Table of Contents
Urea, also known as Carbamide, is a chemical compound with the formula CO(NH2)2. Urea is a nitrogenous compound that is mostly found in the urine of mammals. It is a white crystalline substance that is highly soluble in water and commonly used as a nitrogen fertilizer in agriculture.
Properties of Urea
- Urea is odourless, with the appearance of white crystals or granules.
- It is highly soluble in water, making it easy to use as a fertilizer.
- Urea has a melting point of approximately 132.7 degrees Celsius
- Urea has a boiling point of around 209 degrees Celsius.
- Urea is an organic compound as it contains carbon
Formula and Structure of Urea
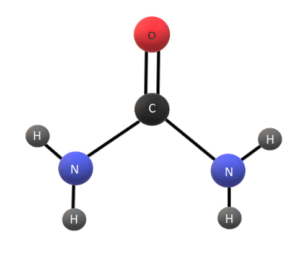
- Urea has a linear structure with two amino groups (- NH2) attached to a central carbon atom, which is double-bonded to an oxygen atom.
- Urea’s chemical formula is CO(NH2)2, which represents two amine groups (NH2) attached to a carbonyl group (C=O).
- The other two valencies of the central carbon atom are occupied by two additional hydrogen atoms.
- The molecular weight of urea is approximately 60.06 g/mol.
With respect to urea can be depicted in the following manner-
To find the molecular formula of the Urea,
First, we have to count the number of each atom in the Urea.
We have
- 1 carbon
- 4 hydrogen
- 2 nitrogen
- 1 oxygen
Now we will place the number of each atom as a subscript to form the formula.
That is, CH4N2O
This is the Molecular Formula of the Urea.
In context to 3-dimensional conformers, it is an interactive chemical structure model that provides the depiction of an animate, stick, ball, and stick, space-filling, show hydrogens, wire-frame.
Urea Structural Formula
- Urea has a planar geometry in its canter as it is a double amide.
- By looking at the structure, we can see that the carbon atom is double-bonded to an oxygen atom. Altogether we called it a carbonyl group.
- Also, Nitrogen is attached to two hydrogen atoms forming an amide group. Therefore, with two amide groups along with a carbonyl then the result would be urea.
Urea Equation
Chemical – CH4N2O
Its solubility is -50g/l (20 degrees), 1670g/l(40 degrees), 2510g/l(60 degrees),400g/l(80 degrees). The melting point is 133 degrees-135 degrees.
Reactivity Profile of Urea Formula
Urea is considered to be a weak base. Reacting with hypochlorites, it forms nitrogen trichloride that explodes impulsively in air. Same holds true for compounds named phosphorus pentachloride. It reacts with compounds such as azo and diazo to produce toxic gas. In addition, urea also reacts with strong decreasing agents to form flammable gases such as (hydrogen).
The heating of inappropriate stoichiometric quantities of urea and sodium nitrite results in an explosion. Heated mixtures of urea and oxalic acid produced speedy evolution of gases, ammonia, carbon dioxide, and carbon monoxide (if hot, can be explosive).
Urea and Titanium tetrachloride slowly produced a complex at 80° C during 6 weeks, decomposed aggressively at 90° C, Urea kindles spontaneously on stirring with nitrosyl perchlorate because of the formation of the diazonium perchlorate.
Urea and Oxalic acid react at high temperatures to produce flammable and toxic ammonia and carbon monoxide gases, as well as inert carbon dioxide gas.
Production of Urea
- Urea is synthesized through the reaction between ammonia and carbon dioxide under high pressure and temperature.
- The reaction occurs in a process called the Haber-Bosch process, which is widely used in the industrial production of urea.
Role of Urea in Agriculture and Other Industries
- Urea is a popular nitrogen fertilizer used in agriculture to enhance plant growth.
- It provides a readily available nitrogen source, an essential nutrient for plant development.
- Urea is often applied to soil or crops in the form of granules or dissolved in water.
- Urea is utilized in the production of various products, including plastics, adhesives, cosmetics, and animal feed.
- It is a raw material in manufacturing urea-formaldehyde resins, which find applications in producing plywood and particleboard.
Environmental Impact
- Urea has the potential to be harmful to the environment when used in excess or without proper management.
- When urea is applied to soil, it can convert into ammonia gas through a process called urea hydrolysis, leading to ammonia volatilization.
- Ammonia volatilization contributes to air pollution and can have detrimental effects on ecosystems.
Safety Precautions
- Urea is relatively safe to handle, but avoiding direct contact with the skin or eyes is recommended.
- When handling urea, it is advisable to wear gloves and protective eyewear.
- In case of accidental ingestion or prolonged exposure, it is essential to seek medical attention.
Solved Examples on Urea formula
Example 1: Which of the following area or field has no usage of urea?
- Agriculture
B. Chemical industry
C. Environmental protection
D. Automobile
Answer. The correct option is C., which is environmental protection. This is because urea has no use or contribution to the area or field of environmental protection.
Example 2: Urea is a very important nitrogenous fertilizer. Its formula is CON2H4 Calculate the percentage of nitrogen in urea (C = 12, O = 16, N = 14, and H = 1).
Answer: Urea has the formula NH2−CO−NH2, i.e. CON2H4
Molecular mass of urea = 60 g/mol
Atomic mass of N = 14 & number of atoms = 2
i.e. 28 g/mol of urea
Thus the % of nitrogen = 28/60×100=46.66%
Example 3: What is the mass of nitrogen in 1000 kg of urea [CO(NH2)2]? (H = 1; C = 12; N = 14; O = 16)
Answer: (H = 1; C = 12; N = 14; O = 16) (Given)
Mass of nitrogen in urea molecule = (2 × 14) g = 28 g
Molecular mass of urea = [12 + 16 + 2 (14 + 1 + 1)] g = 60 g
60 g of urea contains 28 g of nitrogen.
Mass of nitrogen in 1000 kg of urea = 28/60×1000kg=466.7kg
Example 4: Calculate the percentage of nitrogen in Urea.
Answer: We know Urea’s molecular formula is CO(NH2)2
The total mass would be 60g/mol.
We also know the mass of nitrogen is 28g/mol.
Therefore Percentage of nitrogen will be calculated using,
Percentage of Nitrogen = (Mass of nitrogen) × (100) Mass of urea
Percentage of Nitrogen = (28)(100)/60
So the percentage of Nitrogen in urea comes to around 46.66%.
Example 5: Urea [CO(NH2)2] is an important nitrogenous fertilizer and is sold in 50 kg sacks. What is the mass of nitrogen in one sack of urea?
Answer: Mass of the Urea in one sac = 50 kg. = 50000 g.
Chemical Formula of the Urea = [CO(NH2)2]
The molecular mass of the Urea = 60 g/mole.
Mass of the Nitrogen in 1 mole of the Urea = 14 × 2 = 28 g.
60 g of the urea contains 28 g of the N.
1 g of the urea contains 28/60 g of the N.
50000 g of the urea contains 28/60 × 50000 g of the N., ie 23333.33 g of the Nitrogen.
Hence, the mass of the Nitrogen in one sac of the urea is 23,333.33 grams or 23.33 kg.
Related Formulas:
| Aluminium formula | Ammonium carbonate formula |
| Iron oxide formula | Nitride formula |
| Potassium hydroxide formula | Ascorbic acid formula |
FAQs on Urea Formula
What is the chemical formula of urea?
The chemical formula of urea is CONH2. It consists of one carbon atom C, two nitrogen atoms N, and four hydrogen atoms H, along with two oxygen atoms O in the carbonyl group.
What is the structure of urea?
Urea has a planar structure with the carbonyl group in the center and two amino groups NH2 attached to the carbon atom. The two amino groups are connected by a single bond NH–NH, forming the urea molecule.
What are the common uses of urea?
Urea has several applications, including its use as a nitrogen-rich fertilizer in agriculture. It is also used in the production of plastics, resins, adhesives, and cosmetics. In the medical field, urea is used in topical creams and ointments to treat certain skin conditions.
Is urea a natural or synthetic compound?
Urea is a naturally occurring compound that is found in the urine of mammals, including humans. However, the majority of urea available commercially is produced synthetically through chemical processes using ammonia and carbon dioxide.
What are the properties of urea?
Urea is a white, crystalline solid that is soluble in water. It has a relatively high melting point of approximately 132 to 135C 270 to 275F. Urea is odorless in its pure form but can develop a characteristic ammonia like odor when it decomposes. It is a stable compound under normal conditions but can decompose at high temperatures or in the presence of certain catalysts.








