Table of Contents
Phytohormones are trace chemical compounds in plants that control development, growth, longevity, and reproduction. This article explores the structure and functions of key phytohormones such as auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, ethylene, and abscisic acid.
Plant Hormones Definition
Plant hormones, also known as phytohormones, are chemical compound produced in small amounts that regulate various physiological processes in plants. They control growth, development, and responses to environmental stimuli by influencing processes such as cell division, elongation, differentiation, and stress responses.
What are the main types and functions of plant hormones?
Plant hormones regulate essential growth and development processes, including cell division, enlargement, flowering, seed formation, dormancy, and abscission.
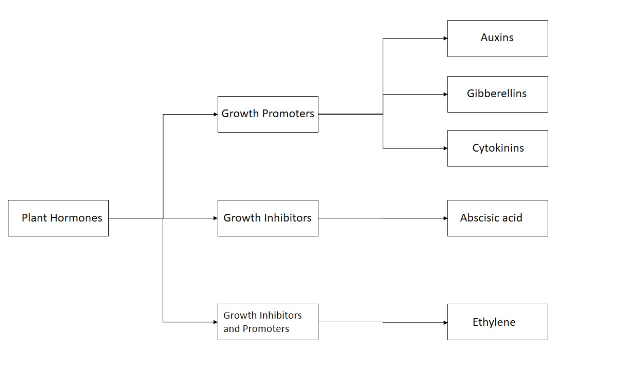
They are classified into two categories based on their function:
- Plant Growth Promoters
- Plant Growth Inhibitors
Also Check: 30+ MCQs on Plant Hormones Class 10
Auxin Hormone
Auxins, derived from the Greek word meaning “to grow,” are crucial in agriculture and horticulture for promoting plant growth. They are primarily located in the growing tips of roots and stems, from where they travel to other parts of the plant to exert their effects.
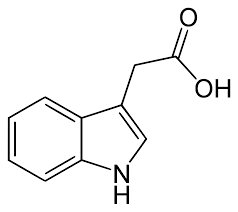
Natural Auxins:
- Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA)
- Indole butyric acid (IBA)
Synthetic Auxins:
- 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D)
- Naphthalene acetic acid (NAA)
Functions
- Cell Elongation: Promotes elongation of stems and roots.
- Apical Dominance: IAA in the apical bud inhibits lateral bud growth.
- Parthenocarpy Induction: Facilitates fruit development without fertilization, such as in tomatoes.
- Prevents Premature Drop: Reduces early shedding of leaves, flowers, and fruits.
- Stem Cuttings and Grafting: Aids in rooting initiation during these processes.
- Flowering Promotion: Encourages flowering in plants like pineapples.
- Herbicide Use: 2,4-D effectively kills dicot weeds without harming monocots.
- Cell Division and Xylem Differentiation: Supports cell division and the formation of xylem
Also Read: Difference Between Auxin And Gibberellin
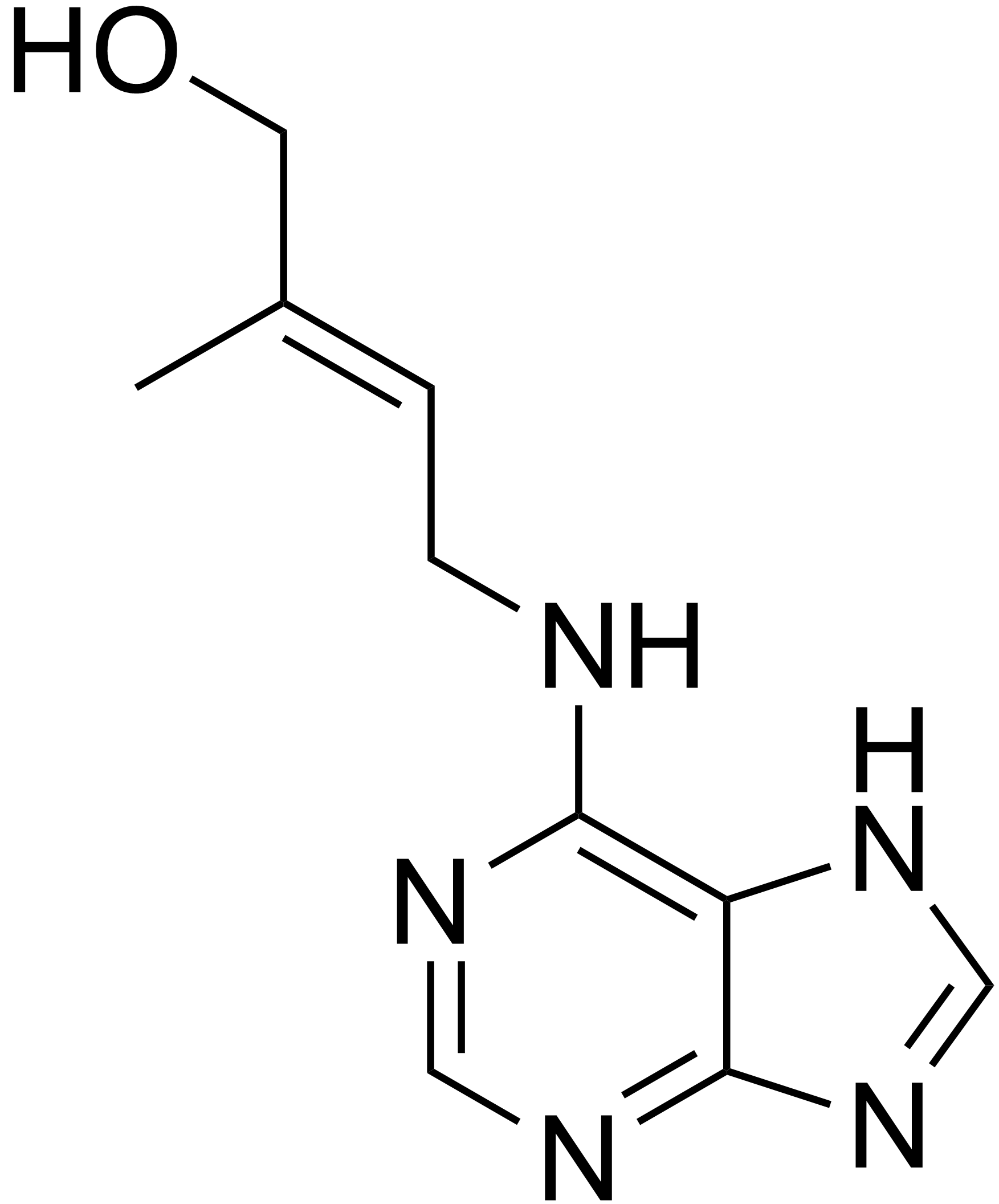
Cytokinins Hormone
Cytokinins are crucial for the cytokinesis process, primarily synthesized in plant regions with rapid cell division like root tips, shoot buds, and young fruits. They move basipetally and polar. Natural cytokinins include zeatin (from corn kernels and coconut milk) and isopentenyladenine, while synthetic ones are kinetin, benzyladenine, diphenylurea, and thidiazuron.
Functions
- It encourages lateral and adventitious shoot growth, aiding in initiating shoot development in culture.
- It helps overcome apical dominance caused by auxins.
- Stimulates chloroplast formation in leaves.
- It promotes nutrient mobilization and delays leaf senescence.
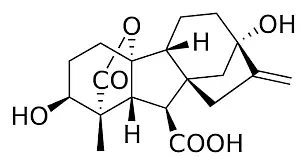
Gibberellins Hormone
There are more than 100 gibberellins (e.g., GA1, GA2, GA3, etc.) are known, characterized by their acidic nature. They are found in higher plants and fungi.
Functions
- Promotes bolting: Encourages rapid internode elongation in rosette plants, such as cabbage and beet, just before flowering.
- Delays senescence: Slows down the aging process in plants.
- Induces parthenocarpy: Stimulates fruit development without fertilization.
- Elongates the stem: Reverses dwarfism by increasing stem length.
- Induces maleness: Promotes male characteristics in certain plants, like cannabis.
- Stimulates enzyme formation: Enhances the production of hydrolytic enzymes like lipase and amylase in germinating cereal grains and barley seeds.
- Breaks seed dormancy: Facilitates the germination of seeds by overcoming dormancy.
Abscisic Acid Function
It is a growth-inhibiting hormone that acts as an antagonist to GAs, inhibiting plant metabolism and regulating abscission and dormancy. Often called the “stress hormone,” it enhances plant tolerance.
Functions
- Promotes leaf and fruit abscission
- Suppresses seed germination
- Triggers leaf senescence
- Enhances seed dormancy for storage
- Stimulates stomatal closure to reduce transpiration during water stress
Ethylene Plant Hormone
It functions both as a growth promoter and inhibitor. Present in gaseous form, it is produced in ripening fruits and aging tissues. This hormone regulates various physiological processes and is extensively used in agriculture.
Functions
- Accelerates fruit ripening.
- Regulates leaf epinasty.
- Overcomes seed and bud dormancy.
- Promotes rapid petiole and internode elongation.
- Encourages leaf and flower senescence and abscission.
- Enhances root growth and root hair development, increasing absorption.
- Induces female characteristics in monoecious plants.
- Facilitates apical hook formation in dicot seedlings.
FAQs on Plant Hormones
What are the 5 plant hormones?
Auxins, Gibberellins, Cytokinins, Abscisic Acid (ABA), Ethylene.
What are the 7 plant hormones?
Auxins, Gibberellins, Cytokinins, Abscisic Acid (ABA), Ethylene, Brassinosteroids, Jasmonic Acid.
What are the plant hormones class 10?
Auxins, Gibberellins, Cytokinins, Abscisic Acid (ABA), Ethylene.
Which of the following is a plant hormone?
It include Auxins, Gibberellins, Cytokinins, Abscisic Acid, and Ethylene.
Which hormone promotes cell division in plants?
Cytokinins promote cell division in plants.
Which plant hormone promotes cell division?
Cytokinins promote cell division.
Give an example of a plant hormone that promotes growth.
Auxins and Gibberellins are examples of plant hormones that promote growth.