Table of Contents
Long Form of the Periodic Table:
- What is a periodic table?
- What is the long form of the periodic table and what is its significance?
Let us look at the answers to all these questions in detail below. The periodic table is a tabular representation of chemical elements. It is also known as the periodic table of (the) (chemical) elements. It is widely used in chemistry, physics, and other sciences and is widely regarded as a chemistry icon. It is a graphical representation of the periodic law, which states that the properties of chemical elements depend on their atomic numbers periodically.
- The table is divided into four blocks, each rectangular.
- The table’s rows are referred to as periods, and its columns are referred to as groups Elements in the same column group of the periodic table have similar chemical properties.
- Nonmetallic character (keeping their electrons) increases from left to right across a period and from down to up across a group.
In contrast, metallic character (surrendering electrons to other atoms) increases in the opposite direction. The underlying cause of these trends is atomic electron configurations. With the advancement of science, the periodic table continues to evolve. Only elements up to atomic number 94 exist in nature; to go further, new elements had to be synthesized in the laboratory. Today, all 118 elements are known, completing the first seven rows of the table. However, the chemical characterization of the heaviest elements is still required to confirm their properties match their positions. It is unknown how far the table will extend beyond these seven rows or whether the patterns of the known region will continue into this unknown region.
Some scientific debate also rages about whether some elements in today’s table are correctly positioned. It wasn’t until the second decade of the twentieth century that it was realized that the periodic system’s order is defined by its atomic numbers, the integers of which are equal to the positive electrical charges of the atomic nuclei expressed in electronic units. In the years since great strides have been made in explaining the periodic law regarding the electronic structure of atoms and molecules. This clarification increased the value of the law, which is still as widely used today as it was at the turn of the twentieth century when it expressed the only known relationship between the elements.
Modern Periodic Table
The modern periodic table, also known as the long-form, is based on modern periodic law. The table is an arrangement of elements in increasing atomic number order. In its current form, the periodic table is known as the modern periodic table. It is made up of 18 vertical columns and 7 horizontal rows.
- 1,2,3,…18 are the names or numbers of the 18 vertical columns. Because each group’s elements have the same amount of valence electrons, their properties are identical. Only the outermost shell is empty; the interior shells are all filled.
- It consists of groups 1 and 2 (alkali metals) and 13 and 17 (alkaline earth metals).
- The outermost shell (next to the outermost shell-penultimate shell) and the second outermost shell (next to the outer shell-penultimate shell) are missing. It consists of elements from groups 3 through 12.
- Lanthanides are elements with atomic numbers ranging from 58 to 71, and the series is known as the Lanthanide series. It’s tucked away beneath the main table.
- Actinides are elements with atomic numbers ranging from 90 to 103, and the series is known as the actinide series. It’s also listed individually with the lanthanide series at the bottom of the main table.
- Inert gases, often known as Noble gases, are elements with fully occupied valence shells.
- The number of shells in an element’s atoms determines its period number. E.g., Three shells are present in a third-period element (K, L, M).
- All elements have distinct electronic configurations over time. Hence their characteristics are different.
Also read: Periodic Table of Elements – Trends and Patterns
Modern periodic table of the elements – Long Form
The current version of the periodic table is the long version, which is commonly used all around the world. In this type of periodic table, the horizontal rows are known as periods, while the vertical columns are known as groups. Groups are formed by elements that have atoms with similar outer shell electrical structures. Previously, the groups were referred to as IA,…VIIIA, VIII, IB…VIIB, and 0. However, they are now known as 1, 2, 3,…18. The seven horizontal rows of the current periodic table are known as periods. The element’s period is determined by the quantum number ‘n.’ One of the four quantum numbers is the principal quantum number (n) (n, l, m, and s). It provides information about the fundamental electron shell. If n=3, for example, the principal shell will be indicated as 3.
- Periods are the horizontal rows in the modern or long form of the periodic table.
- The periodic table has seven periods numbered 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7 from top to bottom. The initial period is made up of only two elements: hydrogen and helium. There are eight elements in each of the second and third periods. There are 18 elements in each of the fourth and fifth periods.
- On the other hand, the sixth period is made up of 32 elements.
- The seventh period of the periodic table now has four new elements.
- The elements are 113-Nihonium, 115-Moscovium, 117-Tennessine, and 118-Oganesson. With this addition, the 7th period now has 32 elements. In addition, the long form of the periodic table has a separate panel at the bottom.
- It comprises 14 elements from the sixth period known as lanthanoids. In the seventh period, there are 14 elements known as actinoids.
- Each period represents the number of shells or energy levels found in an element’s atom.
Long form of the Modern Periodic Table
Moseley’s work demonstrated beyond doubt that the properties of elements are well explained and that most of the anomalies and flaws in Mendeleev’s Periodic Table disappear when the classification basis is changed from atomic masses to atomic numbers. This gives rise to Periodic modern law, which states,
The physical and chemical properties of elements are a regular function of their atomic numbers. To address the shortcomings of Mendeleev’s periodic table, a number of tables for the classification of elements based on modern periodic law have been proposed. The long form Periodic Table, also known as Bohr’s Table, is the most widely used of these various tables.
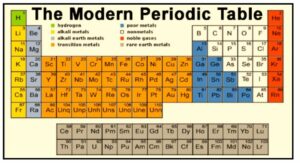 Because it is based on Bohr’s Scheme of categorizing elements into four types based on their electronic configurations, a periodic table is a tabular arrangement of elements in rows and columns in increasing atomic number order, emphasizing the regular repetition of elements’ properties. The periodic table’s basic structure is its division into rows and columns.
Because it is based on Bohr’s Scheme of categorizing elements into four types based on their electronic configurations, a periodic table is a tabular arrangement of elements in rows and columns in increasing atomic number order, emphasizing the regular repetition of elements’ properties. The periodic table’s basic structure is its division into rows and columns.
Periodic table of the elements – long form
The physical and chemical properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers, according to the current periodic law. The elements are ordered in order of increasing atomic number. Element attributes that are related are grouped. A more fundamental property determines the arrangement of the elements, atomic number.
The position of an element in this periodic table is related to the electronic configuration of its atom. It explains the similarities and differences in the properties of the elements in terms of electronic configurations and the long-term trends in chemical properties.
They are arranged in increasing atomic number order. Precision can be achieved in predicting the properties of elements and their compounds. When the elements are arranged according to increasing atomic numbers, all of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table’s flaws are eliminated. They have similar chemical properties because they have the same outer electronic configuration, i.e., the same number of valence electrons. They have gradations due to the nucleus’ and outer valence electrons’ varying attraction as we move down the group.
- First Period: It has two elements, H and He. It is known as the shortest period.
- Second Period: It has eight elements ranging from Li to Ne. It is referred to as a brief period. Second-period elements are also referred to as bridge elements.
- The Third Period: Also known as the short period, contains eight elements ranging from Na to Ar. This period’s elements are also referred to as typical elements.
- Fourth Period: It has 18 elements ranging from K to Kr and is known as the long period.
- Fifth Period: It also has 18 elements, ranging from Rb to Xe. This is referred to as a long period.
- Sixth Period has 32 elements ranging from Cs to Kr. This is the longest period.
- Seventh Period: It is an incomplete period with 29 – elements ranging from Fr to Uuo.
Join our JEE 2024 course to make your IIT dream come true.
Crack NEET 2023 with Result-Oriented Learning Program from Infinity Learn.
FAQs
What exactly is a long-form periodic table?
The modern periodic table, also known as the long-form, is based on modern periodic law. The table is an arrangement of elements in increasing atomic number order.
In the long form of the periodic table, how are the elements arranged?
Elements are arranged in the long form of the periodic table to increase their Atomic number. Elements in each group have the same number of valence electrons, so their properties are similar.
What is the distinction between the long form of the periodic table and the modern periodic table?
No, there is no distinction between the long form of the periodic table and the modern periodic table. Mendeleev proposed the first periodic table concept. This new periodic table version is known as the long form of the periodic table, which we now refer to as the modern periodic table.






