Table of Contents
Class 12 Geography Chapter 5 Primary Activities Questions Answers
Access Class 12 Geography important Questions and Answers for Chapter 5: Primary Activities. These important resources help students to score in their Class 12 board exams. Students can also access CBSE Syllabus for Class 12.
1 Mark Questions
Question 1. State the two groups of factors which affect the profitability of mining. (All Indio 2017)
Answer: The profitability of mining depends on two main factors:
- Physical factors include the size, grade and the mode of occurrence of the deposits.
- Economic factors such as the demand for the mineral, technology available and used.
Question 2. “Agri-business farms are mechanised and large in size.” Examine the statement, HOTS? (Delhi 2016)
Answer: Agri-business farms are large farms where large scale production takes place. Therefore, these farms are mechanised as per the latest scientific technology. The production in these farms is done for commercial purposes.
Question 3. What are the economic activities? (Delhi 2015)
Answer: Human activities that generate income are called economic activities. They are grouped under primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary activities.
Question 4. Who are called red collar workers? (All India 2015)
Answer: People who are engaged in primary activities are called red collar workers due to the outdoor nature of their work.
Question 5. What is truck farming? (Delhi 2014)
Answer: Truck farming specialises in the cultivation of vegetables. It constitutes growing of vegetables around the urban centres to meet the daily requirement of urban areas.
Question 6. Name the two activities on which the earliest human beings were dependent for their sustenance. (Delhi 2011, All Indio 2000)
Answer: The two activities are gathering and hunting.
Question 7. What is nomadic herding? (All Indio 2011)
Answer: Nomadic herding is also called pastoral nomadism. It is basically primitive subsistence activity in which herders depend upon animals for food, clothing, shelter, tools and transport.
Question 8. Name any two areas of high latitudes in the world, where gathering economic activity is practised. (All Indio 2010)
Answer: Two areas of high latitudes where the gathering is practised are Northern Canada and Northern Eurasia.
Question 9. Name the country where practically every farmer is a member of a cooperative society? (Delhi 2008)
Answer: Denmark is a country where every farmer is a member of a cooperative society
Also Check: CBSE Class 12 Date Sheet 2024 Out
3 Marks Questions
Question 10. Explain any three features of underground mining methods in different countries of the world. (All Indio 2010)
Answer: The three features of underground mining methods in different countries of the world are as follows:
- It is done when the ore lies deep below the surface. In this method, vertical shafts have to be sunk, from were underground galleries, radiate to reach the minerals.
- For underground mining, lifts, drills, haulage vehicles, ventilation systems for safe and efficient movement of people and materials are required,
- The method used in underground mining is risky because poisonous gases, fires, floods and caving can lead to fatal accidents.
Question 11. “Dairy farming is the most advanced and efficient type of rearing of milch animals in the world.” Analyse the statement with examples, HOTS? (AII Indio 2009)
Answer: It is true that dairy farming is the most advanced and efficient type of rearing of animals for milk in the world. This is because it is highly capital as well as labour intensive. Animal sheds, storage facilities for fodder, feeding and milking machines add to the cost of dairy farming.
Special emphasis is laid on cattle breeding, health care and veterinary services. It is labour intensive also due to the caring, feeding and milking processes involved. The developed means of transportation, refrigeration, pasteurisation and other preservation processes are used to increase the duration of storage of various dairy products.
Question 12. Study the diagram given below and answer the questions that follow. (Delhi 2008)
(i) Two types of mining are shown in as A and B. Identify them and give the correct name of each.
(ii) State two characteristics of each type of mining.
Answer:
(i) The two types of mining are:
A- Surface mining/Open cast or strip mining
B-Underground mining/Shaft mining
Characteristics of surface mining are:
- It is the cheapest and easiest way of mining.
- The safety precautions and equipment is relatively low.
Characteristics of underground mining are:
- It is done when the ore lies deep below the surface.
- Lifts, drills, haulage vehicles, ventilation system for safe and efficient movement of people and materials are required.
5 Marks Questions
Question 13. Describe the way of life of nomadic herders in the world. (All Indio, 2017)
OR
Define the term nomadic herding?
OR
Explain its any four characteristics. (Delhi 2015)
OR
Explain any five features of nomadic herding in the world. (All Indio 2012 )
Answer:
- Nomadic herding is also called pastoral nomadism. It is basically primitive subsistence activity, in which herders depend upon animals for food, clothing, shelter, tools and transport. Characteristics of nomadic herding are as follows:
- 1They move from one place to other places with their livestock for the quality of pastures and water. Each nomadic community occupies a well-identified territory as a matter of traditions.
- The variety of animals reared in different regions of the world, e.g. in tropical Africa, cattles are most important livestock; in the hilly areas of Tibet and Andes yak and lamas in Arctic and sub-Arctic areas, reindeer is the most important livestock.
- Movement in search of pastures is undertaken either over vast grassland or mountainous regions.
- Nowadays the number of pastoral nomads has been limited and their areas are also decreased due to the imposition of political boundaries and new settlement plans by different countries.
Question 14. Review any five measures adopted to solve the problems of Indian Agriculture, (HOTS; AII Indio 2017)
Answer: Main measures adopted to solve the problems of Indian agriculture are:
- Irrigation System Earlier Indian agriculture was totally depended on rainfall. But now canals, wells, tubewells were made to decrease the dependence of agriculture on rainfall.
- Improvement of Credit Facilities Banks is giving easy credit to the farmer at a very low-interest rate.
- Land Reforms It had changed the distribution of cultivable land and helps in agricultural development.
- Commercialisation This help in increase in the per hectare production increase and also per person production increases.
- High yield variety seeds The HYV Seeds greatly helps Indian agriculture as it requires less water and fertilizer. This increase in production.
Question 15. Classify intensive subsistence agriculture into two categories practised in the world. How are they different from each other? Explain. (HOTS; All India 2017)
Answer: Intensive subsistence agriculture is largely found in densely populated regions of monsoon Asia.
There are two categories practised in the world:
- Intensive subsistence agriculture dominated by wet paddy cultivation.
- Intensive subsistence agriculture dominated by crops other than paddy.
Characteristics of intensive subsistence dominated by wet paddy cultivation are:
- It is characterised by the dominance of rice crop. Landholding is very small due to the high density of population.
- Use of machinery is limited and most of the agricultural operations are done by manual labour.
Characteristics of intensive subsistence dominated by crops other than paddy are:
- Wheat, soybean, barley and sorghum are grown in Northern China Manchuria, North Korea and North Japan. In India, wheat is grown in western parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plains and millets are grown in dry parts of Western and Southern India.
- Irrigation systems are used frequently as this type of agriculture is practiced in dry areas.
Question 16. Differentiate between nomadic herding and commercial livestock rearing, stating any five points of distinction. (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
| Nomadic Herding | Commercial livestock rearing |
| Nomadic herding is a primitive subsistence activity where herders move from one place to another along with their livestock. | Commercial livestock rearing .is an organised activity that is practised on permanent ranches. |
| In nomad to herding, a wide variety of animals are reared. | In commercial livestock, only one type of animal is reared. |
| Nomads heavily rely on their animals for food, clothing, shelter, tools and transport. Here local needs are fulfilled. | In commercial livestock rearing, animal products like meat, wool, hides, skin are processed, packed scientifically and exported to different world markets. |
| Nomadic herding is done in open pastures over vast horizontal distances or vertical elevations in hilly areas and mountains using primitive techniques. | Commercial livestock rearing is done on permanent ranches using the latest scientific technology. |
| Nomadic herding is practised in areas of extreme climatic conditions like in tropical Africa, Asiatic deserts, mountainous regions of Tibet, Arctic and SubArctic areas. | Commercial livestock rearing is associated with Western culture and practised where large areas are available. New Zealand, Australia, Argentina, Uruguay and the United States are important countries where it is practised. |
Question 17. Differentiate between co-operative farming and collective farming, stating five points of distinction. (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
| Co-operative Farming | Collective Farming |
| Cooperative farming takes place when farmers pool their resources voluntarily for efficient and profitable farming. | Collective farming takes place when there is collective labour and there is social ownership of means of production. |
| In co-operative farming, farmers have individual ownership of the resources. | In collective farming, farmers pool all their resources though they are allowed to keep a very small plot of land for their own use. |
| Co-operative societies help farmers in buying farm inputs on favourable terms. | In collective farming, all farm inputs are provided by the government. |
| Co-operative societies also help the farmers in selling the farm products profitably. | Collective farming, farm products are sold to the state at a fixed price. |
| Co-operative farming has been successful in many European countries and that is why it is practised in many other countries of the world. | Collective farming was introduced in the former Soviet Union but after its disintegration, the system of farming has been modified. |
Question 18. Describe any five characteristics of plantation agriculture in the world. (All Indio 2016, 2009)
OR
Name any six crops of plantation agriculture of the world. Describe any four characteristics of plantation agriculture. (All Indio 2008)
Answer: Six crops of plantation agriculture are tea, coffee, rubber, cotton, sugarcane and bananas. Characteristics of plantation agriculture are as follows:
- This kind of agriculture was introduced by Europeans in colonies situated in tropics, e.g. the French established cocoa and coffee plantation in West Africa. British set up large tea gardens in India and Sri Lanka and rubber plantations in Malaysia and banana plantations in West Indies.
- It needs large estates of plantations; large investment and managerial support.
- Technical support and scientific methods of cultivation are required.
- It needs single crop specialisation, cheap, labour and a good system of transportation which connects plantations to factories and factories to markets.
Question 19. Define the term commercial livestock rearing. Explain any four characteristics. (All India 2015)
OR
Describe any five characteristics of ‘commercial livestock rearing’ practised in the world. Delhi 2014,2012
Answer: Commercial livestock rearing is a system in which animals are reared on extensive grasslands with modern scientific methods. This kind of rearing fulfil the demands of milk, meat, wool, etc in worldwide. Animal products are traded at a national and international level to earn money.
The characteristics of commercial livestock rearing are as follows;
- Commercial livestock rearing is totally opposite to the nomadic herding. It is more organised and capital intensive, the commercial livestock rearing is practised on permanent ranches.
- These ranches are of large size and are divided into parcels which are fenced to regulate the grazing. When one parcel is grazed then animals are moved to another parcel. All animals are kept according to the carrying capacity of pasture.
- In the pasture, only one type of animals is reared. Some important animals are sheep, goats, horses, etc. They produce meat, wool, hides and skin. These products are processed and packed scientifically and exported to different world markets.
- Ranches are managed scientifically and they emphasise on breeding, genetic improvement, disease control and health care on the livestock.
- USA, Argentina, New Zealand, Australia and Uruguay are important countries where commercial livestock rearing is practised.
Question 20. Define the term ‘mixed farming’. Explain any four characteristics of mixed farming practised in the world. (All Indio 2014)
Answer: Mixed farming is a type of agricultural farming in which farmers cultivate crops and also rear animals on the farm. The four characteristics of mixed farming are as follows:
- This kind of agriculture is practised in developed parts of the world viz. North-Western Europe, Eastern-North America and parts of Eurasia.
- Mixed farms are moderate in size and usually, the crops associated with it are wheat, barley, rye, maize, fodder and root crops. Fodder crops are an important component of mixed farming.
- The rotation and inter-cropping play an important role in maintaining soil fertility, chemical fertilizers and green manures are used extensively to achieve more output.
- Equal emphasis is laid on crop cultivation and animal husbandry so that farm animals like cattle, sheep, pigs, poultry provide income along with crops.
Question 21. Explain any five characteristics of extensive commercial grain cultivation practised in the world. All India 2014
Answer: The five characteristics of extensive commercial grain cultivation are as follows:
- Commercial grain cultivation is practised in the interior parts of semi-arid lands of the mid-latitudes.
- Wheat is the principal crop, though other crops like corn, barley, oats and rye are also grown.
- The size of the farm is very large and often run into hundreds of hectares.
- This is highly mechanised agriculture in which all operations from ploughing to harvesting are done by machines.
- Yield per acre is low, but yield per person is high because farms are mechanised and the population is sparse.
Question 22. Explain any five characteristics of dairy farming practised in the world. (Delhi 2013)
Answer: The five characteristics of dairy farming practised in the world are as follows:
- This kind of agriculture is the most advanced and efficient type of rearing of milch animals.
- It requires a huge investment of capital. Animal sheds, storage facilities for fodder, feeding and milching machines add to the cost of dairy farming.
- Focus on health care, cattle breeding and veterinary services.
- Here, the labour requirement is high as it is involved in rigorous care in feeding and milking.
- It is practised near urban and industrial regions because these places provide a market for milk and dairy products.
Question 23. Describe any five characteristics of the economic activities of hunting and gathering practised in the world. (Delhi 2012)
Answer: Characteristics of hunting and gathering practised in the world are as follows:
- Gathering and hunting are the well-known oldest economic activities. These are carried out at different levels with different orientations.
- The gathering is practised in a region with harsh climate conditions. It often involves primitive societies, which extract both plants and animals for food, shelter and clothing.
- The early man used stone, tools, twigs or arrows, so animals were hunted in limited number only but now due to excessive and illegal hunting (poaching), many species have become extinct or endangered.
- Gathering leads to collect valuable plant leaves, the bark of trees, gatherers also plant the medicinal trees. After simple processing, they sell the products in the markets.
- Gathering requires a small amount of capital investment and operates at a very low and li.tle bit technology.
Question 24. Where is intensive subsistence agriculture practised in the world? What are its two types? Describe any two characteristics of each type. (All India 2012)
Answer: Intensive subsistence agriculture is largely found in densely populated regions of monsoon Asia.
There are two categories practised in the world:
- Intensive subsistence agriculture dominated by wet paddy cultivation.
- Intensive subsistence agriculture dominated by crops other than paddy.
Characteristics of intensive subsistence dominated by wet paddy cultivation are:
- It is characterised by the dominance of rice crop. The landholding is very small due to the high density of population.
- Use of machinery is limited and most of the agricultural operations are done by manual labour.
Characteristics of intensive subsistence dominated by crops other than paddy are:
- Wheat, soybean, barley and sorghum are grown in Northern China Manchuria, North Korea and North Japan. In India, wheat is grown in western parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plains and millets are grown in dry parts of Western and Southern India.
- Irrigation systems are used frequently as this type of agriculture is practised in dry areas.
Question 25. What is the importance of dairy farming? Why is it mainly practised near urban and industrial centres of the world? Explain two reasons. (Delhi 2011)
Answer: The importance of dairy farming is as follows:
- It provides fresh milk and dairy products to us.
- Due to its labour intensiveness, it provides employment to many people as high labour is involved in rigorous care in feeding and mulching.
- It provides employment throughout the year, as there is no offseason during the year as in the case of crop cultivation.
Dairy farming is mainly practised near urban and industrial centres because of the following reasons:
- These regions provide neighbourhood markets for fresh milk and dairy products.
- Milk and dairy products are perishable goods and need to be transported soon, so to reduce the time of transportation the farms are located near urban centres.
Related Links
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Math Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Hindi Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Syllabus
Question 26. What is subsistence agriculture? Mention any four characteristics of primitive subsistence agriculture. (All India 2011)
Answer: It means agriculture in which farmer and his family consume all or nearly all the locally grown products. It can be divided into two categories i.e. primitive subsistence and intensive subsistence agriculture.
Characteristics of primitive subsistence agriculture are as follows:
- This kind of cultivation is practised by many tribes in tropics.
- Vegetation is cleared by fire and ashes used in the fertility of the soil.
- Cultivated fields are small so that people use only primitive tools such as sticks and hoes.
- After 3 to 5 years when the soil loses its fertility, then farmers clear another patch of forest land for cultivation.
Question 27. ‘There is low yield per acre but high yield per person in the interior parts of semi-arid lands of the mid-latitudes in the world.’ Support the statement with suitable examples. (HOTS; Delhi 2009)
Answer: The interior parts of semi-arid lands of the mid-latitudes in the world are the areas where extensive commercial grain cultivation takes place.
Here the size of the farms is very large and the population is in a small number. That is why entire operations of cultivation right from ploughing to harvesting is mechanised. Therefore, yield per person is high as the number of people working in farms is less and a lot of machines are used. However, the size of the farms is very large due to which per acre production or yield is low even though the total production is high.
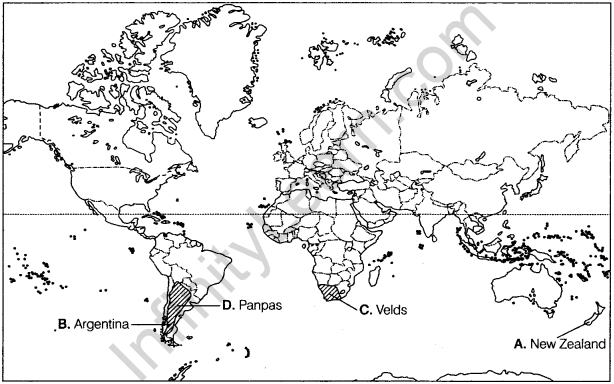
This type of agriculture is practised in Eurasian Steppes, Canadian and American Prairies, Pampas of Argentina, Velds of South Africa, Australian Downs and the Canterbury Plains of New Zealand. Wheat is the principal crop and other crops are corn, barley, oats and rye.
Question 28. What is subsistence agriculture? Name its two categories. State three main features of each category. (All India 200B)
Answer: Intensive subsistence agriculture is largely found in densely populated regions of monsoon Asia.
There are two categories practised in the world:
- Intensive subsistence agriculture dominated by wet paddy cultivation.
- Intensive subsistence agriculture dominated by crops other than paddy.
Characteristics of intensive subsistence dominated by wet paddy cultivation are:
- It is characterised by the dominance of rice crop. The landholding is very small due to the high density of population.
- Use of machinery is limited and most of the agricultural operations are done by manual labour.
Characteristics of intensive subsistence dominated by crops other than paddy are:
- Wheat, soybean, barley and sorghum are grown in Northern China Manchuria, North Korea and North Japan. In India, wheat is grown in western parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plains and millets are grown in dry parts of Western and Southern India.
- Irrigation systems are used frequently as this type of agriculture is practised in dry areas.
It means agriculture in which farmer and his family consume all or nearly all the locally grown products. It can be divided into two categories i.e. primitive subsistence and intensive subsistence agriculture.
Characteristics of primitive subsistence agriculture are as follows:
- This kind of cultivation is practised by many tribes in tropics.
- Vegetation is cleared by fire and ashes used in the fertility of the soil.
- Cultivated fields are small so that people use only primitive tools such as sticks and hoes.
- After 3 to 5 years when the soil loses its fertility, then farmers clear another patch of forest land for cultivation.
Question 29. What is the meaning of market gardening and horticulture? Describe any four characteristics of this type of agriculture of the world. All India 2008
Answer: This type of agriculture specialises in the production of high-value crops such as vegetables, fruits and flowers, solely devoted to the urban markets. These farms are located near urban areas.
Features of market gardening and horticulture are as follows:
- Farms are small in size and located near urban centres where good transportation facilities are available.
- It is both labour and capital intensive and lays emphasis on the use of irrigation, HYV seeds, fertilizers, insecticides, greenhouses and artificial heating systems in colder regions.
- The regions where farmers specialise in the cultivation of vegetables only is known as truck farming as the distance between the urban market and farms can be covered overnight by trucks.
- This type of agriculture is practised in well developed and densely populated regions of North-West Europe, North-Eastern USA and the Mediterranean regions. The Netherlands is specialised in growing flower and horticultural crops, especially tulips.
Map-Based Questions
Question 30. Identify the geographical features shown on the outline map of the world.
A. An area of dairy farming. (All India 2016)
B. An area of nomadic herding. (Delhi 2016. All indian 2011.2009)
C. An area of extensive commercial grain farming. (Delhi 2013. All India 2014.2013)
D. An area of subsistence gathering. (Delhi 2014, All India 2012)
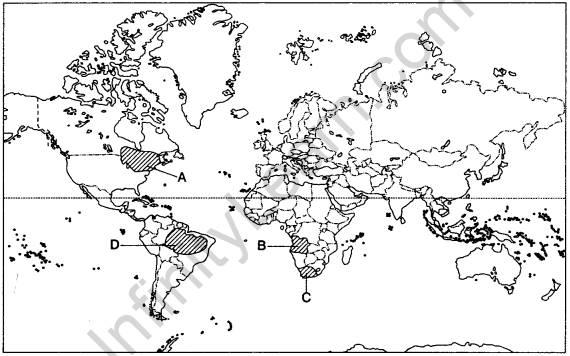
Answer:
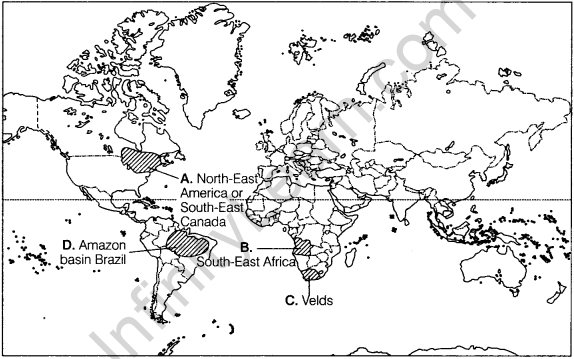
Question 31. Study the given map, showing dairy farming regions, carefully and answer the following questions. Delhi 2013
(i) Identify the areas and name the areas A and B, marked on the map.
(ii) Define dairy farming.
(iii) Explain any three characteristics of dairy farming.
Answer:
1. A. South-East Canada and North-East America.
B. North-Western Europe
2. Dairy farming is a type of farming practice where milch animals are reared. Special emphasis is on cattle breeding, health care and veterinary services.
3. The three characteristics of dairy farming are as follows:
- It is highly capital intensive as it requires animal sheds, storage facilities, fodder, mulching machines, etc.
- It is highly labour intensive also as it involves rigorous care in feeding and mulching.
- It is practised mainly near urban and industrial centres which provide a neighbourhood market for milk, dairy products, etc.
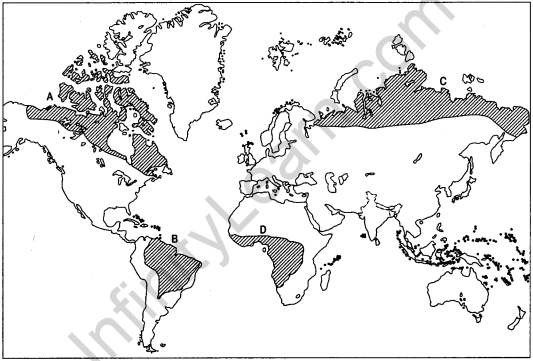
Question 32. Study the given map showing areas of subsistence gathering carefully and answer the following questions. (Delhi 2013)
(i) Identify and name the areas marked A, B > C, D on the map.
(ii) Explain any three characteristics of hunting and gathering.
(iii) Give two reasons why gathering has little chance to become important at a global level.
Answer:
1. A. Northern Canada
B. Amazon Basin
C. Northern Eurasia
D. Tropical Africa
2. The characteristics of hunting and gathering are:
(a) Hunting and gathering are practised in places that have a harsh climate such as very hot or very cold areas.
(b) These activities are done by primitive societies that depend on wild animals and plants.
(c) These activities require a small amount of capital investment and operate at a very low level of technology.
3. The two reasons are:
- Products collected from gathering cannot compete in the world market.
- Synthetic products that are better in quality are available at lower prices than the products collected by gathering.
More Resources for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology
- NCERT Books
- NCERT Books for Class 12
Question 33. Identify the geographical features shown on the outline map of the world.
A. A major area of commercial livestock rearing. (Delhi 2012,2011)B. An important country of commercial livestock rearing. (Delhi 2009)
C. Area of extensive grain farming. (All India 2008)
D. Area of extensive commercial grain farming. (Delhi 2000)
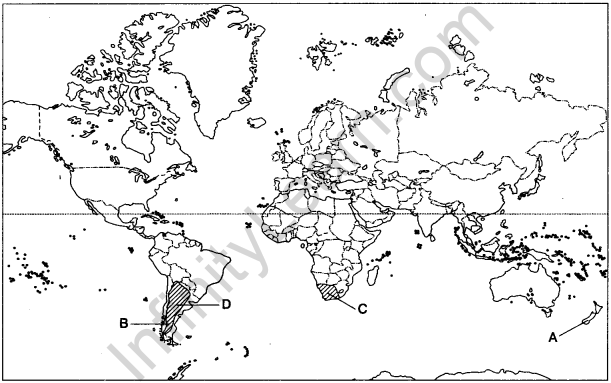
Answer:
Value Based Questions
Question 34. “Dairy farming is the most advanced and efficient type of rearing of milch animals in the world”. Explain the value which helps in the advancement of dairy farming.
Answer: Following values help in the advancement of dairy farming:
- Caring attitude towards animals.
- Participation of community.
- Evolve new techniques.
Question 35. “World food production is enough to feed everyone yet there are millions of people hungry and malnourished, lack of which value leads to this problem.
Answer: Lack of following values leads to millions of people go hungry and malnourished:
- Lack of caring nature for people.
- Lack of Awareness.
- Lack of Political Apathy.








