Table of Contents
Introduction to Ziegler-Natta Catalyst
Ziegler Natta catalyst have revolutionized the field of polymerization and have become essential tools in the synthesis of various plastics and polymers. In the chemical production of polythene, a Ziegler Natta catalyst is used.
There are two kinds of polythene: high density and low density. To make high-density polythene, we use the Ziegler Natta catalyst. Karl Ziegler demonstrated the use of this catalyst for ethylene polymerization in 1950.
In this article, we will delve into the world of Ziegler Natta catalysts, exploring their formula, structure, mechanism, and real-world applications.
Ziegler Natta Catalyst
Ziegler Natta catalysts are specialized compounds used to initiate and control polymerization reactions. Ziegler Natta catalysts consist of transition metal complexes, mainly titanium and aluminum compounds, and play a crucial role in the production of various polymers with specific properties.
Ziegler Natta catalysts are classified into two categories based on their solubility:
- Heterogeneous catalysts
- Homogeneous catalysts
Heterogeneous catalysts
They are titanium-based compounds that are used in the polymerization processes of cocatalysts with organoaluminum (triethylaluminum, which is dominant in industry).
Homogeneous catalysts
Based on metals such as titanium, zirconium, or hafnium, and employed as co-catalysts with various organoaluminium compounds.
Ziegler Natta Catalyst Formula
The ziegler natta catalyst formula varies depending on the specific metal and ligands used. Common examples include TiCl₄, TiCl₃(Al(C₂H₅)₃)₃, and TiCl₃(Al(C₄H₉)₃)₃. These formulas indicate the presence of titanium tetrachloride (TiCl₄) and aluminum alkyl compounds as the key components of the catalyst.
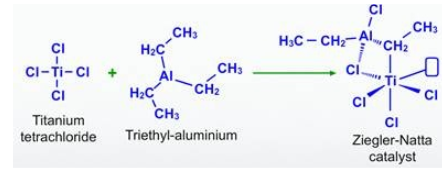
Preparation of Ziegler Natta Catalyst formula
Transition metal halides from groups 4 to 8 of the modern periodic table frequently react with organometallic compounds from groups 1 to 3 of the modern periodic table to form Ziegler-Natta catalysts, with titanium tetrachloride and trimethylaluminum being two common examples.
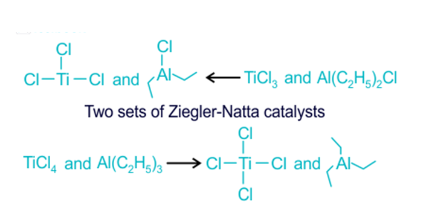
Ziegler Natta Catalyst Structure
Ziegler Natta catalysts have complex structures involving coordination compounds. They typically form active sites that facilitate the polymerization process. The choice of ligands and metals influences the spatial arrangement and reactivity of the catalyst.
Ziegler Natta Catalyst Mechanism
The mechanism of Ziegler Natta polymerization involves the coordination of the catalyst with monomers, resulting in the formation of active species. These active species act as initiators and propagators for the polymerization process, leading to the growth of polymer chains.
Polymerization is often accomplished through the insertion of monomers with transition metal ions attached to the developing chain’s end. Incoming monomers are simultaneously coordinated at unoccupied orbital sites, and lengthy polymer chains develop.
At the active core, the C=C bond is also inserted into the TiC bond. Finally, the chain-growth polymerization reaches the final termination stage, in which “dead” polymers (desired product) are created. These processes are similarly similar to anionic polymerization, which results in the creation of linear and stereo-regular polymers.
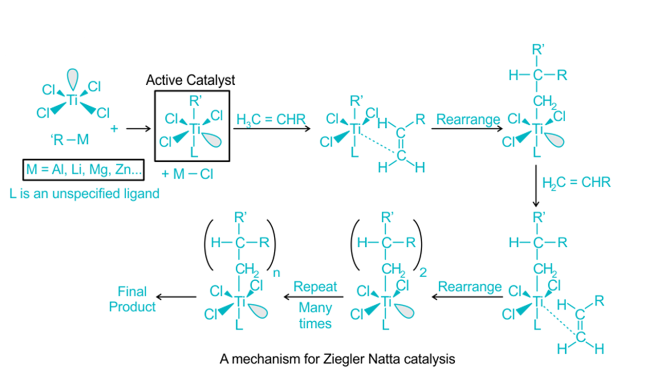
Ziegler Natta Catalyst Polymerization Mechanism PPT
Polymerization with Ziegler Natta catalysts can be understood through a polymerization mechanism PowerPoint (PPT) presentation. This presentation provides a visual representation of the steps involved in the polymerization process with Ziegler Natta catalysts.
Ziegler-Natta Catalysts Examples
Ziegler Natta catalysts find extensive applications in the production of various polymers, including polyethylene, polypropylene, and polystyrene. These polymers are widely used in industries such as packaging, automotive, construction, and consumer goods.
FAQs on Ziegler-Natta Catalysts
What is ziegler natta catalyst?
The Ziegler Natta catalyst is a type of catalyst composed of a mixture of chemical compounds that is mostly utilised in the synthesis of polymers derived from 1-alkenes, such as alpha-olefins, which are hydrocarbons with a double carbon-carbon bond.
How does the Ziegler Natta catalyst formula look like?
To polymerize poly 1-alkene, the Ziegler Natta catalyst is named after Karl Ziegler and Giulio Natta. This catalyst is employed because it is extremely stereoselective and creates a wide range of useful polymers. A Ziegler Natta catalyst is made from titanium tetrachloride TiCl4 and diethyl aluminum chloride Al(C2H5)3.
What metals are present in Ziegler Natta polymerization catalysts?
In the broadest sense, Ziegler Natta catalysts are generated by reactions involving transition metal compounds (most typically halides) from Groups IV-VIII, such as titanium, vanadium, chromium, zirconium, and so on, with alkyl, aryl, or hydrides from Groups I-IV.
What is the Ziegler Natta catalyst mechanism?
At the active core, the C=C bond is also inserted into the TiC bond. Finally, the chain-growth polymerization reaches the final termination stage, in which dead polymers (desired product) are created.








