Table of Contents
Introduction to ductile
The ability of a material to permanently deform in response to stress is referred to as its ductility. The bulk of ordinary steels, for example, are quite ductile and can withstand high stress concentrations. A material’s ductility is greatly influenced by its chemical makeup, crystalline structure, and measurement temperature.
The terms ductility and malleability are not interchangeable. While malleability is concerned with material deformation under compressive stress, ductility is concerned with material deformation under tensile stress. A substance does not have to be both ductile and malleable. It could be both highly malleable and ductile.
We will learn about Ductility in Chemistry, including examples and the way it is distinct from malleability.
Ductility Definition
Ductility is the physical quality of a metal that allows it to be drawn into thin wire, or ductility is the property of a metal related to its capacity to be hammered into thin or stretched into wire without breaking. The most ductile metal is platinum.
Ductile Material
A ductile material is one that can withstand massive plastic deformations before failing, and it is one of the most important properties that engineers evaluate when designing. This property of a ductile material is referred to as ductility.
Ductility Examples
Most metals, including silver, gold, copper, and samarium, are ductility examples. Tungsten and high-carbon steel are two examples of non-ductile metals. Non-metals, in general, are not ductile.
Important Ductile Metal
Ductility Test of Bitumen
Bitumen’s ductility is its ability to extend under traffic pressure without cracking during road construction. The distance in centimeters that bitumen elongates before breaking is measured in a ductility test.
The ductility test of bitumen will be used to determine the following:
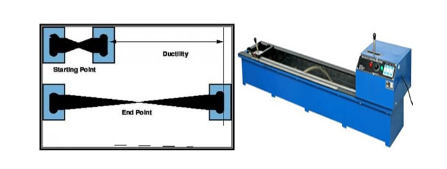
- To determine the ductility of a specific bitumen sample
- To assess the appropriateness of bitumen for use in road building.
Ductility of Steel
There is Ductility of Steel when it can transition from one structure to another. This is due to the fact that this process consumes energy, which can no longer cause damage to the material. Tiny portions in a car body or other steel components then alternate with the two differing atom configurations.
Also Check These Topics:
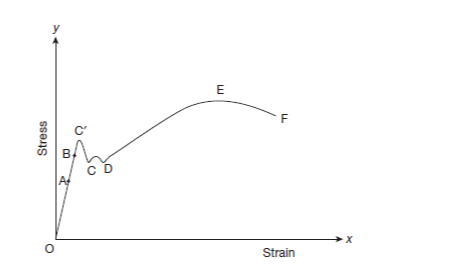
Stress Strain Diagram for Ductile Material
A ductile material exposed to tensile testing goes through several stages before failing. The figure depicts a typical stress strain diagram for ductile material resulting from a tension test on a mild steel bar.
Malleability and Ductility
The two physical qualities linked to the metal are malleability and ductility. This demonstrates that the structure has little resistance to deformation, yet a strong cohesive force maintains it together. The distinction between malleability and ductility is that ductility results from the application of tensile stress to metal, whereas malleability results from the application of compressive stress to metal. The table between malleability and ductility is given below:
| Ductility | Malleability |
| Ductility is a metal attribute that refers to its capacity to be stretched into wire without breaking. | Metal malleability is the ability of a metal to be hammered into a thin sheet without breaking. |
| Tensile stress is a type of external force or stress. | Compressive stress is a type of external force or stress. |
| The nature of ductility is stretching | The nature of malleability is compressive |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Ductile
What is ductility?
Ductility is a physical feature of metal, which means that if we pull it, it will stretch rather than break. In other words, a material's ductile qualities refer to its capacity to undergo significant plastic deformation under tensile stress prior to rapture.
Explain the meaning of malleable and ductile.
The capacity of metals to be crashed into thin sheets is known as malleability, and the metals themselves are known as malleable. For instance, iron, aluminum, and so on. Ductility: The ability of metals to be drawn into thin wires is referred to as ductility, and metals are referred to as ductile.
What is the process of ductility?
The process of ductility is the measuring tensile stress on a metal. Tensile tension is the force that draws the two ends of an object apart.
Which two metals show malleability and ductility?
Copper and silver both show malleability and ductility.
What is the test for malleability and ductility?
Malleability testing is performed by stamping (pressing) the material to determine how much the malleable material can become flat without also breaking. Ductility testing is similar to tensile strength testing in that the material is dragged apart.








