Table of Contents
Chemistry 2016 Set 9
Get CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry on Infinity Learn for free.
Section A
1. Mention a chemical reaction involving a homogeneous catalyst.
2. Write the balanced equation for the reaction of CaNCN with water.
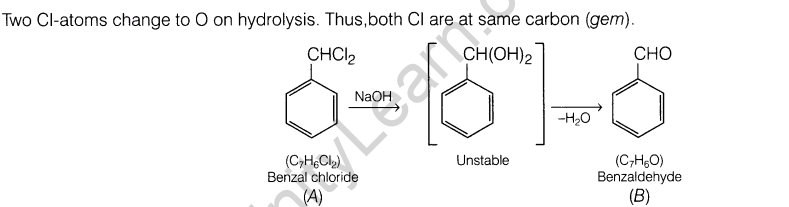
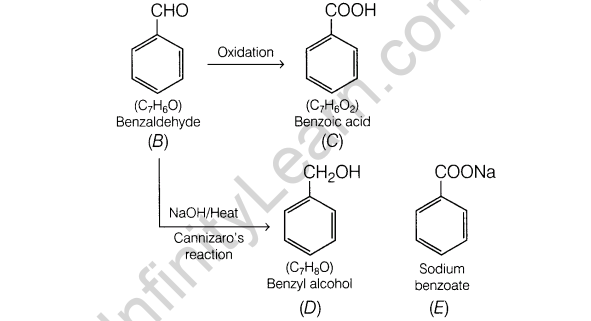
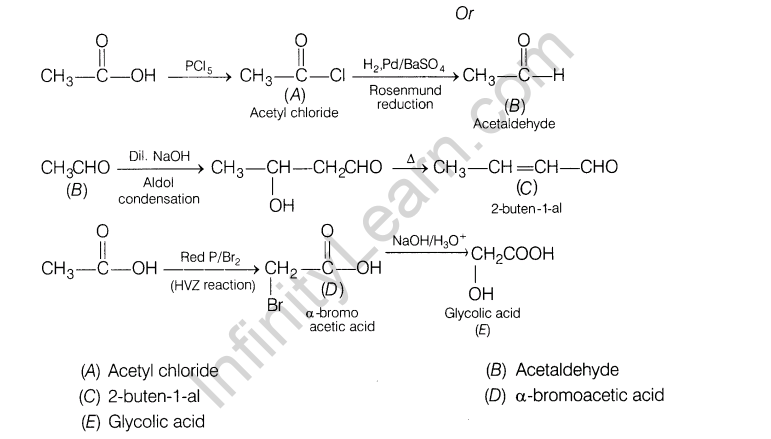
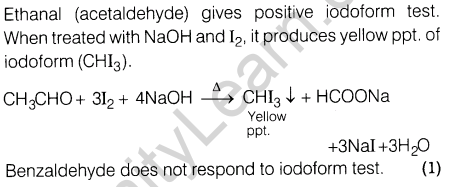
3. Give one chemical test to distinguish between ethanol(acetaldehyde) and benzaldehyde.
4. What type of bonding helps in stabilising the a-helix structure of proteins?
5. Explain, why MeNH2 is a stronger base than MeOH?
Section B
6. While separating a mixture of ortho and para-nitrophenols by steam distillation, name the isomer which will be steam volatile. Give reasons.
7. Niobium crystallises in a body-centred cubic structure. If the density is 8.55 gem-3, calculate the atomic radius of niobium using its atomic mass of 93 u.
8. An alloy of gold and cadmium crystallised with a cubic structure in which gold atoms occupy the corners and cadmium atoms fit into the face centres. Assign formula for this alloy.
Or
Give reasons.
(i)FeO(s) is not formed in the stoichiometric composition.
(ii)The electrical conductivity of semiconductors increases with rising temperature.
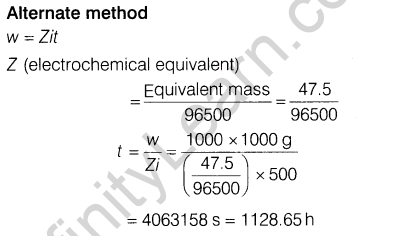
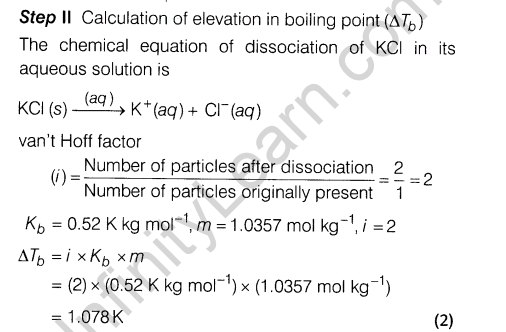
9. If 80% ofHg2Cl2 is ionised in the solution then what will be the can’t Hoff factor of Hg2Cl2 in the given aqueous solution

Section C

12.(i) H3P02 and H3P03 act as good reducing agents while H3P04 does not. Discuss.
(ii) Explain, why both N and Bi do not form pentahalides while phosphorus does?

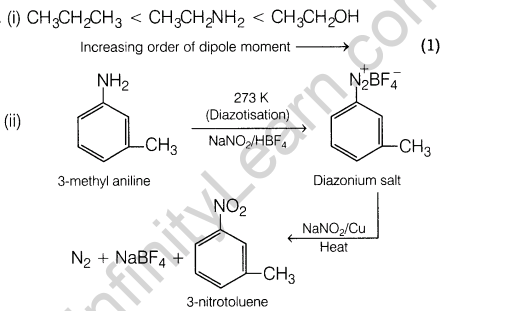
14. (i) Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of dipole moment.CH3CH2 CH3, CH3CH2NH2, CH3CH2OH
(ii) How will you convert 3-methylaniline into 3-nitrotoluene? Give chemical equation.
15. Explain, how does 1, 3-butadiene polymerise by different routes?
16. (i) Explain the formation of nucleic acid.
(ii)Show the peptide linkage in glycylalanine.
17. Write the equations involved in the following reactions.
(i)Williamson’s ether synthesis
(ii)Kolbe’s reaction

19. (i) Name one substance that can act as both
(a)analgesics and antipyretic.
(b)antiseptic and disinfectant.
(ii) Explain broad-spectrum antibiotics with suitable examples.
20. Answer the following:
(i)How is copper extracted from low grade copper ores?
(ii)Although carbon and hydrogen are better reducing agents they are not used to reduce metallic oxides at high temperatures. Why?
(iii)Give two differences between calcination and roasting.
21.(i) What happens when electric field is applied to colloidal solution?
(ii)Why does the white precipitate of silver halide become coloured in the presence of dye eosin?
(iii)What is the role of activated charcoal in gas mask used in coal mines?

Section D

Section E


Ans
Section A
1.Mention a chemical reaction involving a homogeneous catalyst.
Ans.

2.Write the balance equation for the reaction of CaNCN with water.
Ans.

3.Give one chemical test to distinguish between ethanal(acetaldehyde) and benzaldehyde.
Ans.
4.What type of bonding helps in stabilising the a-helix structure of proteins?
Ans.Hydrogen bonding helps in stabilising the a-helix structure of proteins
5.Explain, why MeNH2 is stronger base than MeOH?
Ans.Nitrogen is less electronegative than oxygen. Therefore, lone pair of electrons on nitrogen is readily available for donation. Hence, MeNH2 is more basic than MeOH
Section B
6.While separating a mixture of ortho and para-nitrophenols by steam distillation, name the isomer which will be steam volatile. Give reasons.
Ans.o-nitrophenol is steam volatile due to chelation and hence, can be separated by steam distillation from p-nitrophenol which is not steam volatile because of intermolecular H-bonding
7.Niobium crystallises in body centred cubic structure. If density is 8.55 gem-3 , calculate atomic radius of niobium using its atomic mass 93 u.
Ans.
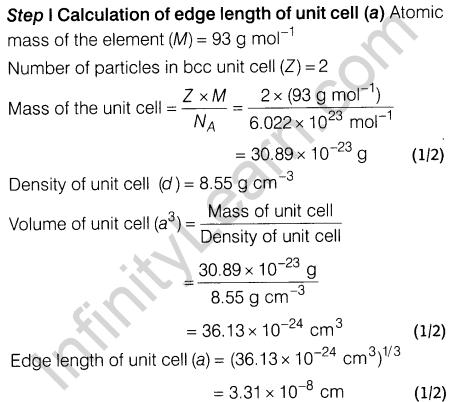
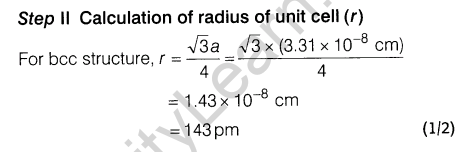
8.An alloy of gold and cadmium crystallised with a cubic structure in which gold atom occupy the corners and cadmium atoms fit into the face centres. Assign formula for this alloy.
Or
Give reasons.
(i)FeO(s) is not formed in stoichiometric composition.
(ii)The electrical conductivity of semiconductors increases with rise in temperature.
Ans.


9.If 80% ofHg2Cl2 is ionised in the solution then what will be the van’t Hoff factor of Hg2Cl2 in the given aqueous solution
Ans.
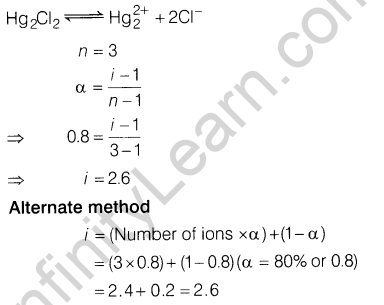

Ans.

Section C

Ans.

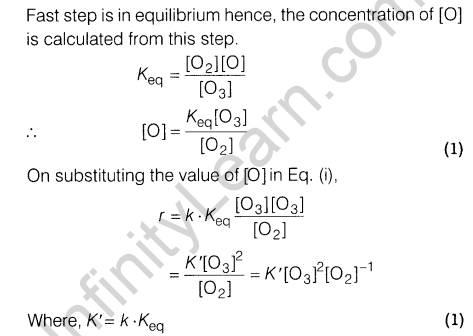
12.(i) H3P02 and H3P03 act as good reducing agents while H3P04 does not. Discuss.
(ii) Explain, why both N and Bi do not form pentahalides while phosphorus does?
Ans.


Ans.

14.(i) Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of dipole moment.CH3CH2 CH3, CH3CH2NH2, CH3CH2OH
(ii) How will you convert 3-methylaniline into 3-nitrotoluene? Give chemical equation.
Ans.
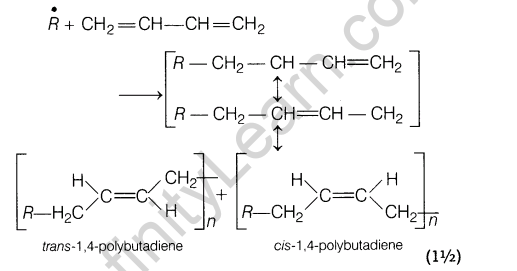
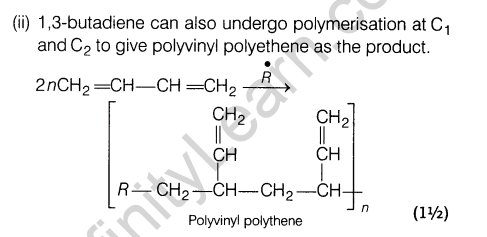
15.Explain, how does 1, 3-butadiene polymerise by different routes?
Ans.1,3-butadiene is a conjugate diene and its free radical polymerisation can occur in following two ways :
(i) When the polymerisation takes place at C-| and C4 of butadiene, an unbranched polymer is formed.
It can exist either as trans-polybutadiene or as c/s-isomer or as a mixture of both
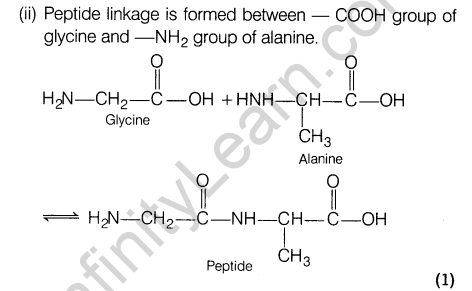
16.(i) Explain the formation of nucleic acid.
(ii)Show the peptide linkage in glycylalanine.
Ans.(i) Nucleic acids are biopolymers made up of nucleotide which are joined together to form a long chain. Each nucleotide is composed of a nucleoside bonded to a phosphate group and each nucleoside is composed of an aldopentose sugar linked to a heterocyclic purine or pyrimidine base
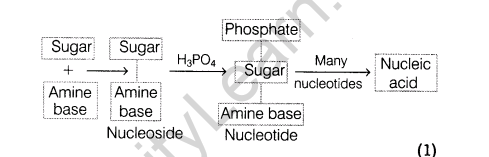
The nucleic acids, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), (the sugar component in RNA is ribose and the sugar in DNA is 2’-oxyribose) are the chemical carriers of a cell’s genetic information. DNA has all the information that determines the nature of the cell, controls cell growth and division, and directs biosynthesis of the enzymes and other proteins required for all cellular functions
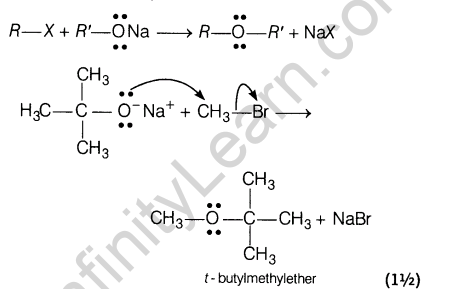
17.Write the equations involved in the following reactions.
(i)Williamson’s ether synthesis
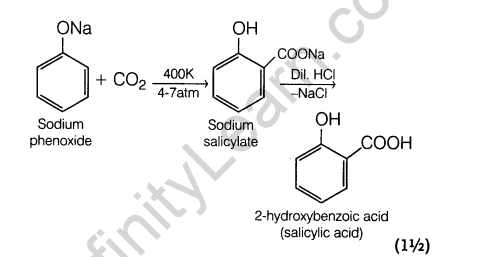
(ii)Kolbe’s reaction
Ans.(i) Williamson’s synthesis The reaction of alkyl halides with sodium alkoxide or sodium phenoxide to form ethers is called Williamson’s synthesis.
(ii) Kolbe’s reaction Sodium phenoxide reacts with carbon dioxide under pressure (4-7 atm) at 400 K to form salicylate which upon acidification with mineral acids gives salicylic acid. This reaction called Kolbe’s reaction.

Ans.

19.(i) Name one substance which can act as both
(a)analgesics and antipyretic.
(b)antiseptic and disinfectant.
(ii) Explain broad spectrum antibiotics with suitable example.
Ans.(i) (a) Aspirin acts as both analgesics and antipyretic
(b) 0.2% solution of phenol is an antiseptic while, its 1 % solution is disinfectant.
(ii) Antibiotic which kill or inhibit the growth of wide range of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria are called broad spectrum antibiotics, e.g. chloramphenicol
20.Answer the following:
(i)How is copper extracted from low grade copper ores?
(ii)Although carbon and hydrogen are better reducing agents but they are not used to reduce metallic oxides at high temperatures. Why?
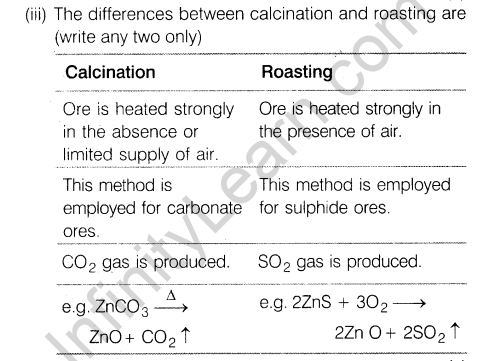
(iii)Give two differences between calcination and roasting.
Ans.

21.(i) What happens when electric field is applied to colloidal solution?
(ii)Why does the white precipitate of silver halide become coloured in the presence of dye eosin?
(iii)What is the role of activated charcoal in gas mask used in coal mines?
Ans.(i) When electric field is applied to colloidal solution then the charged particles of colloid start moving towards oppositely charged electrodes.
(ii) Eosin is adsorbed on the surface of silver halide precipitate making it coloured.
(iii)Activated charcoal acts as an adsorbent of various poisonous gases present in the coal mines.

Ans.
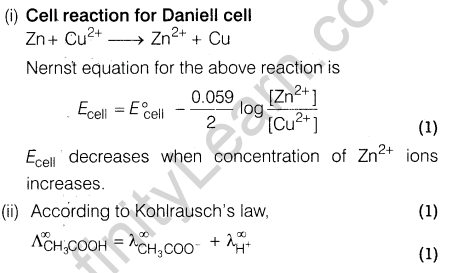
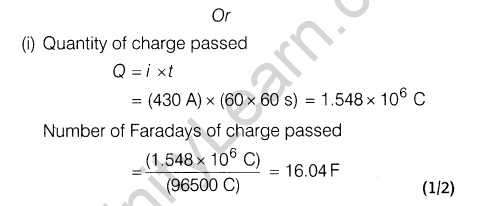
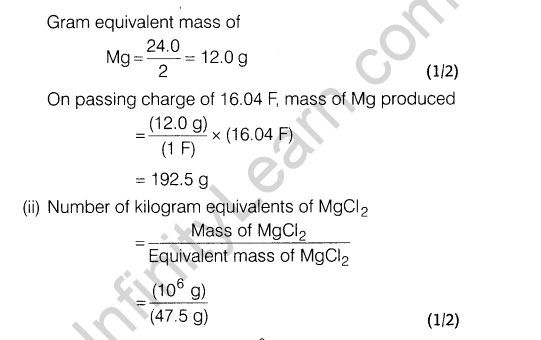
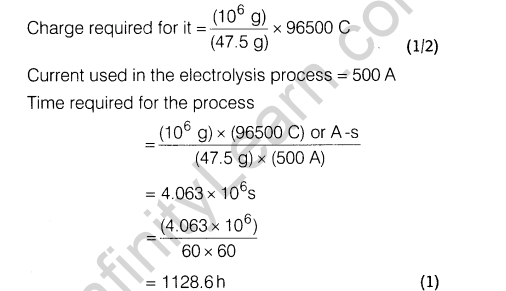
Section D

Ans.
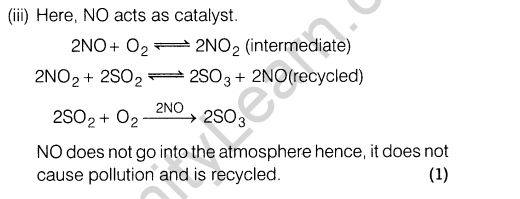
(i) The given reaction is exothermic and thus, low temperature may favour forward reaction. But at low temperature, rate of formation of S03 (and thus FI^O^ is very slow. Thus, temperature is kept about 700 K. At low temperature, forward reaction is favoured but takes longer time and thus, is not economical.
(ii)Contact process is adopted by Industry A Since, it is
environment friendly. Lead chamber process uses lead and causes pollution.
Section E

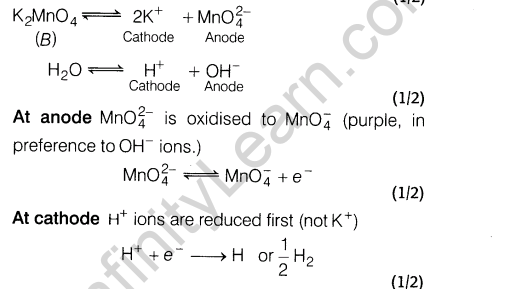
Ans.
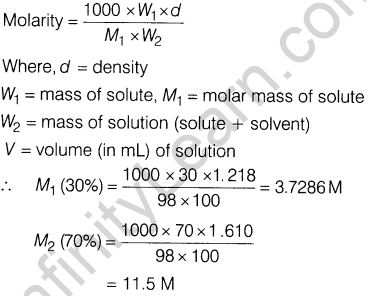

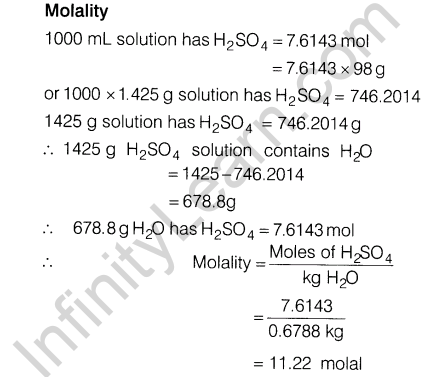



Ans.


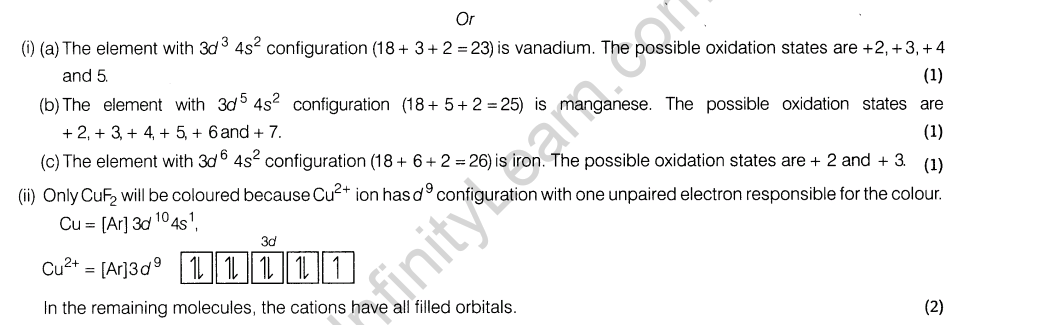

Ans.