Table of Contents
CBSE Class 6 Geography Notes Chapter 3 Motions of the Earth
Understanding the Earth’s movements is essential for students following the CBSE syllabus. These CBSE notes on Chapter 3 of the Class 6 NCERT textbook gets into the captivating dynamics of the Earth’s motion. The notes are crafted to offer a clear and concise summary of the key concepts from the chapter, tailored specifically to align with the CBSE syllabus for class 6 social science.
Motions of the Earth Class 6 Notes Social Science Geography Chapter 3
Here all the important topics from class 6 NCERT textbook book of Geography in the form of notes for better understanding and quick revision:
Rotation
The movement of the earth on its axis is known as rotation.
- Rotation is the movement of the Earth, on its axis.
- The axis of the Earth, which is an imaginary line, makes an angle of 66/2° with its orbital plane.
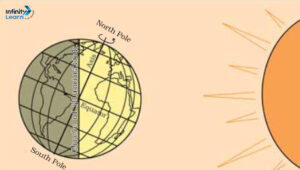
- The portion facing the Sun experiences day, while the other half away from the Sun experiences night.
- The circle that divides the day from night on the globe is called the circle of illumination.
- The Earth takes about 24 hrs to complete one rotation around its axis, it is known as earthday.
Revolution
The movement of the earth around the sun in a fixed path or orbit is known as revolution.
- The movement of the Earth around the Sun in a fixed path or orbit is called revolution.
- Earth takes 365)4 days to revolve around the Sun.
- Every fourth year, February is of 29 days instead of 28 days. Such a year with 366 days is called a leap year.
- Earth is going around the Sun in an elliptical-orbit.
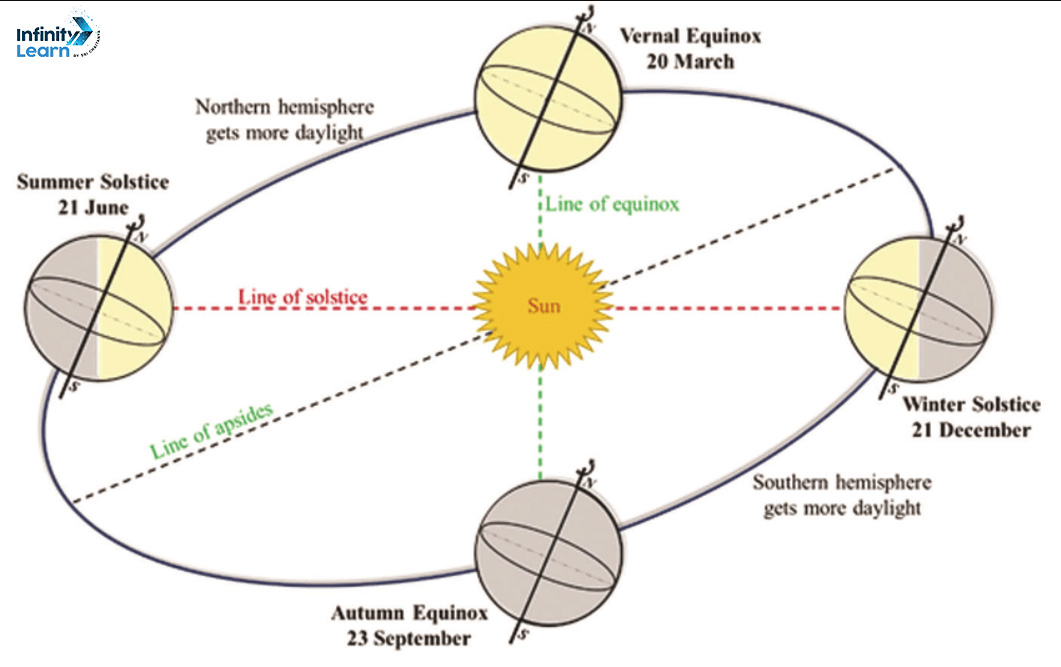
- Seasons change due to change in the position of the Earth around the Sun.
- Summer solstice is the position of the Earth when the Northern Hemisphere has the longest day and the shortest night. It
- occurs on 21st June.
- In the Southern Hemisphere, it is winter season at this time. The days are short and the nights are long.
- Winter Solstice is the position of the earth when Southern Hemisphere has long days and shorter nights. In the Northern
- Hemisphere, the days are short and the nights are long. It occurs on 22nd December.
- On 21st March and September 23rd, direct rays of the sun fall on the equator and the whole earth experiences equal days
- and equal nights. This is called an equinox.
Types of Motions
The earth has two types of motions—rotation and revolution.
Rotation is the movement of the earth on its axis. In revolution the earth moves around the sun in a fixed path or orbit.
The axis of the earth is an imaginary line.
The earth receives light from the sun. As the shape of the earth is spherical, only half of it gets light from the sun at a time. The other half remains dark. In this way day and night are caused.
The earth completes one rotation around its axis in about 24 hours. This rotation is the daily motion of the earth.
The earth takes 365 14 days or one year to complete one revolution around the sun.
There are four seasons in a year—summer, winter, spring and autumn. Seasons change due to the change in the position of the earth around the sun.
The rays of sun fall directly on the Tropic of Cancer. Hence, these areas are hot.
The areas near the poles receive less heat as the rays of the sun are slanting.
In the Northern Hemisphere the longest day and the shortest night occur on 21st June. In the Southern Hemisphere the shortest day and the longest night occur on this day. This position of the earth is known as the summer solstice.
When there is summer in the Northern Hemisphere, Southern Hemisphere enjoys winter season and vice-versa.
In the Northern Hemisphere the shortest day and the longest night occur on 22nd December. In the Southern Hemisphere the longest day and the shortest night occur on this day. This position of the earth is known as the winter solstice.
On 21st March and September 23rd the whole earth experiences equal’days and equal nights. This is phenomenon is known as equinox.
On 23rd September, it is autumn in the Northern Hemisphere and spring in the Sourthern Hemisphere.
On 21st March, it is spring in the Northern Hemisphere and autumn in the Sourthern Hemisphere.
Days and nights occur due to rotation while changes in seasons occur due to revolution.
Orbital plane
The plane formed by the orbit is known as the orbital plane.
Circle of illumination
The circle that divides the day from night on the globe is called the circle of illumination.
Leap year
The year in which February is of 29 days instead of 28 days is called a leap year.
Elliptical Orbit
An elliptical orbit is the path an object takes around another object in space, shaped like an elongated circle or an oval. This type of orbit is common for planets, including Earth, as they move around the sun.
Summer Solstice
In the Northern Hemisphere the longest day and the shortest night occur on 21st June. In the Southern Hemisphere, the shortest day and the longest night occur on this day. This position of the earth is called summer solstice.
Winter solstice
In the Northern Hemisphere the shortest day and the longest night occur on 22nd December. In the Southern Hemisphere, the longest day and the shortest night occur on this day. This position of the earth is called winter solstice.
Equinox
On 21st March and September 23rd the entire earth experiences equal days and equal nights. This is known as the equinox.
We hope the given Motions of the Earth Class 6 Notes Social Science Geography Chapter 3 SST Pdf free download will help you. If you have any query regarding Motions of the Earth Class 6 Geography Chapter 3 Notes, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
- Chapter 1 The Earth in the Solar system
- Chapter 2 Globe: Latitudes and Longitudes
- Chapter 3 Motions of the earth
- Chapter 4 Maps
- Chapter 5 Major Domains of the Earth
- Chapter 6 Major Landforms of the Earth
- Chapter 7 Our Country – India
- Chapter 8 India: Climate, Wildlife, and Vegetation
Why to Choose Infinity learn for Class 6 Geography Notes Chapter 3
- Comprehensive Coverage: Infinity Learn provides detailed and easy-to-understand notes that cover every aspect of Chapter 3, ensuring that students grasp the concepts of the Earth’s movements effectively.
- Aligned with CBSE Syllabus: The notes are specifically tailored to meet the requirements of the CBSE curriculum, ensuring that all the key topics and objectives outlined by the board are covered.
- Expertly Crafted Materials: Our resources are created by educational experts who have a deep understanding of the needs of Class 6 students, making complex topics like elliptical orbits and Earth’s rotations accessible and engaging.
- Interactive Learning Experience: Infinity Learn offers more than just notes. Our platform includes interactive quizzes, engaging videos, and practice tests that reinforce learning and make studying Geography fun and interactive.
- 24/7 Learning Support: Students can access our learning resources anytime, from anywhere, allowing them to study at their own pace and on their own schedule. Plus, our dedicated support team is always ready to help with any academic inquiries.
- Track Your Progress: With tools to monitor learning progress, students can see exactly how they’re doing and where they need to focus more, helping them prepare more effectively for their exams. Choosing Infinity Learn for Class 6 Geography means ensuring that students have a solid foundation in understanding the Earth’s motions, enhanced by innovative teaching methods and reliable support.
| Other Resources for Class 6 | |
| Worksheet for Class 6 All subjects | CBSE Notes Class 6 |
| NCERT Books for Class 6 | Online Tuition for Class 6 |
FAQs on Class 6 Geography Notes Chapter 3 Motions of the Earth
What are Earth's two main motions called?
The Earth's two main motions are rotation and revolution. Rotation is the spinning of the Earth on its axis, while revolution is its orbit around the Sun.
What causes the movement of the Earth to take place Class 6?
The movement of the Earth is caused by the gravitational forces exerted by the Sun and other celestial bodies. These forces keep the Earth in constant motion in its orbit.
What is the motion of the earth in one word?
The motion of the Earth in one word can be described as orbital, referring to its elliptical path around the Sun.
What is orbit class 6?
In Class 6, an orbit is defined as the path that a celestial body follows around another body due to gravitational forces. For example, Earth's orbit around the Sun.
What is leap year class 6?
A leap year is a year with an extra day added to keep the calendar year synchronized with the astronomical year. February has 29 days in a leap year.









