Table of Contents
Sodium carbonate, also known as soda ash or washing soda, is a versatile chemical compound with the formula Na2CO3. It is an essential compound in various industrial processes and has multiple applications. In this note, we will explore the formula and structure of sodium carbonate, as well as its chemical and physical properties.
Formula and Structure of Sodium Carbonate
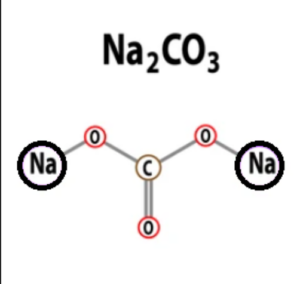
The formula of sodium carbonate, Na2CO3, indicates that it consists of two sodium (Na) atoms, one carbon (C) atom, and three oxygen (O) atoms. The presence of two sodium atoms suggests that sodium carbonate is a binary compound containing one cation (Na+) and one anion (CO3 2-). The carbonate ion (CO3 2-) is made up of one carbon atom bonded to three oxygen atoms, forming a trigonal planar arrangement.
Sodium Carbonate Chemical Properties
- Solubility: Sodium carbonate is highly soluble in water, forming a strongly alkaline solution. This property makes it useful in various applications, including water treatment and the manufacturing of soaps and detergents.
- Acid-Base Reactions: Sodium carbonate is a basic compound and can react with acids to form salts, water, and carbon dioxide. This reaction is commonly used as a mild antacid to neutralize excess stomach acid.
- Thermal Decomposition: When heated, sodium carbonate undergoes thermal decomposition, releasing carbon dioxide gas (CO2) and forming sodium oxide (Na2O). This process is utilized in the production of soda lime, which is used to absorb carbon dioxide in applications such as rebreathing systems and carbonation of beverages.
- Reaction with Metals: Sodium carbonate reacts with certain metals, such as zinc and aluminum, to produce hydrogen gas (H2) and the corresponding metal carbonate. This reaction is commonly used to remove rust from metal surfaces.
Also read: Sodium Bicarbonate Formula
Sodium Carbonate Physical Properties
- Appearance: Sodium carbonate occurs as a white, crystalline powder or granules. It has no distinct odor but has a slightly alkaline taste.
- Melting and Boiling Points: The melting point of sodium carbonate is approximately 851 degrees Celsius (1564 degrees Fahrenheit), and it does not have a specific boiling point. Instead, it undergoes thermal decomposition upon heating.
- Density: The density of sodium carbonate varies depending on its hydration state. Anhydrous sodium carbonate (without water) has a density of around 2.54 grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm3), while the densest hydrated form, known as the decahydrate (Na2CO3·10H2O), has a density of about 1.46 g/cm3.
- Hygroscopicity: Sodium carbonate is hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the atmosphere. This property can cause the compound to clump together or form lumps when exposed to humid conditions.
In conclusion, sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) is a chemical compound widely used in various industries. It possesses several chemical properties, such as solubility, acid-base reactions, thermal decomposition, and reactivity with certain metals. The physical properties of sodium carbonate include its appearance as a white crystalline powder, its melting point, density, and hygroscopic nature. Understanding these properties is essential for comprehending the behavior and applications of this important compound in both industrial and domestic settings.
Also Read
Solved Examples on Sodium Carbonate Formula
Example 1: Calculate the molar mass of sodium carbonate (Na2CO3).
Solution: To calculate the molar mass of sodium carbonate, we need to determine the atomic masses of each element present and multiply them by their respective subscripts in the formula.
Atomic mass of sodium (Na) = 22.99 g/mol
Atomic mass of carbon (C) = 12.01 g/mol
Atomic mass of oxygen (O) = 16.00 g/mol
Molar mass of (Na2CO3) = (2 * atomic mass of Na) + atomic mass of C + (3 * atomic mass of O)
= (2 * 22.99 g/mol) + 12.01 g/mol + (3 * 16.00 g/mol)
= 45.98 g/mol + 12.01 g/mol + 48.00 g/mol
= 105.99 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) is 105.99 g/mol.
Example 2: How many moles of sodium carbonate are present in 500 grams of Na2CO3?
Solution: To determine the number of moles of sodium carbonate, we need to divide the given mass by the molar mass of Na2CO3.
Molar mass of (Na2CO3) = 105.99 g/mol (calculated in Example 1)
Number of moles = Mass (g) / Molar mass (g/mol)
= 500 g / 105.99 g/mol
≈ 4.71 mol (rounded to two decimal places)
Therefore, there are approximately 4.71 moles of sodium carbonate in 500 grams of (Na2CO3).
Frequently asked Question on Sodium Carbonate Formula
The chemical formula of sodium carbonate is Na2CO3. It indicates that each molecule of sodium carbonate contains two sodium atoms Na, one carbon atom C, and three oxygen atoms O.
Sodium carbonate is commonly known as soda ash or washing soda.
The systematic name of sodium carbonate is disodium carbonate.
The formula mass or molar mass of sodium carbonate, Na2CO3, is approximately 105.99 grams per mole. It is calculated by adding up the atomic masses of the constituent elements.
Sodium carbonate can exist in hydrated forms with varying degrees of water molecules incorporated into the crystal structure. The most common hydrated form is the decahydrate, known as sodium carbonate decahydrate or soda ash decahydrate, with the formula Na2CO3·10H2O. The chemical formula of sodium carbonate is Na2CO3. It indicates that each molecule of sodium carbonate contains two sodium atoms Na, one carbon atom C, and three oxygen atoms O. What is the chemical formula of sodium carbonate?
What is the common name of sodium carbonate?
What is the systematic name of sodium carbonate?
What is the formula mass of sodium carbonate?
What is the hydrated form of sodium carbonate?






