Table of Contents
Lymph is a transparent or white fluid containing: White blood cells, especially lymphocytes, which fight bacteria in the blood and body tissues. It also includes a fluid from the intestines called chyle, which holds proteins and fats.
Also Check: Anaerobic Respiration
What is the Lymphatic System?
Your lymphatic system is like a team of organs, tubes, and tissues that cooperate to carry a clear, watery liquid called lymph back into your bloodstream.
It’s a crucial part of your immune system, shielding you from infections and getting rid of old or odd cells your body doesn’t want. The lymphatic system also helps keep the right balance of fluids in your body and takes in fats and certain vitamins, guiding them into your bloodstream.
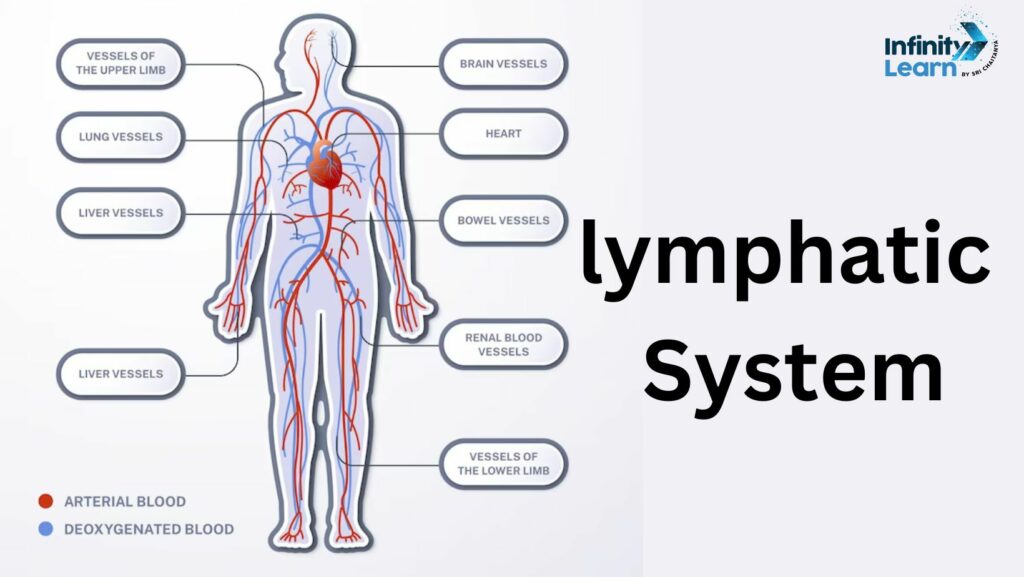
Lymph System
The lymphatic system acts like a complex network of small tubes spread throughout our body. Its job is to gather up a watery substance called lymph, which escapes from our blood vessels and seeps into our tissues. After gathering the lymph, the system sends it back into our bloodstream through tiny structures known as lymph nodes. Essentially, the lymphatic system plays a crucial role in regulating the fluid levels within our body.
Also Check: Life Process
lymphatic system function
The lymphatic system has three main jobs: first, it helps keep the balance of fluids in the body; second, it helps absorb fats from food in the gut and sends them into the bloodstream for energy or storage; and third, it helps make the immune system stronger and more effective.
Lymphatic Vessels
A lymphatic vessel is a slender tube responsible for transporting lymph, a clear fluid containing white blood cells, throughout the lymphatic system. This intricate network of vessels and organs, including lymph nodes, tonsils, thymus, spleen, and bone marrow, plays a crucial role in defending the body against infections and diseases. It acts as a drainage system, removing waste and excess fluid from tissues and returning them to the bloodstream.
Also Check: Organisms Reproduce Class 10
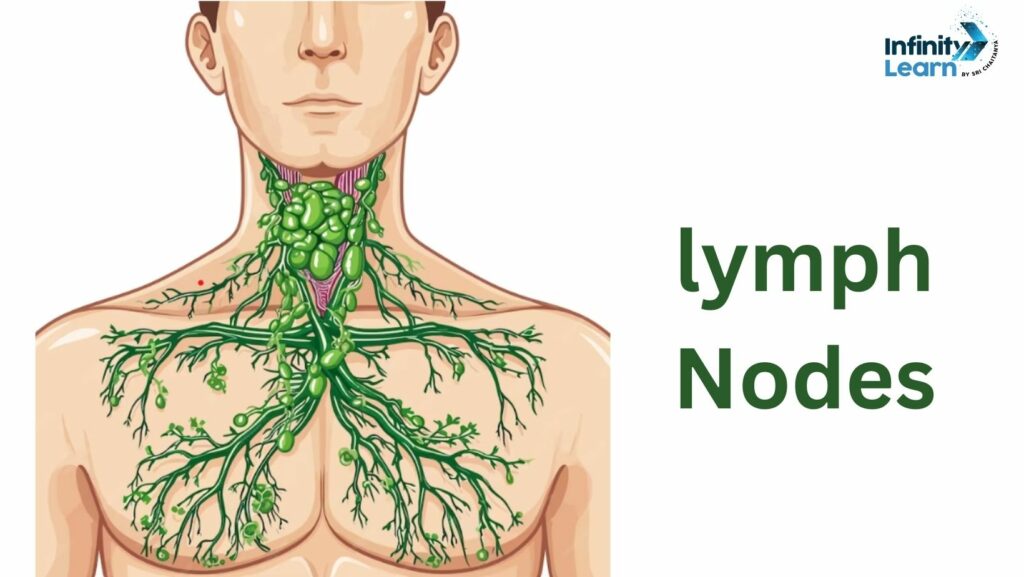
Lymph Nodes
A small bean-shaped thing in your body that helps your immune system. These little things filter stuff that moves through the lymphatic fluid. Inside them are white blood cells called lymphocytes that help fight infections and sickness. You have lots of these all over your body, and they’re connected by lymph vessels. Bunches of them are in places like your neck, underarms, chest, belly, and groin. For instance, you have about 20-40 of them in your armpits. They’re also called lymph glands.
Also Check: Duodenum
Swallow Lymph Nodes
Enlarged lymph nodes often happen because of infections caused by bacteria or viruses. Sometimes, though not often, swollen lymph nodes can be caused by cancer. Lymph nodes, also called lymph glands, are crucial for your body’s defense against infections. They act as filters, capturing viruses, bacteria, and other harmful agents to prevent them from spreading to other parts of your body. Swollen lymph nodes are commonly noticed in areas such as the neck, under the chin, in the armpits, and in the groin.
Also Check: CBSE Class 10 Science Syllabus
Lymph Fluid
This is a clear liquid produced by the body. It surrounds all body tissues. Extra liquid from body tissues goes into small tubes called lymph vessels. This liquid goes through the lymph nodes, gets filtered, and goes back into the bloodstream.
How is Lymph Formed?
Blood plasma separates from the blood and moves through tiny blood vessels. At one end, it seeps out into the body’s tissues. Then, the fluid starts collecting, and small vessels called lymphatic vessels pick it up. They carry this fluid, now called lymph, back to the blood.
Also Check: CBSE Syllabus for Class 10
Lymph Capillaries
Small tubes called lymphatic capillaries are present in the tissues of almost all organs in your body. They carry a fluid called lymph from the cells and tissues of your body. These tubes help maintain steady blood pressure and volume and stop fluid from building up.
Lymph FAQs
What is the function of lymph?
Lymph helps remove waste and toxins from tissues, carries white blood cells, and maintains fluid balance in the body.
What organ is lymph?
Lymph is a clear fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, which includes lymph nodes, vessels, spleen, thymus, and tonsils.
What are the 4 lymph nodes?
The four main groups of lymph nodes are cervical (neck), axillary (armpits), inguinal (groin), and mesenteric (abdomen).
What is the function of lymph vessels?
Lymph vessels collect excess fluid from body tissues, filter it through lymph nodes, and return it to the bloodstream.
Why are lymph capillaries absent in CNS?
Lymph capillaries are absent in the central nervous system (CNS) to protect the brain and spinal cord from harmful substances.
How many vessels are there in a lymph node?
A lymph node has one incoming vessel (afferent) and one outgoing vessel (efferent) for lymph flow.
What are the five lymphatic organs?
The five lymphatic organs are the tonsils, thymus, spleen, lymph nodes, and Peyer's patches in the small intestine.








