Table of Contents
Potassium dichromate formula
Potassium dichromate is a chemical compound with the formula K₂Cr₂O₇. Here’s some information about its structure, physical and chemical properties, as well as its uses:
Formula of Potassium dichromate
The chemical formula of potassium dichromate is K₂Cr₂O₇. It indicates that the compound contains two potassium ions (K⁺) and two dichromate ions (Cr₂O₇²⁻).
Structure of Potassium dichromate
Potassium dichromate has a crystalline structure, consisting of potassium cations (K⁺) and dichromate anions (Cr₂O₇²⁻). The dichromate ion consists of two chromium atoms (Cr) bonded to seven oxygen atoms (O).
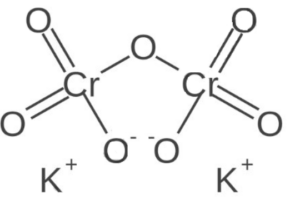
Physical properties of Potassium dichromate
– Appearance: Potassium dichromate is a bright orange-red crystalline solid.
– Molecular weight: The molar mass of potassium dichromate is 294.18 g/mol.
– Melting point: It has a high melting point of approximately 398 °C.
– Solubility: Potassium dichromate is highly soluble in water, and the resulting solution is acidic.
Chemical properties of Potassium dichromate
– Oxidizing Agent: Potassium dichromate is a powerful oxidizing agent, meaning it can readily accept electrons from other substances during chemical reactions.
– Color Change: It can undergo reduction reactions, resulting in a change of its orange color to green as it converts to chromium(III) compounds.
– Reaction with Acid: When reacted with acid, potassium dichromate produces chromic acid (H₂CrO₄) and other byproducts.
Uses of Potassium dichromate
– Industrial Applications: Potassium dichromate is used in various industrial processes, including the production of pigments, dyes, and tanning agents. It is also utilized in the synthesis of certain chemicals.
– Analytical Chemistry: It is employed as a reagent in laboratory analyses, such as the determination of reducing agents in samples.
– Wood Preservation: Due to its strong oxidizing properties, potassium dichromate has been used in wood preservation to protect against decay and insect infestation. However, its use has declined due to environmental concerns associated with chromium compounds.
Solved Examples on Potassium dichromate formula
Example 1: Calculate the molar mass of potassium dichromate (K₂Cr₂O₇).
Solution:
– Molar mass of potassium (K) = 39.1 g/mol
– Molar mass of chromium (Cr) = 52.0 g/mol
– Molar mass of oxygen (O) = 16.0 g/mol
– Number of potassium ions in the formula = 2
– Number of dichromate ions in the formula = 1
– Molar mass of potassium dichromate = (2 * 39.1 g/mol) + (2 * 52.0 g/mol) + (7 * 16.0 g/mol)
= 294.18 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of potassium dichromate is 294.18 g/mol.
Example 2: A solution contains 0.25 moles of potassium dichromate (K₂Cr₂O₇). Calculate the number of moles of dichromate ions present in the solution.
Solution:
– Number of moles of potassium dichromate = 0.25 moles
– Number of dichromate ions in one mole of potassium dichromate = 1
– Number of moles of dichromate ions = Number of moles of potassium dichromate * Number of dichromate ions
= 0.25 moles * 1
= 0.25 moles
Therefore, there are 0.25 moles of dichromate ions present in the solution.
Frequently asked question on Potassium dichromate
1: What are 3 uses for potassium dichromate?
Answer: Potassium dichromate (K₂Cr₂O₇) has several uses in various industries. Here are three common applications of potassium dichromate:
– Industrial Applications: Potassium dichromate is widely used in various industrial processes, including the production of pigments, dyes, and tanning agents. It is employed as an oxidizing agent in the synthesis of organic compounds, such as pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and specialty materials.
– Laboratory Reagent: Potassium dichromate is utilized as a reagent in analytical chemistry and laboratory experiments. It is commonly employed in redox titrations to determine the concentration of reducing agents in a sample. Its strong oxidizing properties make it suitable for these types of analyses.
– Wood Preservation: In the past, potassium dichromate was used as a wood preservative due to its ability to protect against decay and insect infestation. It was applied to timber and wood products to extend their lifespan and improve durability. However, the use of potassium dichromate as a wood preservative has decreased significantly due to environmental and health concerns associated with chromium compounds.
It is important to note that potassium dichromate is a toxic compound and should be handled with caution. Proper safety measures should be followed when working with it to avoid exposure and potential health risks.
2: Why potassium dichromate is used as an indicator?
Answer: Potassium dichromate (K₂Cr₂O₇) is not commonly used as an indicator in acid-base titrations or pH measurements. Instead, it is primarily used as an oxidizing agent and a primary standard in analytical chemistry. Potassium dichromate is known for its intense orange color, which changes to a green color upon reduction.
However, there is an exception where potassium dichromate can be used as an indicator. In a redox titration involving the determination of iron(II) ions (Fe²⁺) with a standard solution of potassium dichromate, the color change of the potassium dichromate solution is used as an indicator. In this case, potassium dichromate acts as both the oxidizing agent and the indicator.
During the titration, as the potassium dichromate is reduced by the iron(II) ions, the orange color of the potassium dichromate solution changes to a green color. The endpoint of the titration is reached when the green color persists for a specified period, indicating that all the iron(II) ions have been oxidized.
3: Why is K₂Cr₂O₇ not a self indicator?
Answer: Potassium dichromate (K₂Cr₂O₇) is not a self-indicator because it does not exhibit a distinct color change that can be used to determine the endpoint of a titration or the pH of a solution. A self-indicator is a compound that can act as both the analyte and the indicator in a titration, where the color change of the compound itself indicates the endpoint of the reaction.
4: What are the hazards of potassium dichromate?
Answer: Potassium dichromate (K₂Cr₂O₇) poses several hazards due to its toxic and oxidizing properties. Here are some of the hazards associated with potassium dichromate:
– Toxicity: Potassium dichromate is highly toxic if ingested, inhaled, or comes into contact with the skin. It can cause severe irritation and damage to the respiratory system, eyes, and skin. Prolonged or repeated exposure to potassium dichromate may lead to serious health issues, including respiratory problems, kidney damage, and an increased risk of cancer.
– Sensitization: Potassium dichromate is a known sensitizer, which means that repeated exposure to even small amounts of the compound can cause individuals to develop an allergic reaction. Sensitization can result in dermatitis, characterized by redness, itching, swelling, and blisters upon contact with the skin.
– Environmental Impact: Potassium dichromate is harmful to the environment. If released into water bodies or soil, it can contaminate the ecosystem and have detrimental effects on aquatic life and plant growth. Additionally, it can persist in the environment for an extended period, leading to long-term contamination.
– Fire and Explosion Hazards: Potassium dichromate is a strong oxidizing agent, which means it can promote the combustion of other substances. It can cause or intensify fires and explosions when in contact with flammable materials, reducing agents, or organic compounds.
5: What is salt used for?
Answer: Potassium Dichromate is an Associate in Nursing odourless, orange to red, crystalline (sand-like) solid or powder. It’s used as an Associate in Nursing analytical chemical agents and in tanning, painting, printing, electroplating, and pyrotechnics.
6: What is the distinction between KMnO4 and K2Cr2O7?
Answer: Potassium permanganate and salt area unit metallic element salts. The key distinction between permanganate of potash and salt is that permanganate of potash includes a dark violet colour, whereas salt includes a red-orange colour.
7: Where is K2Cr2O7 used?
Uses of salt (K2Cr2O7) – K2Cr2O7 is an Associate in Nursing oxidant for a range of reactions in laboratories and industries. It’s employed in the animal skin trade for chrome tanning by acting as a precursor for metallic element mordant. It’s employed in the volumetrical analysis. It’s employed in coloring and calico printing.
8: Definition of dichromate?
Answer: An orange-to-red chromium salt usually contains the anion Cr2O72− dichromate of potassium. — also called bichromate.







