Table of Contents
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) is a colorless gas with a pungent odor. It is highly reactive and has various industrial and environmental applications. It is used as a preservative in the food and beverage industry to prevent spoilage. Sulfur dioxide is also used in the production of sulfuric acid, a widely used industrial chemical. It is an acidic gas that can react with water to form sulfurous acid. Sulfur dioxide is emitted as a byproduct of industrial processes, contributing to air pollution and environmental concerns.
Formula of Sulfur dioxide
The chemical formula for sulfur dioxide is SO2. Sulfur dioxide is a gaseous compound composed of one sulfur atom (S) and two oxygen atoms (O).
Sulfur dioxide is produced through the burning of sulfur-containing materials, such as fossil fuels and certain industrial processes. It is also released during volcanic eruptions and some biological processes.
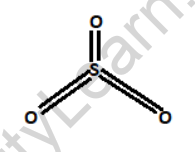
In terms of its chemical structure, sulfur dioxide consists of a sulfur atom bonded to two oxygen atoms through double bonds. The molecule has a bent shape due to the repulsion between the lone pairs of electrons on the sulfur atom. This bent structure gives sulfur dioxide its unique properties and reactivity.
Sulfur dioxide is known for its pungent odor and suffocating smell. It is a toxic gas and can be harmful to human health and the environment. It is also a major contributor to air pollution, particularly in areas with high industrial activity.
Sulfur dioxide is highly soluble in water, and when dissolved, it forms sulfurous acid (H2SO3). Sulfurous acid is a weak acid and can undergo various reactions, including oxidation to form sulfuric acid (H2SO4) in the presence of oxidizing agents.
In conclusion, sulfur dioxide, with the chemical formula SO2, is a toxic and pungent gas that is formed through the burning of sulfur-containing materials and volcanic activity. It has a bent molecular structure and is highly soluble in water, forming sulfurous acid. Sulfur dioxide is a major contributor to air pollution and can have adverse effects on human health and the environment.
Structure of Sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide consists of one sulfur atom bonded to two oxygen atoms.
Physical properties of Sulfur dioxide
– Sulfur dioxide is a colorless gas with a pungent odor.
– It has a molecular weight of 64.06 g/mol.
– Its boiling point is -10°C (-50°F), and its melting point is -75°C (-103°F).
– Sulfur dioxide is soluble in water and forms sulfurous acid.
– It is denser than air and can accumulate in low-lying areas.
Chemical properties of Sulfur dioxide
– Sulfur dioxide is a highly reactive gas and is considered a strong reducing agent.
– It readily reacts with various substances, such as metals, to form sulfites or sulfates.
– It can undergo oxidation reactions to form sulfur trioxide (SO3) and other sulfur compounds.
– Sulfur dioxide is acidic in nature and can react with water to form sulfurous acid (H2SO3), which can further dissociate to release hydrogen ions.
Uses of Sulfur dioxide
– Sulfur dioxide is commonly used as a preservative in the food and beverage industry to inhibit microbial growth and prevent spoilage.
– It is used in the production of sulfuric acid, a widely used industrial chemical.
– Sulfur dioxide is used in the bleaching and disinfection of various materials, including textiles, paper, and water.
– It finds applications in the production of chemicals, such as sulfites, sulfuric acid, and sodium bisulfite.
– Sulfur dioxide is also emitted as a by product of various industrial processes, such as the combustion of fossil fuels and the smelting of metal ores, contributing to air pollution and environmental concerns.
Solved examples on sulfur dioxide (SO2):
Example 1: What happens when sulfur dioxide reacts with water?
Solution: When sulfur dioxide reacts with water, it forms sulfurous acid (H2SO3). The reaction can be represented as follows:
SO2 + H2O -> H2SO3
Example 2: How is sulfur dioxide commonly produced?
Solution: Sulfur dioxide is commonly produced by the burning of sulfur-containing fuels, such as coal and oil, in industrial processes. It is also produced during volcanic eruptions and as a byproduct of certain chemical reactions.
Frequently asked questions about Sulfur dioxide (SO2):
1: Is sulfur dioxide harmful to human health?
Answer: Yes, high concentrations of sulfur dioxide can be harmful to human health. Inhalation of sulfur dioxide can irritate the respiratory system, leading to breathing difficulties, coughing, and throat irritation. It can also exacerbate respiratory conditions such as asthma.
2: What are the main sources of sulfur dioxide emissions?
Answer: The main sources of sulfur dioxide emissions are industrial processes, particularly the burning of fossil fuels containing sulfur compounds. Power plants, industrial boilers, and vehicles are significant contributors to sulfur dioxide emissions.
3: How does sulfur dioxide contribute to air pollution?
Answer: Sulfur dioxide is a major contributor to air pollution. It reacts with other compounds and sunlight to form fine particulate matter known as PM2.5, which can have adverse effects on air quality and human health. Sulfur dioxide also contributes to the formation of acid rain.
4: What are the environmental effects of sulfur dioxide?
Answer: Sulfur dioxide can have detrimental effects on the environment. It can damage plants and crops, leading to reduced agricultural productivity. When sulfur dioxide combines with moisture in the atmosphere, it forms sulfuric acid, which contributes to the acidification of soil and water bodies, harming aquatic life.
5: How is sulfur dioxide regulated?
Answer: Sulfur dioxide emissions are regulated in many countries to mitigate their environmental and health impacts. Regulations often include emission limits for industrial sources, the use of cleaner fuels, and the implementation of emission control technologies such as scrubbers in power plants.
6: What is Valency of SO2?
Answer: The valency of SO2, which stands for sulfur dioxide, is 4. This means that sulfur dioxide has the ability to form four bonds or combine with four other atoms or groups of atoms.
7: Is SO2 acidic or basic gas?
Answer: SO2 is an acidic gas. When sulfur dioxide dissolves in water, it forms sulfurous acid (H2SO3), which is a weak acid. Sulfurous acid can release hydrogen ions (H+) in solution, leading to an acidic pH.
8: Does SO2 cause acid rain?
Answer:
Yes, SO2 is one of the main contributors to acid rain. When sulfur dioxide is released into the atmosphere through industrial processes or burning of fossil fuels, it can react with oxygen, moisture, and other atmospheric components to form sulfuric acid (H2SO4). Sulfuric acid is a strong acid that can contribute to the acidity of rainwater, resulting in acid rain. Acid rain can have detrimental effects on ecosystems, forests, bodies of water, and human-made structures.








