Table of Contents
Introduction to Zinc Chloride Formula
Zinc chloride (ZnCl2) is an inorganic compound composed of zinc and chlorine. It is a white crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water. Zinc chloride is widely used in various industrial applications and chemical processes due to its unique properties.
The formula of Zinc Chloride
The chemical formula of Zinc Chloride is ZnCl2.
Structure of Zinc Chloride
Zinc Chloride consists of one zinc cation (Zn2+) and two chloride anions (Cl-). The zinc cation is positively charged and the chloride anions are negatively charged. The zinc cation is surrounded by two chloride ions, forming an ionic compound.
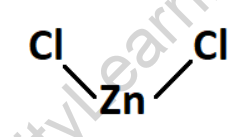
Physical properties of Zinc Chloride
- Appearance: Zinc Chloride is a white crystalline solid.
- Odor: It has a mild odor.
- Density: The density of Zinc Chloride varies depending on the form, but it is generally around 2.91 g/cm3.
- Melting Point: The melting point of Zinc Chloride is approximately 283 °C.
- Solubility: It is highly soluble in water and forms a colorless solution.
Chemical properties of Zinc Chloride
- Hygroscopic: Zinc Chloride is hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the air.
- Deliquescent: It is deliquescent, which means that it can absorb enough moisture from the air to dissolve and form a liquid solution.
- Corrosive: Zinc Chloride is corrosive to metals and can cause damage to certain materials.
- Lewis Acid: It acts as a Lewis acid, meaning it can accept a pair of electrons from a Lewis base during a chemical reaction.
- Conductivity: Zinc Chloride solutions conduct electricity due to the dissociation of ions in water.
Uses of Zinc Chloride
- Galvanizing: Zinc Chloride is used in the galvanizing process to provide corrosion protection to metals such as steel.
- Wood Preservation: It is used in wood preservation treatments to protect against decay and insect infestation.
- Flux Agent: Zinc Chloride serves as a flux in soldering and brazing processes to facilitate the flow of molten metal.
- Chemical Synthesis: It is employed as a catalyst or reagent in various chemical reactions and organic synthesis.
Zinc Chloride (ZnCl2) Conclusion
In conclusion, zinc chloride (ZnCl2) is an important inorganic compound with various applications in industries, laboratories, and other fields. It is formed by the combination of zinc (Zn) and chlorine (Cl) atoms, resulting in a white crystalline solid.
Zinc chloride is widely used as a versatile chemical reagent. It acts as a Lewis acid, capable of accepting electron pairs from Lewis bases, and finds application in organic synthesis and chemical reactions. It can be used as a catalyst or as a reagent in processes such as Friedel-Crafts acylation, Beckmann rearrangement, and other reactions involving the formation of carbon-carbon and carbon-nitrogen bonds.
Solved Questions on the Zinc Chloride (ZnCl2) Formula
Example 1: What is the molar mass of zinc chloride?
Solution:
To calculate the molar mass of zinc chloride (ZnCl2), we need to determine the atomic mass of each element and multiply it by the respective number of atoms in the formula.
Molar mass of zinc (Zn) = 65.38 g/mol
Molar mass of chlorine (Cl) = 35.45 g/mol
Since there are two chlorine atoms in the formula, we multiply the molar mass of chlorine by 2.
Molar mass of ZnCl2 = (65.38 g/mol) + (35.45 g/mol × 2)
= 65.38 g/mol + 70.90 g/mol
= 136.28 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of zinc chloride is 136.28 g/mol.
Example 2: How many moles of zinc chloride are present in 50 grams of ZnCl2?
Solution:
To determine the number of moles of zinc chloride, we divide the given mass (50 grams) by the molar mass of zinc chloride (136.28 g/mol).
Number of moles = Mass / Molar mass
= 50 g / 136.28 g/mol
≈ 0.367 moles
Therefore, there are approximately 0.367 moles of zinc chloride in 50 grams of ZnCl2.
Frequently Asked Questions on Zinc Chloride
Is zinc harmful or not?
Zinc is essential for the body in small amounts. However, excessive intake can be harmful, leading to side effects like nausea and weakened immunity.
Is zinc chloride a salt?
Yes, zinc chloride is a salt formed from the reaction of zinc and hydrochloric acid.
Is zinc chloride an antibiotic?
No, zinc chloride is not an antibiotic. It's a chemical compound with various industrial and medicinal applications.
Is zinc chloride safe for humans?
Zinc chloride is safe in small quantities, but excessive or direct exposure can be harmful, causing skin irritation and other health issues.
Why is zinc used for skin?
Zinc is used for the skin because of its anti-inflammatory properties, ability to protect against UV rays, and role in promoting wound healing.
What is zinc chloride used for?
Zinc chloride is used in various industries, including soldering fluxes, textile processing, wood preservatives, and in some mouthwashes and deodorants.
Why ZnCl2 is used in dry cell?
ZnCl2 is used in dry cells because it acts as an electrolyte, promoting the flow of electrons, and enhances the battery's overall performance.
What are the hazards of zinc chloride?
Exposure to zinc chloride can cause skin and eye irritation, respiratory issues when inhaled, and digestive problems if ingested in large amounts.
What acid is used in zinc chloride?
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) reacts with zinc metal to produce zinc chloride.








