Table of Contents
Electrostatics is the study of charges at rest. Charge of a material body or molecule is the property because of which it creates and encounters electrical and magnetic impacts. A portion of the normally happening charged particles are electrons, protons and so on Unit of charge is Coulomb. The fundamental law of electrostatics is coulomb’s law.
Electrostatics is one of the significant section in the schedule of Physics for JEE Main and JEE Advanced. Around 2-3 questions are being posed from this section every year.
Latest: JEE Main 2024: Rank predictor | College predictor
Join Our Courses: JEE Class 11 Students | JEE Class 12 Students | JEE Dropper
Electrostatics Formulas for JEE
1. Coulombs force between two-point charges:
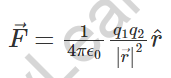
- Now, K = 1/4πε0 = 9 x 109 Nm2/C2
- q1 and q2 are the charges isolated by a distance r
Join our JEE course to make your IIT dream come true.
JEE Advanced 2025 Paper 1 Analysis by Infinity Learn Experts
2. Electric field:
The electric field a ways off r from the charge q
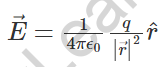
3. Electric field Intensity:
![]()
Where F is the power on the charge q because of the electric field E
4. Electrostatic Energy:
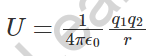
- q1,q2 are the charges
- r is the distance between the charges
5. Electric Potential
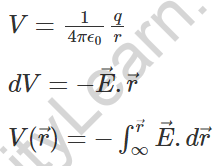
JEE Advanced 2025 Paper 2 Analysis by Infinity Learn Experts
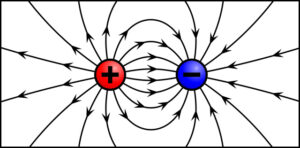
6. Electric dipole moment
- It is the result of a charge (q) and the distance between the two charges (d)
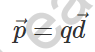
7. Potential of a dipole
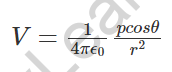
8. Field of a dipole
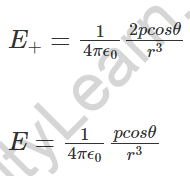
9. Force on a dipole put in the electric field
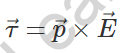
10. Potential energy of a dipole
![]()
Electric Charge
- Electrical peculiarities brought about by erosion are important for our regular day-to-day existences and can be perceived in terms of electrical charge.
- Electrical charge is that substance because of the presence of which a fixed molecule can react in an electrostatic field.
- The effects of charged bodies can be observed in the attraction/repulsion of various
objects when “charged.” - The charge comes in two variations called “positive” and “negative.”
- Objects conveying a net positive charge draw in those conveying a net negative charge and repulse those carrying a net positive charge.
- Objects conveying a net negative charge draw in those conveying a net positive charge and repulse those carrying a net negative charge.
- On a nuclear scale, electrons are contrarily charged and cores are emphatically charged.
- Electric charge is innately quantized to such an extent that the charge on any article is a whole number different of the littlest unit of charge which is the greatness and the electron charge e = 1.602 * 10-19C.
- On the naturally visible level, we can expect that charge is “nonstop.”
Coulomb’s Law
-
Coulomb’s law is the “law of action” between two charged bodies.
- Coulomb’s regulation gives the electric power between two point charges in a generally unfilled universe.
- A point charge is a charge that consumes a locale of room which is unimportantly little contrasted with the distance between the point charge and any other object.
- The power on Q1 because of Q2 is equivalent in size yet inverse in course to the power on Q2 because of Q1.
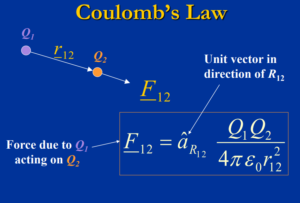
Electric Field
- Suppose a point charge Q placed at the origin of a coordinate system in an otherwise empty universe.
- A test charge Q*t brought near Q experiences a force:
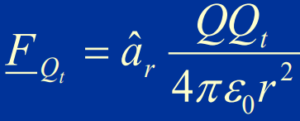
- The existence of the force on Q*t can be attributed to an electric field produced by Q.
- The electric field created by Q at a point in space can be characterized as the power per unit charge acting on a test charge Q*t placed at that point.
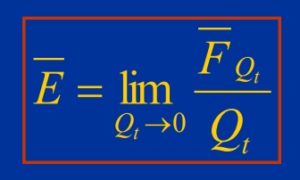
Electric Field
- The fundamental units of electric field are newtons per coulomb.
- By and by, we normally use volts per meter.
Continuous Distributions of Charge
-
- Charge can occur as
- point charges (C)
- volume charges (C/m3) surface charges (C/m2)
- line charges (C/m)
Electrostatic Potential
- An electric field is a force field.
- In the event that a body being followed up on by a power is moved starting with one point then onto the next, then, at that point, work is finished.
- The idea of scalar electric potential gives a proportion of the work done in moving charged bodies in an electrostatic field.
Representation of Electric Fields
- An electric field (like any vector field) can be imagined utilizing motion lines (likewise called smooth out
or then again lines of power). - A motion line is drawn to such an extent that it is all over digression to the electric field.
- A quiver plot is a plot of the field lines built by making a lattice of focuses. A bolt whose tail is associated with the point shows the heading and greatness of the field by then.
Representation of Electric Potential
- The scalar electric potential can imagined use equipotential surfaces.
- An equipotential surface is a surface over which V is a consistent. Since the electric field is the negative of the
slope of the electric scalar potential, the electric field lines are wherever ordinary to the equipotential surfaces and point toward
diminishing potential.
Faraday’s Experiment
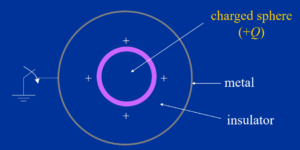
Faraday’s Experiment (Cont’d)
- Two concentric directing circles are isolated by a protecting material.
- The inward circle is charged to +Q. The external circle is at first uncharged.
- The external circle is grounded quickly.
- The charge on the external circle is found to be – Q.
- Faraday closed there was a “uprooting” from the charge on the inward circle through the internal circle through the
protector to the external circle. - The electric uprooting (or electric transition) is equivalent in size to the charge that produces it, autonomous of the protecting
material and the size of the circles.
Gauss’ Law
- Gauss’ law expresses that “the net electric transition radiating from a nearby surface S is
equivalent to the absolute charge contained inside the volume V limited by that surface.”
Application of Gauss’ Law
- Gauss’ regulation is a fundamental condition for the obscure electric transition thickness coming about
from a given charge dissemination.
Application of Gauss’ Law (Cont’d)
- By and large, answers for basic conditions should be gotten utilizing mathematical
methods. - Be that as it may, for specific symmetric charge dispersions shut structure answers for
Gauss’ regulation can be acquired. - Shut structure answer for Gauss’ regulation depends on our capacity to build an appropriate family
of Gaussian surfaces. - A Gaussian surface is a surface to which the electric motion thickness is typical and over
which equivalent to a consistent worth.
Fundamental Laws of Electrostatics
- The basic types of the central regulations are more broad since they apply over districts of space.
- The differential structures are just legitimate at a point.
- From the basic types of the basic regulations both the differential conditions administering the field inside a medium and the limit conditions at the connection point between two media can be inferred.

JEE Foundation Class for 10
JEE Foundation Class for 10 enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills through engaging activities and advanced learning techniques, ensuring academic excellence.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Are formulas significant for JEE?
The JEE Main significant recipes can help applicants in different ways: It helps in saving time for the test. Makes the computations simpler. Lessens the gamble of mix-ups.
How significant is electrostatics for JEE Advanced?
Electrostatics holds around 6% to 7% of weightage in the JEE Advanced paper and it is likewise vital in the last assessment too.