Table of Contents
CBSE Class 6 Geography Chapter 3 Extra Questions and Answers
Enhance your understanding of Earth’s movements Motions of the Earth class 6 Social Science Geography chapter 3, aligned with CBSE syllabus from the Class 6 NCERT textbook of Geography. These important questions for CBSE Class 6 Social Science chapter 3, tailored to the CBSE syllabus for class 6, encourage students to get deeper into the subject beyond the NCERT textbook. By engaging with these extra questions, students can strengthen their grasp of the chapter’s concepts, preparing them thoroughly for exams and expanding their knowledge of Earth’s motion. This resource is particularly beneficial for students seeking to reinforce their understanding through comprehensive notes and stimulating questions.
NCERT Extra Questions for Class 6 Social Science Geography Chapter 3 Motions of the Earth
Here are long and short answer type NCERT class 6 Geography chapter 3 extra questions and answers:
Motions of the Earth Class 6 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1. Define rotation and revolution of the Earth.
Answer:
Rotation:
Rotation refers to the Earth’s movement on its axis, completing one rotation approximately every 24 hours. This movement is also known as the daily rotation of the Earth.
Revolution:
Revolution is the Earth’s movement around the Sun along a fixed path or orbit.
Question 2.What are axis and orbit?
Answer:
Axis:
The axis of the Earth is an imaginary line that connects the North and South poles, tilted at an angle of about 66.5° to its orbital plane.
Orbit:
An orbit is the elliptical path followed by celestial bodies as they move around the Sun or another planet.
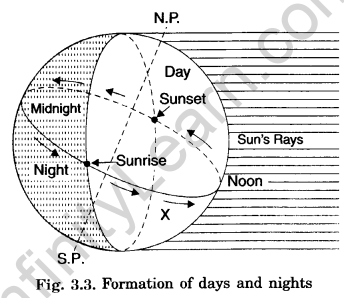
Question 3. What is the circle of illumination? Why does it not coincide with the axis of the Earth?
Answer:
- The circle of illumination is the boundary separating day from night on Earth’s surface.
- This circle does not align with the Earth’s axis due to the planet’s axial tilt of approximately 23.5° towards the east.
- It takes the Earth about 24 hours to complete one full rotation around its axis, resulting in the cycle of day and night.
Motions of the Earth Class 6 Extra Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1. Explain the difference between rotation and revolution.
Answer:
The distinction between rotation and revolution is as under:
|
Rotation |
Revolution |
| 1. Rotation refers to the Earth’s spinning on its axis. | 1. Revolution is the annual motion of the Earth around the Sun. |
| 2. The Earth completes one rotation in about 24 hours. | 2. The time taken for one revolution is 365 days and 6 hours. |
| 3. Rotation causes the succession of day and night worldwide. | 3. Revolution leads to changes in seasons on Earth. |
Question 2. How do days and nights occur?
Answer: Days and nights occur due to the Earth’s rotation on its axis. As the Earth spins, different parts receive sunlight, creating daytime in the illuminated areas and nighttime in the shadowed regions. This phenomenon is responsible for the regular cycle of day and night on Earth.
- Chapter 1 The Earth in the Solar system
- Chapter 2 Globe: Latitudes and Longitudes
- Chapter 3 Motions of the earth
- Chapter 4 Maps
- Chapter 5 Major Domains of the Earth
- Chapter 6 Major Landforms of the Earth
- Chapter 7 Our Country – India
- Chapter 8 India: Climate, Wildlife, and Vegetation
Motions of the Earth Class 6 Extra Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1: Explain the following: Revolution of the Earth. Leap year.
Answer:
- Revolution of the Earth:
- The Earth’s movement around the Sun on its orbit is known as revolution.
- It takes the Earth approximately 365.25 days (one year) to complete one revolution around the Sun.
- To simplify the calendar, we consider a year to have 365 days and add an extra day (leap day) every four years to account for the remaining 0.25 days.
- Leap Year:
- Every four years, we add a leap day (February 29th) to the calendar.
- This adjustment helps keep our calendar year aligned with the astronomical year.
- A year with 366 days, including the leap day, is called a leap year.
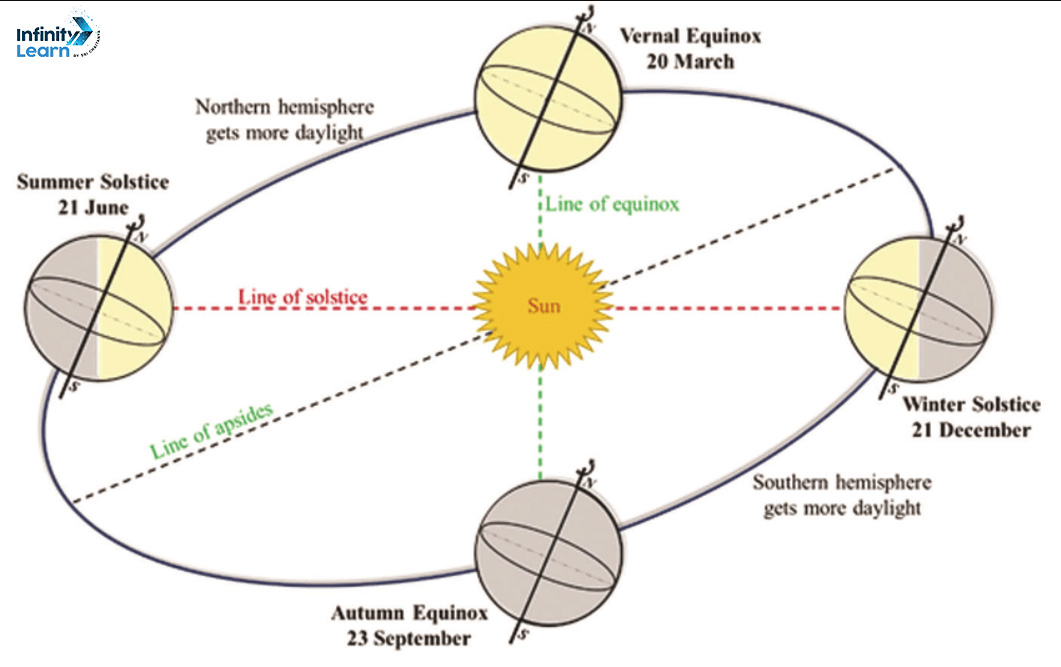
Question 2: How are seasons caused?
Answer:
- The Earth follows an elliptical path around the Sun.
- Its axis is tilted at an angle of 23.5° in the same direction (east) along its orbit.
- This tilt and the Earth’s orbit cause the seasons to change.
- The year is divided into four seasons: Spring, Summer, Autumn, and Winter.
- The changing of seasons is a result of the Earth’s position relative to the Sun.
On 21st June, the Northern hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun.
- On that day, the Sun shines directly on the Tropic of Cancer (23½° N), resulting in these areas receiving more heat.
- The areas near the poles receive less heat because the rays of the Sun are slanting there.
- The North hemisphere is inclined towards the Sun, and places beyond the Arctic Circle experience continuous daylight.
- As a large portion of the Northern hemisphere receives light from the Sun, it is Summer in the Northern hemisphere.
- The duration of the day is longer, and that of the night is shorter here.
- At this time, in the Southern hemisphere, all these conditions are opposite.
- It is winter season there.
- Nights are longer than days.
- This position of the Earth is called the summer solstice.
On 22nd December, the Tropic of Capricorn receives the direct rays of the Sun, and the Southern hemisphere tilts towards it.
- On this day, the Sun shines vertically on the Tropic of Capricorn (23½° S).
- Hence, a larger portion of the Southern Hemisphere receives light.
It is summer in the Southern hemisphere with longer days and shorter nights. - The opposite conditions are prevalent in the Northern hemisphere.
This position of the Earth is called the winter solstice.
On 21 March and 23 September, The Sun shines vertically on the equator.
- In this position, neither of the hemispheres is tilted towards the Sun, so the whole of the Earth experiences equal days and equal nights.
- It is neither very cold nor very hot all over the world.
The Northern hemisphere experiences spring on 21st March and autumn on 23rd September. - Exactly the opposite happens in the Southern hemisphere. Here, it is spring on September 23rd and autumn on March 21st.
- These positions are called Spring and Autumn Equinoxes respectively.
Motions of the Earth Class 6 Extra Questions Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the Correct Answer:
Question: Motion of the earth on its axis in about 24 hours is called
- (a) revolution
- (b) rotation
- (c) both (a) and (b)
- (d) none of these
Answer: rotation
Question: Motion of the earth around the sun is known as
- (a) revolution
- (b) rotation
- (c) both (a) and (b)
- (d) none of these
Answer: revolution
Question: What is the orbital plane?
- (a) Plane formed by the axis
- (b) Plane formed by the orbit
- (c) Both (a) and (b)
- (d) None of these
Answer: Plane formed by the orbit
Question: Which one of the following is the source of light on the earth?
- (a) The moon
- (b) The sun
- (c) The satellite
- (d) The space
Answer: The sun
Question: The circle that divides the globe into day and night is called
- (a) circle of darkness
- (b) circle of day and night
- (c) circle of illumination
- (d) none of these
Answer: circle of illumination
Question: The period of one rotation of the earth is known as
- (a) the sun day
- (b) the moon day
- (c) the earth day
- (d) none of these
Answer: the earth day
Question: What would have happened if the earth did not rotate?
- (a) Cold conditions on earth’s half portion
- (b) Warm conditions on earth’s another half portion
- (c) No life possible in such extreme conditions
- (d) All of these
Answer: All of these
Question: A year with 366 days is called
- (a) leap year
- (b) normal year
- (c) both (a) and (b)
- (d) none of these
Answer: leap year
Question: Why do seasons change on the earth?
- (a) Due to change in the position of the earth around the sun
- (b) Due to no change in the earth’s position
- (c) Both (a) and (b)
- (d) None of the above
Answer: Due to change in the position of the earth around the sun
Question: When do the longest day and the shortest night occur in the northern hemisphere?
- (a) June 21
- (b) September 23
- (c) December 22
- (d) March 21
Answer: June 21
Question: In which season is Christmas celebrated in Australia?
- (a) Winter season
- (b) Summer season
- (c) Autumn season
- (d) Spring season
Answer: Summer season
Question: When do equinoxes occur on the earth?
- (a) March 21
- (b) September 23
- (c) Both (a) and (b)
- (d) None of these
Answer: Both (a) and (b)
Question: Days and nights occur on earth due to
- (a) rotation
- (b) revolution
- (c) both (a) and (b)
- (d) none of these
Answer: rotation
Question: Change of seasons occurs on earth due to
- (a) rotation
- (b) revolution
- (c) both (a) and (b)
- (d) none of these
Answer: revolution
| Other Resources for Class 6 | |
| Worksheet for Class 6 All subjects | CBSE Notes Class 6 |
| NCERT Books for Class 6 | Online Tuition for Class 6 |
FAQs on Extra Questions Class 6 Social Science The Earth Our Habitat Chapter 3
Which describes the two main motions of Earth?
The two main motions of Earth are rotation, where the Earth spins on its axis, and revolution, where it orbits around the Sun.
What causes the movement of the Earth to take place Class 6?
The movement of the Earth in Class 6 Geography is primarily caused by the gravitational pull from the Sun, which governs both its rotation and revolution.
What is circle illumination?
Circle illumination refers to the way light from the sun falls on the Earth, creating day and night through the Earth's rotation. It's a key concept in studying Earth's motions.
Where to Download Class 6 Geography Chapter 3 Extra Questions and Answers?
You can download Class 6 Geography Chapter 3 extra questions and answers from educational platforms like Infinity Learn, which provide resources aligned with the CBSE syllabus.
What keeps the Earth spinning?
The Earth keeps spinning due to the conservation of angular momentum, a physics principle that maintains its rotation unless acted upon by an external force.








