosphorus atom (P), and 4 oxygen atoms (O).
Atomic masses:
Na = 22.99 g/mol
H = 1.01 g/mol
P = 30.97 g/mol
O = 16.00 g/mol
Molar mass of disodium phosphate (Na2HPO4):
(2 x Na) + H + P + (4 x O)
= (2 x 22.99) + 1.01 + 30.97 + (4 x 16.00)
= 45.98 + 1.01 + 30.97 + 64.00
= 141.96 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of disodium phosphate (Na2HPO4) is 141.96 g/mol.
Example 2: Precipitation Reaction of Calcium Phosphate (Ca3(PO4)2).
When calcium chloride (CaCl2) reacts with sodium phosphate (Na3PO4), a precipitation reaction occurs, resulting in the formation of calcium phosphate (Ca3(PO4)2) and sodium chloride (NaCl).
The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is:
3CaCl2 + 2Na3PO4 → Ca3(PO4)2 + 6NaCl
In this reaction, calcium phosphate is the precipitate, which means it forms a solid that settles out of the solution.
Frequently Asked Questions on Phosphate Formula
1: How is phosphate formula formed?
Answer: A phosphate salt is obtained when a positively charged ion gets attached to the oxygen atoms that are negatively charged and forms an ionic compound.
2: Is phosphate polar or nonpolar?
Answer: Phosphate (PO4) is a polyatomic ion and does not have a specific polarity. However, the individual bonds within the phosphate ion can be polar. The oxygen atoms in the phosphate ion are more electronegative than the phosphorus atom, resulting in partial negative charges on the oxygen atoms and a partial positive charge on the phosphorus atom. Overall, the phosphate ion can be considered polar due to the presence of polar bonds.
3: What is the main purpose of phosphate?
Answer: Phosphate is essential for the development and maintenance of strong bones and teeth. It serves as a building block for various vital substances within the body. These include molecules involved in energy production, the composition of cell membranes, and the synthesis of DNA.
4: How many types of phosphate are there?
Answer: Phosphate refers to a group of compounds containing the phosphate ion (PO43-). There are several different types of phosphate compounds based on their chemical composition and structure. Here are some common types of phosphates:
- Orthophosphates: These are the simplest form of phosphates and consist of a single phosphate ion. Examples include monopotassium phosphate (KH2PO4) and monosodium phosphate (NaH2PO4).
- Pyrophosphates: These compounds contain two phosphate ions linked together. An example is tetrasodium pyrophosphate (Na4P2O7), commonly used as a food additive.
- Tripolyphosphates: These phosphates contain three phosphate ions joined in a linear chain. Sodium tripolyphosphate (Na5P3O10) is a well-known example and is used in various applications, including as a cleaning agent and water treatment chemical.
- Organic phosphates: These are phosphates that are part of organic compounds. They can be found in biological molecules such as nucleic acids (DNA, RNA) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy currency of cells.
5: Is phosphate acidic or basic?
Answer: The acidity or basicity of phosphate depends on its environment and the specific phosphate compound.
In general, phosphates can act as either acids or bases, depending on the conditions. Phosphates can donate or accept protons (H+) due to the presence of multiple oxygen atoms in the phosphate ion (PO43-).
6: What phosphate is used for?
Answer: Phosphates play a crucial role in many biological processes, such as energy production, DNA and RNA synthesis, and bone mineralization. They are also commonly used as fertilizers, food additives, and water treatment agents. Phosphate compounds can exist in various forms, including sodium phosphate, calcium phosphate, and ammonium phosphate, among others.
7: What is the full name of phosphate?
Answer: The full name of phosphate can vary depending on the specific compound or context. However, in the case of phosphoric acid and orthophosphate, the full names are as follows:
- Phosphoric acid: The chemical formula for phosphoric acid is H3PO4. It is an inorganic acid that consists of three hydrogen atoms (H) bonded to a central phosphorus atom (P) and four oxygen atoms (O). The full name for phosphoric acid is “orthophosphoric acid.”
- Orthophosphate: Orthophosphate refers to the anion derived from phosphoric acid (H3PO4) when it loses one or more hydrogen ions. It is also known as the “phosphate ion” (PO43-). Orthophosphate is an important component of various biological and environmental systems. It is commonly found in minerals, soils, and natural water sources.
Therefore, the full name of phosphate can be specified as “orthophosphate” when referring to the anion or “orthophosphoric acid” when referring to phosphoric acid.
8: Which food has phosphate?
Answer: Phosphate is a naturally occurring mineral that can be found in various foods. It is particularly abundant in protein-rich foods, such as meat, poultry, fish, and dairy products. Additionally, phosphate can be present in smaller amounts in plant-based foods, including legumes, nuts, whole grains, and certain vegetables.
Processed foods and beverages, such as carbonated drinks, processed meats, and packaged snacks, may also contain phosphate additives. These additives, such as sodium phosphate or calcium phosphate, are used for various purposes, including as preservatives, pH adjusters, or leavening agents.
It’s important to note that while phosphate is an essential nutrient for the body, excessive intake of phosphate, especially from processed foods and drinks, may have potential health implications. It is always advisable to maintain a balanced and varied diet to ensure adequate intake of essential nutrients, including phosphate. If you have specific dietary concerns or conditions, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian.








