Table of Contents
In Class 8 Mathematics, Chapter 3 focuses on Understanding Quadrilaterals, which are shapes with four sides. To help students practice and understand this chapter better, extra questions have been created. These extra questions are like bonus exercises that give students more practice and help them explore quadrilaterals in more detail.
The Class 8 Maths Chapter 3 Extra Questions cover various aspects of quadrilaterals, such as their properties, types, and how they are used. By solving these extra questions, students can improve their knowledge and skills in working with quadrilaterals. The questions also come with solutions, making it easier for students to check their answers and learn from their mistakes.
These extra questions provide a fun and engaging way for students to learn more about quadrilaterals. They can practice identifying different types of quadrilaterals, understanding their features, and solving problems related to them. By working through these extra questions, students can boost their confidence in math and be better prepared for tests and exams.
Class 8 Maths Chapter 3 Extra Questions with Solutions – Understanding Quadrilaterals
For Class 8 students learning about quadrilaterals, extra questions with solutions are a helpful tool. These extra questions from chapter 3 class 8 maths cover different aspects of quadrilaterals and come with answers to check your work. By practicing with these questions, students can improve their understanding of quadrilaterals and how to solve related problems.
The solutions provided not only give the correct answers but also explain how to solve each question step by step. This resource helps students identify areas where they need more practice and enhances their overall grasp of quadrilaterals in a clear and straightforward manner.
Get Extra Questions for Class 8 Maths on Infinity Learn for free.
Very Short Answer Type
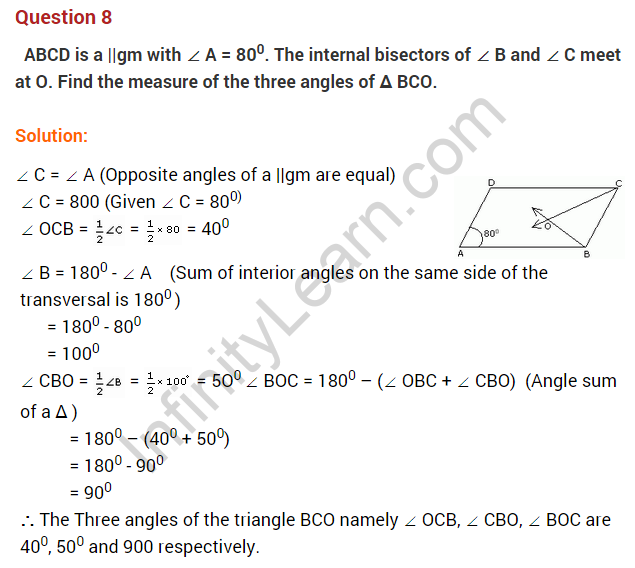
Question 1. In the given figure, ABCD is a parallelogram. Find x.
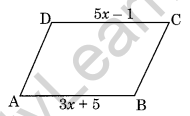
Solution: AB = DC [Opposite sides of a parallelogram]
3x + 5 = 5x – 1
⇒ 3x – 5x = -1 – 5
⇒ -2x = -6
⇒ x = 3
Question 2. In the given figure find x + y + z.
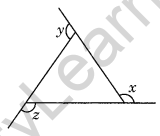 Solution: We know that the sum of all a polygon’s outside angles equals 360°.
Solution: We know that the sum of all a polygon’s outside angles equals 360°.
x + y + z = 360°
Question 3. In the given figure, find x.
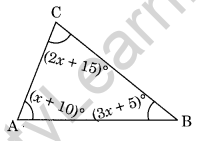 Solution: ∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180° [Angle sum property]
Solution: ∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180° [Angle sum property]
(x + 10)° + (3x + 5)° + (2x + 15)° = 180°
⇒ x + 10 + 3x + 5 + 2x + 15 = 180
⇒ 6x + 30 = 180
⇒ 6x = 180 – 30
⇒ 6x = 150
⇒ x = 25
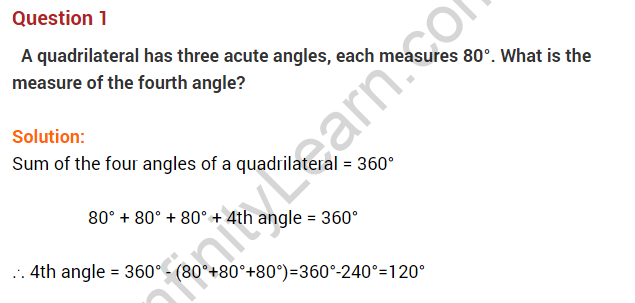
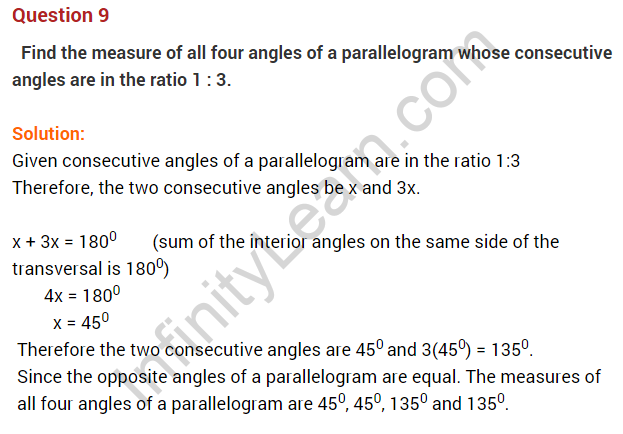
Question 4. The angles of a quadrilateral are in the ratio of 2 : 3 : 5 : 8. Find the measure of each angle.
Solution: The sum of a quadrilateral’s internal angles equals 360°.
Let the quadrilateral’s angles be 2x°, 3x°, 5x°, and 8x°.
2x + 3x + 5x + 8x = 360°
⇒ 18x = 360°
⇒ x = 20°
Hence the angles are
2 × 20 = 40°,
3 × 20 = 60°,
5 × 20 = 100°
and 8 × 20 = 160°.
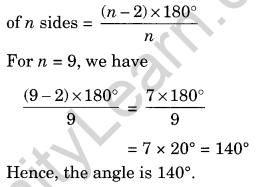
Question 5. Find the measure of an interior angle of a regular polygon of 9 sides.
Solution: Measure of an interior angle of a regular polygon

Question 6. Length and breadth of a rectangular wire are 9 cm and 7 cm respectively. If the wire is bent into a square, find the length of its side.
Solution: Perimeter of the rectangle = 2 [length + breadth]
= 2[9 + 7] = 2 × 16 = 32 cm.
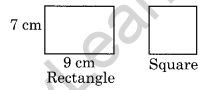
Now perimeter of the square = Perimeter of rectangle = 32 cm.
Side of the square = \(\frac { 32 }{ 4 }\) = 8 cm.
Hence, the length of the side of square = 8 cm.
Question 7. In the given figure ABCD, find the value of x.
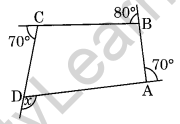
Solution: 360° is the sum of all a polygon’s outside angles.
x + 70° + 80° + 70° = 360°
⇒ x + 220° = 360°
⇒ x = 360° – 220° = 140°
Question 8. In the parallelogram given alongside if m∠Q = 110°, find all the other angles.
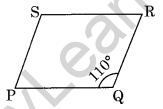
Solution: Given m∠Q = 110°
Then m∠S = 110° (Opposite angles are equal)
Since ∠P and ∠Q are supplementary.
Then m∠P + m∠Q = 180°
⇒ m∠P + 110° = 180°
⇒ m∠P = 180° – 110° = 70°
⇒ m∠P = m∠R = 70° (Opposite angles)
Hence m∠P = 70, m∠R = 70°
and m∠S = 110°
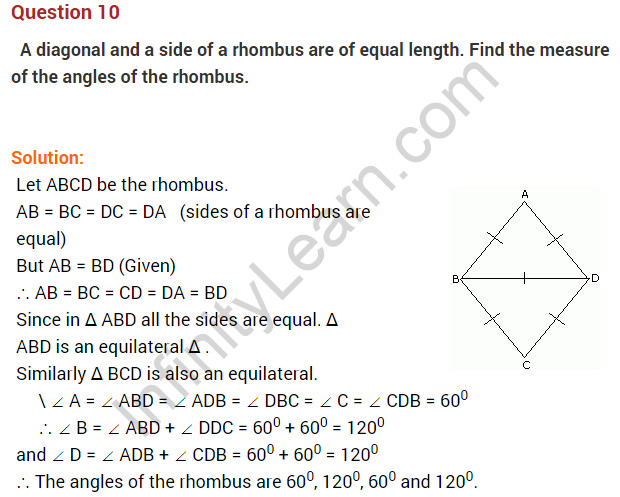
Question 9. In the given figure, ABCD is a rhombus. Find the values of x, y and z.
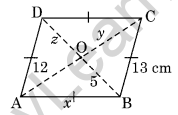
Solution: AB = BC (Sides of a rhombus)
x = 13 cm.
Since the diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other
z = 5 and y = 12
Hence, x = 13 cm, y = 12 cm and z = 5 cm.
Question 10. In the given figure, ABCD is a parallelogram. Find x, y and z.
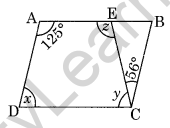 Solution: ∠A + ∠D = 180° (Adjacent angles)
Solution: ∠A + ∠D = 180° (Adjacent angles)
⇒ 125° + ∠D = 180°
⇒ ∠D = 180° – 125°
x = 55°
∠A = ∠C [Opposite angles of a parallelogram]
⇒ 125° = y + 56°
⇒ y = 125° – 56°
⇒ y = 69°
∠z + ∠y = 180° (Adjacent angles)
⇒ ∠z + 69° = 180°
⇒ ∠z = 180° – 69° = 111°
Hence the angles x = 55°, y = 69° and z = 111°
Question 11. Find x in the following figure. (NCERT Exemplar)
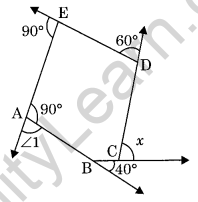 Solution: In the given figure ∠1 + 90° = 180° (linear pair)
Solution: In the given figure ∠1 + 90° = 180° (linear pair)
∠1 = 90°
Now, sum of exterior angles of a polygon is 360°, therefore,
x + 60° + 90° + 90° + 40° = 360°
⇒ x + 280° = 360°
⇒ x = 80°
Short Answer Type
Question 12. In the given parallelogram ABCD, find the value of x andy.
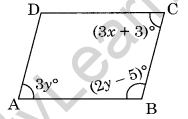
Solution: ∠A + ∠B = 180°
3y + 2y – 5 = 180°
⇒ 5y – 5 = 180°
⇒ 5y = 180 + 5°
⇒ 5y = 185°
⇒ y = 37°
Now ∠A = ∠C [Opposite angles of a parallelogram]
3y = 3x + 3
⇒ 3 × 37 = 3x + 3
⇒ 111 = 3x + 3
⇒ 111 – 3 = 3x
⇒ 108 = 3x
⇒ x = 36°
Hence, x = 36° and y – 37°.
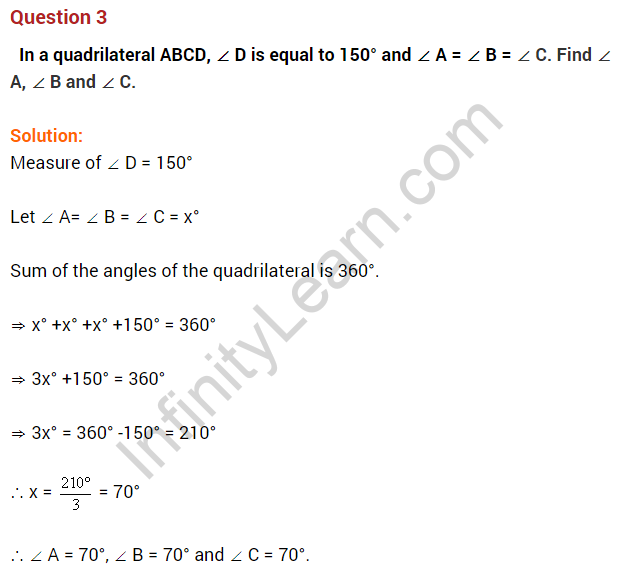
Question 13. ABCD is a rhombus with ∠ABC = 126°, find the measure of ∠ACD.
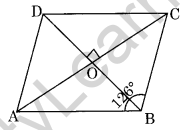
Solution:
∠ABC = ∠ADC (Opposite angles of a rhombus)
∠ADC = 126°
∠ODC = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × ∠ADC (Diagonal of rhombus bisects the respective angles)
⇒ ∠ODC = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × 126° = 63°
⇒ ∠DOC = 90° (Diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other at 90°)
In ΔOCD,
∠OCD + ∠ODC + ∠DOC = 180° (Angle sum property)
⇒ ∠OCD + 63° + 90° = 180°
⇒ ∠OCD + 153° = 180°
⇒ ∠OCD = 180° – 153° = 27°
Hence ∠OCD or ∠ACD = 27°
Question 14. Find the values of x and y in the following parallelogram.
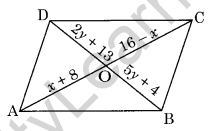
Solution: Since, the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other.
OA = OC
x + 8 = 16 – x
⇒ x + x = 16 – 8
⇒ 2x = 8
x = 4
Similarly, OB = OD
5y + 4 = 2y + 13
⇒ 3y = 9
⇒ y = 3
Hence, x = 4 and y = 3

The Class 8 HOTS Course enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills through engaging activities and advanced learning techniques, ensuring academic excellence.
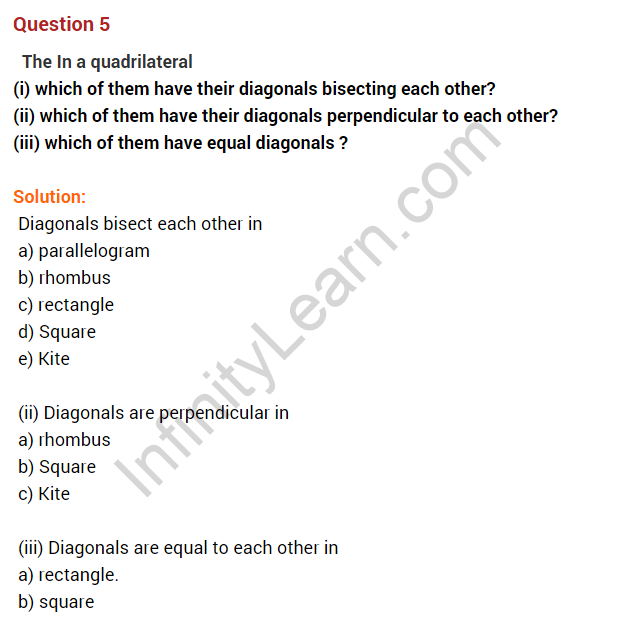
Question 15. Write true and false against each of the given statements.
(a) Diagonals of a rhombus are equal.
(b) Diagonals of rectangles are equal.
(c) Kite is a parallelogram.
(d) Sum of the interior angles of a triangle is 180°.
(e) A trapezium is a parallelogram.
(f) Sum of all the exterior angles of a polygon is 360°.
(g) Diagonals of a rectangle are perpendicular to each other.
(h) Triangle is possible with angles 60°, 80° and 100°.
(i) In a parallelogram, the opposite sides are equal.
Solution:
(a) False
(b) True
(c) False
(d) True
(e) False
(f) True
(g) False
(h) False
(i) True
Question 16. The sides AB and CD of a quadrilateral ABCD are extended to points P and Q respectively. Is ∠ADQ + ∠CBP = ∠A + ∠C? Give reason.
Solution:
Join AC, then
∠CBP = ∠BCA + ∠BAC and ∠ADQ = ∠ACD + ∠DAC (Exterior angles of triangles)
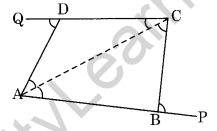
Therefore,
∠CBP + ∠ADQ = ∠BCA + ∠BAC + ∠ACD + ∠DAC
= (∠BCA + ∠ACD) + (∠BAC + ∠DAC)
= ∠C + ∠A
Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS)
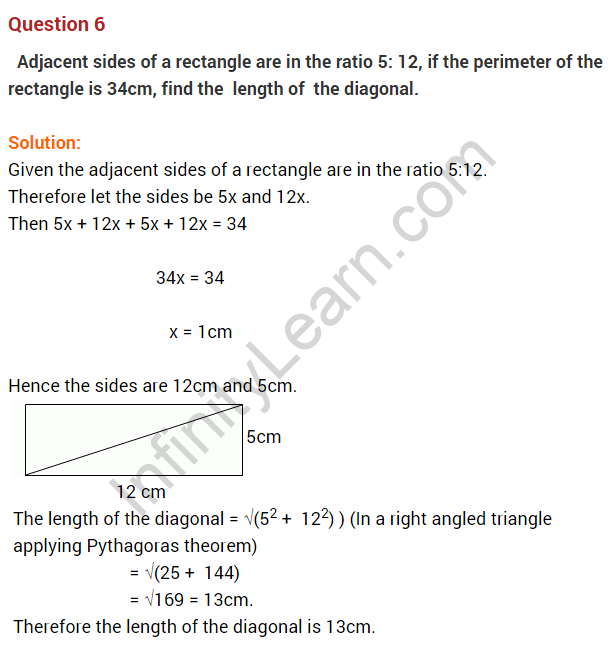
Question 17. The diagonal of a rectangle is thrice its smaller side. Find the ratio of its sides.
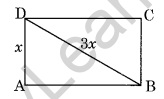
Solution:
Let AD = x cm
diagonal BD = 3x cm
In right-angled triangle DAB,
AD2 + AB2 = BD2 (Using Pythagoras Theorem)
x2 + AB2 = (3x)2
⇒ x2 + AB2 = 9x2
⇒ AB2 = 9x2 – x2
⇒ AB2 = 8x2
⇒ AB = √8x = 2√2x
Required ratio of AB : AD = 2√2x : x = 2√2 : 1
Question 18. If AM and CN are perpendiculars on the diagonal BD of a parallelogram ABCD, Is ∆AMD = ∆CNB? Give reason. (NCERT Exemplar)
Solution:
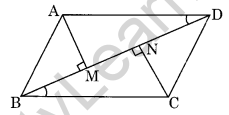 In triangles AMD and CNB,
In triangles AMD and CNB,
AD = BC (opposite sides of parallelogram)
∠AMB = ∠CNB = 90°
∠ADM = ∠NBC (AD || BC and BD is transversal.)
So, ∆AMD = ∆CNB (AAS)