Table of Contents
Diversity in Living Organisms Class 9 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1. Which organisms are called primitive?
Answer: Primitive organisms are those which have ancient body design and have not changed very much with the passage of time.
Question 2. Name the branch of science that deals with classification.
Answer: Taxonomy
Question 3. What is biological classification?
Answer: The system of arrangement of different plants and animals in different groups on the basis of their similarities and differences is called biological classification.
Question 4. Who was the first to classify animals according to their habitats?
Answer: Aristotle was the first one to classify animals according to whether they lived on land, in water or in air.
Also Check: CBSE Syllabus for Class 1 to 12
Question 5. What is ‘binomial nomenclature’?
Answer: It is the system of naming in which the scientific name of an organism hasTwo components, i.e., genus and species.
Question 6. What is evolution?
Answer: The life forms that exist today have risen because of changes in their body design over a course of time to adapt themselves in the changing conditions. This is called evolution.
Question 7. Who gave the idea of evolution for the first time in the book ‘Origin of Species’?
Answer: Charles Darwin
Question 8. What is a genus?
Answer: A genus is a group of related species.
Question 9. Which groups of organisms do not have a defined nucleus or organelles?
Answer: Monera
Question 10. Name the largest animal on the planet.
Answer: Blue whale (30 metres)
Question 11. Name the largest tree on the Earth.
Answer: Redwood (100 metres)
Question 12. Which plant has life span of more than one thousand years?
Answer: Pine trees
Question 13. What are the three aspects of systematics?
Answer: Identification, nomenclature and classification.
Question 14. Name a coelenterate that occurs singly and is commonly found in freshwater ponds.
Answer: Hydra
Question 15. Name the group of sessile animals.
Answer: Porifera
Question 16. Name an organism that possesses flagella.
Answer: Euglena
Question 17. What are corals?
Answer: Corals are marine coelenterates that live in colonies firmly attached to rocks.
Question 18. Name two marine solitary coelenterates.
Answer: Jelly fish and sea anemone.
Question 19. Name the group of animals, which developed nervous system for the first time.
Answer: Coelenterates
Question 20. In which sub-division does xylem possess vessels?
Answer: Angiosperms
Question 21. Name the organism which has nervous system but no brain.
Answer: Hydra
Question 22. Which plants are perennial, evergreen and woody?
Answer: Gymnosperms
Question 23. Name the reproductive organs of gymnosperms.
Answer: Cone
Question 24. Name free living and parasitic flatworms.
Answer: Free living: Planaria; Parasitic: Tapeworm and liver fluke.
Question 25. What are hermaphrodites?
Answer: The animal that possess both male and female reproductive organ is called hermaphrodite, e.g., earthworm.
Question 26. Name the group of animals, which has primitive nervous system but with brain which is developed for the first time.
Answer: Platyhelminthes
Question 27. Name the first group of animals with true coelom.
Answer: Annelida
Question 28. Define metameric segmentation.
Answer: Metameric segmentation is a type of segmentation where external divisions correspond to internal divisions.
Question 29. Name the cavity present in the coelenterates.
Answer: Coelenteron
Question 30. What is haemocoel?
Answer: When a well-defined cavity is absent and the spaces present contain colourless blood, i.e., haemolymph, it is called haemocoel.
Question 31. Give the names of two groups of animals that are haemocoelomate.
Answer: Molluscs and arthropods
Question 32. What are the skeletal elements in sponges?
Answer: Needles called spicules and spongin fibres are the skeletal elements in sponges.
Question 33. What are the excretory organs in flatworm?
Answer: Protonephridia or flame cells.
Question 34. What are cnidoblasts?
Answer: The stinging cells present on the tentacles of coelenterates like Hydra, which inject hypnotoxin into the prey to hypnotise it.
Question 35. What is the name given to the body cavity of nematodes?
Answer: Pseudocoel
Question 36. Name a parasitic annelid.
Answer: Leech
Question 37. What is polymorphism? Give an example.
Answer: The presence of more than two types of individuals in a colony which differ in their structure as well as function is called polymorphism. E.g., honey bees.
Question 38. Name two phyla which have open circulation.
Answer: Mollusca and echinodermata
Question 39. Name two phyla which have radial symmetry.
Answer: Echinodermata and coelenterata
Question 40. Why do amphibians do not possess exoskeleton?
Answer: Amphibians do not possess exoskeleton as their skin is thin, moist and act as a respiratory organ.
Question 41. Why do birds possess hollow bones?
Answer: To make their body light in weight so as to make flying easier.
Question 42. In which phylum are pharyngeal gill slits present?
Answer: Phylum chordata
Question 43. What do you mean by ‘characteristics’?
Answer: Characteristics means a particular form or a particular function of any organism. For example, the presence of five fingers on each hand of a human being is a characteristic.
Diversity in Living Organisms Class 9 Extra Questions Short Answer Questions-I
Question 1. Why was the method of classification of animals proposed by Aristotle not accepted?
Answer: Aristotle classified animals on the basis of their habitat, i.e., whether they live on land or in water. But these animals, otherwise are very different from each other in many respects and such a classification does not prove much helpful. So, the method of classification by Aristotle was not accepted.
Question 2. Describe the hierarchical system of classification currently followed.
Answer: Hierarchy of classification categories was established and designed by Linnaeus. Hierarchy of classification is a system of arrangement of a framework in order of logical sequence. The currently followed hierarchical system for all organisms is
- Kingdom
- Phylum/Division
- Class
- Order
- Family
- Genus
- Species.
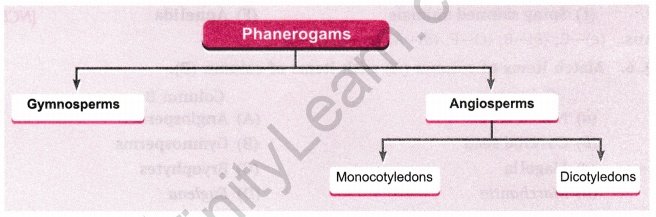
Question 3. What are phanerogams?
Answer: Phanerogams or spermatophyta are the most advanced type of plants bearing seeds. They have roots, stems, leaves and flowers. They include gymnosperms and angiosperms.
Question 4. What are mycoplasma?
Answer: Mycoplasmas are the smallest and the simplest organisms. They are prokaryotes having nucleoid. They have heterotrophic mode of nutrition and their body can change forms easily. They are also called as MLO, i.e., Mycoplasma Like Organisms.
Question 5. List in tabular form, two distinguishing features of dicot plants with monocot plants.
Answer:
| Monocots | Dicots |
| 1. Possess one cotyledon.
2. Fibrous roots. 3. Parallel venation. |
1. Possess two cotyledons.
2. Taproots. 3. Reticulate venation. |
Question 6. What are lichens?
Answer: Lichens are compound plants as algae and fungi live together in close association, as a result of which both are benefited. This relationship is called symbiosis. They occur as greyish green growths on rocks, bark of the tree or on the ground.
Question 7. On which basis is the plant kingdom classified?
Answer: The plants have been classified on the following basis:
- Phylogeny and evolution.
- Presence or absence of vascular tissue for transport of food and water.
- Presence or absence of seeds.
- Presence or absence of fruits.
Question 8. Why are bryophytes called the amphibians of the plant kingdom?
Answer: The plant bodies of bryophytes are devoid of vascular tissues and roots. So they live in moist habitats in order to obtain water directly or through rhizoids. Moreover, like the amphibians of animal kingdom, the sperms of bryophytes require an external water medium for reaching the eggs. Due to this reason, bryophytes are called the amphibians of the plant kingdom.
Question 9. What are amphibians?
Answer: Amphibians are the vertebrates that can live both on land and in water. That is why they are also called the vertebrates leading two lives. Their body varies in form and the skin is not covered with scales. They lay eggs in water and their larval forms always live in water. Also, amphibians are cold blooded animals having a three-chambered heart. They breathe through lungs or gills or skin.
Question 10. What are reptiles?
Answer: Reptiles are the crawling vertebrates that are cold-blooded and have dry horn scales. They are mostly terrestrial and live in warmer regions. They breathe through lungs. The heart is three-chambered, except for crocodiles which have four-chambered heart. Reptiles lay eggs with thick coverings.
Examples: Snakes, lizards, crocodiles, turtles, etc.
Question 11. What is notochord? What is its function?
Answer: Notochord is a long rod-like support structure that runs along the back of the animals, separating the nervous tissue from the gut. It acts as a supporting structure by providing a place for muscles to attach for the ease of movement.
Question 12. Why do we keep both snake and turtle in the same class? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer: Both snake and turtle are kept in the same class because both are
- cold-blooded,
- have scales,
- breathe through lungs
- have three-chambered hearts, and
- lay eggs with thick covering.
Question 13. Give reasons why mosses are found in humid and moist areas.
Answer: The entire body of moss in damp humid places can absorb water. Moreover, sperms in mosses are flagellated and so they can reach the archegonia only in presence of water. Thus, water is indispensable in the life cycle of mosses for reproduction as well as for performing other physiological functions.
Question 14. What is binomial nomenclature?
Answer: In binomial nomenclature, name of every organism is composed of two components—the first one is generic (genus) and the second one is specific (species). Also, the generic name starts with a capital letter whereas the specific name starts with small letter. For example, the scientific name of man is “Homo sapiens”. Here “Homo” is the generic and “sapiens” is the specific name.
Question 15. Which organism is more complex and evolved among bacteria, mushroom and mango tree? Give reasons. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer: Mango tree is more complex and evolved because, it is eukaryotic, autotrophic, terrestrial and a sporophyte with covered seed. The bacteria is a unicellular prokaryote and fungi is heterotrophic, simple thallophyte with no tissue system.
Question 16. Endoskeleton of fishes are made up of cartilage and bone. Classify the following fishes as cartilagenous or bony:
Torpedo, Sting ray, Dog fish, Rohu, Angler fish, Exocoetus [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer: Torpedo — Cartilagenous,
Dog fish — Cartilagenous
Angler fish — Cartilagenous
Sting ray — Cartilagenous
Rohu — Bony
Exocoetus — Bony
Diversity in Living Organisms Class 9 Extra Questions Short Answer Questions-II
Question 1. What is a species? Give its main features.
Answer: Species is defined as a dynamic group of organisms, which resemble each other in all essential aspects, i.e., structure and function, and interbreed to produce fertile young ones of their own kind. The members of a species are reproductively isolated from other groups. They have descended from a common ancestor and have similar genetic material.
Question 2. State reasons for each of the following:
- Echidna and platypus lay eggs but are considered as mammals.
- Forelimbs of birds are modified.
- Crocodiles have four-chambered heart but are still reptiles.
Answer:
- They have mammary glands for the production of milk to nourish their young ones.
- To reduce body weight for flight, forelimbs of birds are modified.
- Crocodiles are cold blooded, lay eggs and have scale on their body. These characteristics make them reptile.
Question 3. Differentiate between species and taxon.
Answer: Species and taxon differ in the following ways:
- Species represents the basic taxonomic category while the taxon represents any level of taxonomic category.
- Species is always monophyletic while a taxon may be monophyletic or polyphyletic.
- Species, being a rank, is an abstract term while a taxon represents a group of various living beings.
Question 4. Give the general characters of kingdom Animalia.
Answer:
- In kingdom Animalia, all the members are multicellular eukaryotes with tissue differentiation.
- They are heterotrophic with ingestive mode of intake of food.
- They possess a well developed nervous system.
- Muscular system is also well developed for locomotion.
- They exhibit sexual reproduction.
Sponge, molluscs, fishes, birds, reptiles and mammals all belong to kingdom Animalia.
Question 5. Enlist the main features of organisms placed under Protista.
Answer:
- Most of the members are unicellular and primarily aquatic.
- They have nucleus and typical eukaryotic cell organelles.
- Most of the organisms bear flagella or cilia for movements.
- Mode of nutrition is absorptive, ingestive or photo-autotrophic.
- Reproduction may be asexual or sexual.
Question 6. Give the main features of kingdom Fungi.
Answer:
- They are non-green because of the absence of chlorophyll.
- They are heterotrophic and obtain food from dead and decaying organic matter by absorption.
- The body organisation is mycelial or secondarily unicellular.
- Cell wall is chitinous and cellulosic.
- Asexual reproduction is by spore formation. Some also exhibit sexual reproduction.
Question 7. Write the main characteristics of kingdom Plantae.
Answer:
- They are all complex multicellular plants which prepare their own food by photosynthesis.
- They possess cell wall made of cellulose.
- Plants are immobile and do not show locomotion.
- They have unlimited growth and grow throughout their lives.
Question 8. Write similarities between plants and animals.
Answer:
- Plants and animals are both made up of cells.
- Both contain protoplasm and the genetic material, DNA.
- Both plants and animals show growth.
- Both show response to external stimuli.
- Both plants and animals reproduce and pass on their characters to the offspring by the same mechanism.
Question 9. Give the main features of algae.
Answer:
- They are autotrophic as they possess chlorophyll.
- They are mainly aquatic but some also grow in moist places.
- The body is not divided into root, stem and leaves.
Question 10. Give the important features of division Bryophyta.
Answer:
- Bryophytes are called the amphibians of the plant kingdom.
- The plant body is commonly differentiated to form stem and leaf-like structures. But there is no specific tissue for conduction of water and other substances.
- Vegetative reproduction is very common.
- Sexual reproduction is of oogamous type, i.e., the male gamete is small and motile and female gamete is non-motile and large, e.g., moss, Funaria and Marchantia.
Question 11. Give the main features of Pteridophyta.
Answer: Following are the main features of Pteridophyta:
- The plant body is divided into root, stem and leaves.
- The fertilised eggs form embryo.
- They are also called vascular cryptogams as they have a developed vascular system.
- They have multicellular reproductive system.
Question 12. Give the important features of class Mammalia.
Answer: The important features of class Mammalia are:
- They are warm-blooded animals.
- Their heart is four-chambered.
- They have mammary glands which produce milk with which they nourish their young ones.
- They give birth to young ones, with the exception of platypus and echidna. Kangaroos give birth to very poorly developed young ones.
Question 13. Blue green algae have been included under the group Monera and not under Plantae. Why?
Answer: Monera is a kingdom of prokaryotes while organisms of kingdom Plantae are eukaryotes with definite nucleus, membrane-bound organelles and multicellular body design. Blue-green algae are prokaryotes having nucleoid with naked DNA. The cell organelles are also not enclosed in membrane. As they also do not possess multicellular body design, these characters bring them closer to Monera and exclude them from the kingdom Plantae.
Question 14. What is the difference between bilateral and radial symmetry?
Answer: An animal is said to have bilateral symmetry if it has two equal but opposite right and left halves when cut lengthwise in the middle vertical plane, e.g., frog. On the other hand, an animal is said to have radial symmetry, if it is symmetrical with respect to any plane passing through its longitudinal axis. In other words, any plane passing longitudinally through any diameter divides the body into equal halves, e.g., Hydra.
Question 15. How is notochord different from nerve cord?
Answer: Notochord is the skeletal rod which lies lengthwise between the central nervous system and the alimentary canal or the gut and the chordates possess it at young stage of development. In adult vertebrates, it is replaced by vertebral column. On the other hand, a nerve cord is a solid strand of nervous tissue, forming part of central nervous system, especially of invertebrates. The main difference between the two is that notochord is a part of skeleton system whereas nerve cord is a part of nervous system.
Question 16. Write names of few thallophytes. Draw a labelled diagram of Spirogyra. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer: Ulothrix, Spirogyra, Cladophora, Ulva and Chara are few thallophytes.
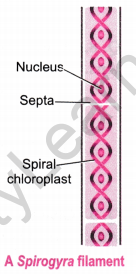
Question 17. Define the terms and give one example of each.
(i) Coelom
(ii) Triploblastic [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
(i) Coelom is the internal body cavity between visceral organs and body wall in which well ‘ developed organs can be accommodated, e.g., in butterfly.
(ii) Animals having three layers of cells from which differentiated tissue can be made are called triploblastic, e.g., star fish.
Question 18. You are given leech, Nereis, Scolopendra, prawn and scorpion and all have segmented body organisations. Will you classify them in one group? If no, give the important characters based on which you will separate these organisms into different groups. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer: All organisms given in the question do not belong to same group. Leech and Nereis belong to phylum annelida because they have metamerically segmented body, i.e., body is divided into many segments internally by septa. Body segments are lined up one after the other from head to tail. But Scolopendra, prawn and scorpion belong to phylum arthropoda as these have jointed legs and open circulatory system.
Question 19. Classify the following organisms based on the absence/presence of true coelom (i.e., acoelomate, pseudocoelomate and coelomate):
Spongilla, Sea anemone, Planaria, Liver fluke, Wuchereria,Ascaris, Nereis, Earthworm, Scorpion,Birds, Fishes, Horse.
Answer:
Spongilla — Acoelomate
Planaria — Acoelomate
Wuchereria — Pseudocoelomate
Nereis — Coelomate
Earthworm — Coelomate
Sea anemone — Acoelomate
Liver fluke — Acoelomate
Ascaris — Pseudocoelomate
Scorpion — Coelomate
Birds, Fishes and Horse — Coelomate
Question 20. Fill in the boxes given in figure with appropriate characteristics/plant group(s). [NCERT Exemplar].
Answer:
(a) Thallophyta
(b) Without specialised vascular tissue
(c) Pteridophyta
(d) Phanerogams
(e) Bear naked seeds
(f) Angiosperms
(g) Have seeds with two cotyledons
(h) Monocots
Question 21. Label a,b,c and d given in figure. Give the function of part (b).
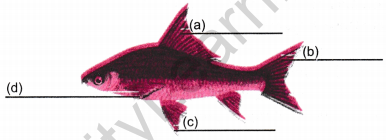
Answer:
(a) Dorsal fin
(b) Caudal fin
(c) Pelvic fin
(d) Pectoral fin
Function of caudal fin: Caudal fin helps in streamlined movement in water.
Question 22. List out some common features in cat, rat and bat.
Answer: Bat, rat and cat belong to the class mammalia and all have following common features:
- have notochord at some stage of life cycle.
- are warm-blooded.
- have four-chambered heart.
- have skin covered with hair and sweat and oil glands.
Diversity in Living Organisms Class 9 Extra Questions Long Answer Questions
Question 1. Describe the three main characteristics that are used for a hierarchical classification.
Answer: The three main characteristics used for a hierarchical classification are:
(i) Complexity of cell structure, i.e., type of cell—prokaryotic or eukaryotic. As a eukaryotic cell has membrane-bound organelles including a nucleus, the cellular processes can be carried out efficiently in isolation from other cells. On the other hand, the organisms without a clearly demarcated nucleus and other organelles need to have very different biochemical pathways. This would naturally have a great effect on every aspect of cell design. Moreover, the nucleated cells would have the capacity to participate in making a multicellular organism as they are capable of taking up specialised functions.
(ii) Body organisation, i.e., whether the organism is unicellular or multicellular. In a eukaryotic multicellular organism, cells that group together to form a single organism use the principle of division of labour. In this type of body design, all cells would not be identical. Rather, groups of cells will carry out specialised functions. Thus, this makes a very basic distinction in the body designs of organisms. As a result, an amoeba will be very different in its body design from a fish.
(iii) Mode of nutrition: autotrophic or heterotrophic. Plants make their own food while animals depend on plants or other animals for their food. For this they will definitely have different body design.
Question 2. Give the main features of the phylum Porifera.
Answer:
- They are primitive animals.
- They are generally multicellular organisms with specialised cells but these cells do not group together to form tissues.
- Most of them are marine, i.e., found in the seas. Some of them are also found in ponds and rivers.
- They possess pores all over the body.
- Reproduction can be by both sexual and asexual methods.
- Sensory system is absent.
- Mouth and anus are absent.
- A distinct canal system with inlets and outlets for water circulation inside the body is present. They obtain food and oxygen by means of water. The collar cells filter out food particles from the water current flowing through the canal system.
Examples are: Sycon, Spongilla and Euplectella.
Question 3. Give the main features of coelenterates.
Answer:
- Diploblastic animals with tissue level organisation in the body.
- The body is radially symmetrical.
- The body bears tentacles supplied with special stinging cells called cnidoblasts.
- There is a cavity in the body.
- Body is made of two layers of cells.
- Simple gonads without gonoducts are present.
- Reproduction is usually asexual (budding) in polyp form and sexual in medusae form.
- They show polymorphism.
Examples: Hydra, Obelia and jelly fish.
Question 4.(i) List three characteristics which help us to distinguish amphibians from pisces.
(ii) Classify the following living organisms as cold-blooded and warm- blooded animals:
Shark, Lizard, Sparrow, Rohu.
Answer:
(i) Following characteristics distinguish amphibians from pisces:
- Amphibians lack scales whereas skin of pisces are covered with scales.
- Amphibians have mucous glands.
- Amphibians have a three-chambered heart unlike pisces, their hearts have only two chambers.
(ii) Cold-blooded: Shark, Rohu, Lizard
Warm-blooded: Sparrow
Question 5. Describe the features of phylum Platyhelminthes.
Answer:
- They show bilateral body symmetry.
- Their body is dorsoventrally flattened like a ribbon. So they are also called flatworms.
- Most of them are parasitic, only a few are free living.
- They are mostly hermaphrodites.
- There are three embryonic layers of cells in their body. So, they are triploblastic.
- The body does not have any pore or cavity.
- They have power of regeneration.
Examples: Fasciola (Liver fluke), and Taenia solium.
Question 6. Write the important features of phylum Aschelminthes (Nematoda).
Answer:
- Most of them are small and cylindrical. So they are also called as round worms.
- The body size ranges from microscopic to a few centimetres in length.
- They all are mainly heterotrophic animals.
- They are triploblastic.
- Body cavity has a true coelom.
- Respiratory and circulatory systems are absent.
- They have a complete alimentary canal.
- Sexes are separate.
Examples: Ascaris (roundworm), Enterobius, and Wuchereria (filarial worm).
Question 7. Enlist the main features of phylum Annelida. Give examples.
Answer:
- Body of annelids are bilaterally symmetrical.
- They are triploblastic.
- Metameric segmentation is present.
- Closed circulatory system with respiratory pigment dissolved in the plasma.
- Nephridia for excretion and osmoregulation are present.
- These animals are found in a variety of habitats like fresh water, marine water as well as on land.
Examples are: Nereis (sand worm or clam worm), Aphrodite (sea mouse), Pheretima (earthworm).
Question 8. Give the important distinguishing features of Arthropoda.
Answer:
- These animals are bilaterally symmetrical and segmented.
- Body is covered with chitinous exoskeleton.
- One or two pairs of jointed legs are present.
- The body cavity is blood-filled and is called haemocoel.
- Body bears jointed appendages, and is divided into head, thorax and abdomen.
- Circulatory system is open, i.e., blood doesn’t flow in blood vessels.
Examples: Palaemon, cockroach and butterfly.
Question 9. Give the main distinguishing features of phylum Mollusca.
Answer: Following are the main distinguishing features of phylum Mollusca:
- The animal shows bilateral symmetry.
- They have soft bodies, so they are also called soft bodied animals.
- Body is segmented and divided into head, foot and visceral mass.
- A glandular fold, the mantle, is present over the body.
- There is a calcareous shell around the body in some molluscs.
- They have open circulatory system.
- Kidney-like organs for excretion are present.
Examples: Pila, Sepia, octopus.
Question 10. What are vertebrates? What are their main features?
Answer: Vertebrates are the animals included in the phylum chordata in which the spinal chord is made of small vertebrae.
There are five classes of vertebrates:
- Pisces
- Amphibians
- Reptiles
- Aves and
- Mammalia.
The main features of vertebrates are given as under:
- They possess a solid notochord.
- The body has bilateral symmetry.
- They have a true vertebral column.
- They have a dorsal hollow nerve cord.
- They are triploblastic.
- The terrestrial forms respire through lungs and the aquatic forms through gills.
- They are coelomate.
Question 11. Give the point of differences between non-chordates and chordates.
Answer:
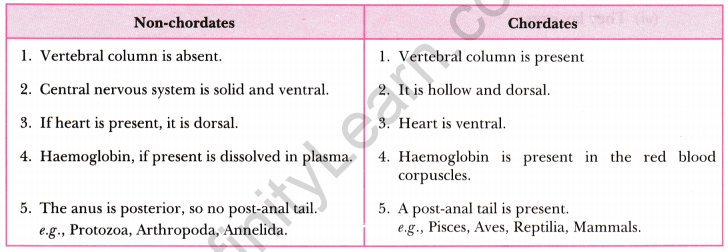
Question 12. What are the characteristics of kingdom Monera?
Answer: Following are the characteristics of kingdom Monera:
- The organisms do not possess a clearly defined nucleus, i.e., the nucleus is not enclosed by a nuclear membrane.
- Cell organelles are also not covered with a membrane.
- Organisms are unicellular, microscopic prokaryotes living in moist conditions.
- Cell wall may or may not be present.
- The mode of nutrition may be autotrophic or heterotrophic.
- Reproduction is primarily asexual by binary fission or budding.
Question 13. Thallophyta, Bryophyta and Pteridophyta are called as ‘Cryptogams’. Gymnosperms and Angiosperms are called as ‘Phanerogams’. Discuss why. Draw one example of a gymnosperm. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer: The thallophyta, bryophyta and pteridophyta are called as ‘cryptogams’ because the reproductive organs of these groups are inconspicuous or hidden. Seeds are absent. On the other hand ‘Phanerogams’ include gymnosperms and angiosperms which have well differentiated reproductive tissue and the embryo with stored food. Their embryo develops into seed.

Question 14. Give the salient features of class Pisces.
Answer: The main features of Pisces are:
- They are exclusively water living animals and include the fishes.
- Their skin is covered with scales/plates.
- They obtain oxygen dissolved in water by using gills.
- Their body is streamlined, and a muscular tail is used for movement.
- They are cold-blooded and their hearts have only two chambers.
- They lay eggs.
- Some fish varieties have their skeletons made of both bone and cartilage, such as Anabas, Sea horse, Rohu, and some have their skeletons made entirely of bone, e.g., Torpedo fish and Sting ray (Trygon).
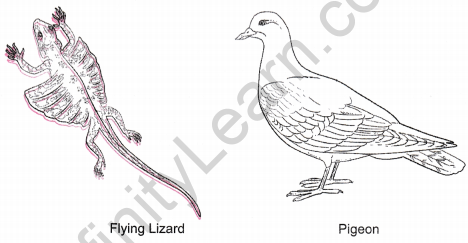
Question 15. Differentiate between flying lizard and bird. Draw the diagram. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer: Flying lizard belongs to the group ‘reptiles’ and is characterised as cold blooded, body covered with scales and have three chambered heart. Whereas the birds belong to the group ‘aves’ and have characteristics of being warm blooded, having feather covered body, forelimbs modified as wings and four chambered heart.
Question 16. Distinguish between the five classes of vertebrates on the basis of characters like habitat, kind of exoskeleton, respiratory organs and other distinct features.
Answer: Differences between Pisces, Amphibia, Reptilia, Aves and Mammals are as follows:
Question 17. How are the phanerogams classified?
Answer: Phanerogams are classified depending on the presence or absence of fruits. They are of two types:
- Gymnosperm possesses naked seeds, i.e., not enclosed by fruits.
- Angiosperms, in which the seeds are enclosed within the fruit.
Angiosperms are further divided into two types:
- Monocotyledons, which have a single cotyledon in their seeds, e.g., wheat, rice, etc.
- Dicotyledons, which have two cotyledons in their seeds, e.g., gram, pea, etc.
Diversity in Living Organisms Class 9 Extra Questions HOTS (Higher Order Thinking Skills)
Question 1. Meena and Hari observed an animal in their garden. Hari called it an insect while Meena said it was an earthworm. Choose the character from the following which confirms that it is an insect.
(a) Bilateral symmetrical body
(b) Body with jointed legs
(c) Cylindrical body
(d) Body with little segmentation [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer: (b)
Question 2. You are provided with the seeds of gram, wheat, rice, pumpkin, maize and pea. Classify them whether they are monocot or dicot.
Answer: Monocots — wheat, rice, maize
Dicots — gram, pumpkin, pea
Question 3. Classify the following based on number of chambers in their heart: Rohu, Scoliodon, Frog, Salamander, Flying lizard, King Cobra, Crocodile, Ostrich, Pigeon, Bat, Whale. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Rohu, Scoliodon — 2-chambered.
Frog, Salamander, Flying lizard, King Cobra — 3-chambered.
Crocodile, Ostrich, Pigeon, Bat, Whale — 4-chambered.
Question 4. Classify Rohu, Scoliodon, Flying lizard, King Cobra, Frog, Salamander, Ostrich, Pigeon, Bat, Crocodile and Whale into cold-blooded or warm-blooded animals. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer: Cold-blooded — Rohu, Scoliodon, Frog, Salamander, Flying Lizard, King Cobra, Crocodile. Warm-blooded — Ostrich, Pigeon, Bat, Whale.
Question 5. Match items of column (A) with items of column (B). [NCERT Exemplar]

Answer: (a)—C; (b)—B; (c)—F; (d)— A; (e)—E; (f)—D
Question 6. Match items of column (A) with items of column (B). [NCERT Exemplar]

Answer: (a)—B; (b)—A; (c)—D; (d)—C; (e)—F; (f)—E; (g)—G


