Table of Contents
CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Geography 2016 Outside Delhi
Time allowed : 3 hours
Maximum marks: 70
General Instructions :
- There are 22 questions in all.
- All questions are compulsory.
- Question number 1 to 7 are very short-answer questions carrying 1 mark each. Answer to each of these questions should not exceed 40
- Question numbers 8 to 13 are short-answer questions carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each of these questions should not exceed 80-100 words.
- Question numbers 14 to 20 are long-answer questions carrying 5 marks each. Answer to each of these questions should not exceed 150
- Question numbers 21 to 22 are related to identification or locating and labelling of geographical features on maps, carrying 5 marks each.
- Outline maps of the World and India provided to you must be attached within your answer-book.
- Use of templates or stencils for drawing outline maps is allowed.
** Answer is not given due to change in present syllabus
CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Geography 2016 Outside Delhi Set – I
Question 1.
Name the country where sex ratio is most unfavourable to women in the world. [1]
Answer:
Qatar—311 males per 100 females.
Question 2.
Define the concept of human development. [1]
Answer:
Human development is defined as process of enlarging people’s freedoms and opportunities and improving their well being.
Question 3.
How has the ‘New Ruhr’ landscape emerged ?
Answer:
In Ruhr region, the demand for coal declined and iron ore was exhausted, industries used imported iron ore leading to the shrinking of the region.
Question 4.
Assess the positive aspect of ‘trade liberalisation’. [1]
Answer:
Trade liberalization is removal or reduction of restriction or barriers and allows the free exchange of goods between the nation.
Question 5.
“The proportion of workers in the agricultural sector in India has shown a declining trend over the last few decades.” What does this trend indicate ? [1]
Answer:
This trend indicates a shift of dependence of workers, from farm based occupation to non- farmed based one. It shows a sectoral shift in the economy of the country.
Question 6.
Why do people migrate in large number from rural to urban areas in India ? [1]
Answer:
In India, people migrate from rural to urban areas mainly due to variety of factors such as social, economic and political factors which are :
- Employment
- Lack of basic infrastructure facility, i.e., education, healthcare.
Question 7.
Name the two countries which are the largest trading partners of India as per economic survey report of 2011-12. [1/2 + 1/2 = 1]
Answer:
- U.A.E.
- China.
Question 8.
“The knowledge and understanding of the laws of nature are extrememly valuable to human kind”. Explain the values that can help to use the gifts of nature in a sustainable manner. [3]
Answer:
The knowledge of laws of nature are highly valuable for mankind.
- Better knowledge is developed because of better knowledge of laws of nature.
- The understanding of concept of friction and heat helped discover fire.
- We use law of aerodynamics of develop faster planes.
- Harmony with their natural environment.
Thus law of nature, if known to man are extremely valuable.
Question 9.
Study the table given below and answer the questions that follow:
Continent-wise Distribution of Million Cities
| Continent | Early 1950 | Mid 1970s |
Mid
2000 |
| Europe | 23 | 30 | 58 |
| Asia | 32 | 69 | 206 |
| North and Central America | 16 | 36 | 79 |
| South America | 18 | 17 | 43 |
| Africa | 3 | 8 | 46 |
| Australia | 2 | 2 | 6 |
| World Total | 84 | 162 | 438 |
Source : www.ciPfpopulation.delworld.html
Question 9.1.
Name the two continents which have shown the highest growth rate of million cities from 1950 to 2000.
Answer:
- Africa,
- Asia
Question 9.2.
What could have been the reason for such a growth of million cities ?
Answer:
Migration of people in large numbers from rural areas to urban areas for the purpose of livelihood mainly in big cities is the reason for such a growth.
Question 9.3.
Give the meaning of a ‘million city’. [3]
Answer:
The city which has one million or more than one million citizens is known as ‘million city’.
Question 10.
Differentiate between ‘Hamleted’ and
Answer:
| Hamleted Settlement | Dispersed Settlement |
| (i) It is fragmented into several units. | (i) It appears in form of isolated huts. |
| (ii) It is being separated bear the same name or common name. | (ii) It is isolated in remote jungle or hilly areas and have extreme dispersion. |
| (iii) It is known by different local names such as Palli, Panna, Para, Nangla, Dhani etc. | (iii) It is in extreme isolation and have no such local names. |
Question 11.
How is rainwater harvesting helped in the development of certain areas of India ? Explain with examples. [3 × 1 = 3]
Answer:
Rainwater harvesting helps in development of certain area in India by :
- It helps to capture and store rainwater for various uses.
- It helps to recharge groundwater aquifier.
- In Rajasthan rainwater harvesting structures locally known as Kund and Tanka are constructed near or in the house or village to store harvested rainwater.
- It prevents soil erosion and flooding.
- It helps to provide water supply in case of drought.
- It improves quality of ground water by reducing salinity and other salts.
Question 12.
Study the diagram given below and answer the questions that follow:
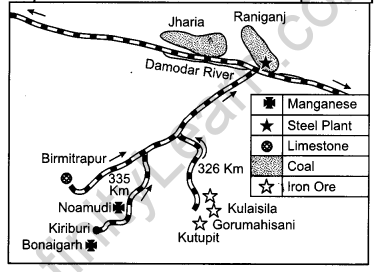
Question 12.1.
Identify and name the steel plant shown in the diagram.
Answer:
Durgapur Steel Plant.
Jharia and Raniganj supply coal to this steel plant.
Question 12.2.
Name the mining areas which supply coal and manganese to this plant.
Answer:
Noamundi and Bonaigarh supply manganese to this plant.
Question 12.3.
Which is the source of water supply to this plant ?
Answer:
Damodar river is the source of water supply to this plant.
Question 13.
Examine the success of watershed management programme implemented in Jhabua district of Madhya Pradesh. [3]
Answer:
The watershed management program is highly successful because 20% of the total area of Jhabua district has been treated under this program.
- It helps in prevention of land degradation.
- Improves the soil quality.
- Improves the growth of natural vegetation.
- Improves the source of livelihood for the tribals.
Question 14.
Explain any three ‘push’ and any two ‘pull’ factors that influence the migration of population in the world. [3 + 2 = 5]
Answer:
The push and pull factors make their influence on the migration of population in the world.
- Push factors influencing migration :
- Unemployment : High population in towns often imposes pressure on agricultural land. This pressure and closing down of multiple industries, leads to unemployment.
- Natural Disasters : Due to natural disasters such as flood, draught and earthquake, shelters are destroyed and agricultural production and other sources of income suffer; such factors force people to migrate to safer places.
- Political Unrest: Political turmoil or situations like civil war make the surroundings insecure. Therefore, people move from such place to more safe places. Example : People migrating from Syria to European countries.
- Pull factors :
- Better Employment Opportunities :
Industrialised and developed areas are able to provide better job opportunities and higher wages, attracting more people and causing migration. - Better Health and Education Facilities : Urban or developed areas have better healthcare, education and other facilities which attract people. For example, people migrate from less developed towns to more developed towns and cities in search of better educational and health facilities.
- Better Employment Opportunities :
Question 15.
Describe any five characteristics of plantation agriculture in the world. [5]
Answer:
Plantation agriculture is a form of commercial farming where crops are grown for profit.
- Plantation crops are generally raised on large estates of more than 40 hectares.
- Scientific methods of cultivation is used.
- It requires large capital investments.
- Estate farming is the feature of plantation agriculture which is owned by foreigners employing local labour.
- It focuses on the cultivation of cash crops for experts.
- Tea, coffee, cocoa, rubber, cotton, sugarcane, banana, coconut etc., are the examples of plantation crops.
Question 16.
Explain the importance of ‘communication services’ in the world. [5]
Answer:
Importance of communication services in the world is :
- Communication induces transmission of words, messages, facts and ideas from one place to another.
- Communication through satellites have connected remote corners of the globe.
- The use of internet has expanded the contemporary economic and social space of no mass through e-mail, e-commerce, clearing etc.
- It helps to spread the message from one place to another very quickly.
- The time has reduced to spread the message.
- Global communication has revolutionised the world.
- The whole wind has became one global village.
Question 17.
“The Rhine waterways is the world’s most heavily used inland waterway.” In the light of this statement examine the significance of this waterway. [5]
Answer:
The significance of Rhine waterways.
- The Rhine flows through Germany and the Netherlands.
- It is navigable for 700 km from Rotterdum; at its mouth in the Netherlands to Basol in Swit2erland.
- Ocean going vessels can reach up to Cologne. The Ruhr river joins the Rhine from the east.
- It flows through a rich coal field and the whole basin has become prosperous manufacturing area.
- Dusseldorf is the Rhine post for the region.
- Huge tonnage moves along the stretch soon of the Ruhr and it is the world’s most heavily used waterway.
- It connects the industrial areas of Switzerland; Germany, France, Belgium and Netherland with the North Adantic Sea Route.
Question 18.
Examine the economic and social consequences of migration in India. [21/2 + 21/2 = 5]
Answer:
The economic consequences of migration are:
- The major benefits for the source region is the remittance sent by the migrants which is the major sources of foreign exchange.
- In year 2002, India received US 11 $ billion as remittances from international migrants.
- Punjab, Kerala and Tamil Nadu receive very significant amount form their international migrants.
- The remittances sent by the internal migrants play very important role in the growth of economy of the source area.
- Unregulated migration to the metropolitan cities of India has caused over crowding.
- It leads development of slums in industrially developed states.
Social consequences of migration :
- Migrants act as agent of social change. The new ideas get diffused from urban to rural areas through them.
- It leads to intermixing of people from diverse cultures.
- It helps in the evaluation of composite culture and widens up the mental horizon of the people.
- It creates social vacuum and sense of dejection among individuals which motivate people to fall in the trap of anti social activities.
Question 19.
‘Fragmentation of land holdings’ and ‘degradation of cultivable land’ are the serious problems of India agriculture. Suggest and explain measures to overcome these problems. [2 + 3 = 5]
Answer:
Fragmentation of land holdings and degradation of cultivable land are serious problems of Indian agriculture.
Measures for fragmentation of land holdings :
- Consolidation of land holdings.
- Strict implementation of land reforms.
Loose implementation leads to exploitation of farmers and workers. Strict and better implementation may act as a measure to prevent the same.
Measures to overcome degradation of cultivable land:
- Check water logging.
- Use of organic manure : Use of chemical manure deterioates the quality of soil, fertility is lost, to reduce the effect organic manure should be used.
- Cultivation of leguminous crops: Leguminous crops helps in fixing the nitrogen component and makes the soil ready for cultivation.
- Rotation of crops.
Question 20.
Which is the apex body in India to improve the quality of National Highways ? Examine the significance of National Highways. [1 + 4 = 5]
Answer:
The apex body in India to improve the quality of National Highways is National Highway Authority of India (NHAI).
Significance of National Highways :
- National Highways passes across the country connecting major state capitals, major cities, important ports and railway junctions.
- National highways are meant for interstate transport and for the movement of defence men and materials in strategic areas.
- The National Highways constitute approximately 2% of total road length carries 40% of the total road traffic.
- They are 4-6 lane and make journey fast and easy.
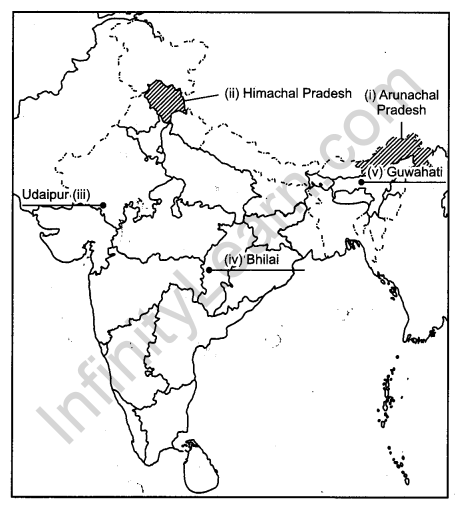
Question 21.
Identify the five geographical features shown on the political outline map of the world as A, B, C, D and E and write their correct names on the lines marked near them with the help of following information : [5 × 1 = 5]
(A) The country with largest area in Africa.
(B) An area of dairy farming.
(C) A major sea port.
(D) An international airport.
(E) A mega city.
Question 22.
Locate and label the following features with appropriate symbols on the given outline political map of India: [5 × 1 = 5]
(i) The state with lowest density of population.
(ii) The state with highest percentage of rural population Uttar Pradesh.
(iii) A major copper mining area in southern Rajasthan.
(iv) The integrated iron and steel plant located in Chhattisgarh.
(v) The international airport located in Assam.
Answer:
CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Geography 2016 Outside Delhi Set – II
Note : Except for the following questions, all the remaining questions have been asked in previous set.
Question 1.
What is the average sex ratio in the world ? [1]
Answer:
The average sex ratio in the world is 990 females per 1000 males or 102 males per 100 females.
Question 3.
Mention any two major problems of Ruhr-industrial region. [1/2 + 1/2 = 1]
Answer:
Problems of Ruhr industrial region are :
- Industrial waste disposal
- Pollution
- Iron ore and coal ore.
Question 4.
How is the favourable balance of trade an indicator of economic development of a country ? [1]
Answer:
If the value of export is more than the value of import than the country has positive or favourable balance of trade. Favourable balance of trade is the indicator of economic development of the country.
Question 5.
What is the main thrust of the National Youth Policy of Government of India, 2003 ? [1]
Answer:
The main thrust of the National Youth Policy of 2003 is Youth Empowerment in terms of their effective participation in decision making and carrying the responsibility of an able leader.
Question 7.
Explain one reason for the import of petroleum and its products in large quantities in India [1]
Answer:
Reasons for the import of petroleum and its products in large quantities in India are as follows :
- Production of petroleum and its product is less than the requirement in India.
- It is used as a fuel.
- It is also used as an industrial raw material.
- Demand increased due to rise in population and no. of vehicles on the roads.
Question 9.
Study the table given below and answer the questions that follow :
Continent-wise Distribution of Million Cities
| Continent | Early
1950 |
Mid
1970s |
Mid
2000 |
| Europe | 23 | 30 | 58 |
| Asia | 32 | 69 | 206 |
| North and Central America | 16 | 36 | 79 |
| South America | 18 | 17 | 43 |
| Africa | 3 | 8 | 46 |
| Australia | 2 | 2 | 6 |
| World Total | 84 | 162- | 438 |
Source : www.citypopulation.delworld.html
Question 9.1.
Name the two continents which have shown lowest growth rate of million cities as compared to others.
Answer:
Australia and Europe.
Question 9.2.
What reasons will you assign for this growth rate ?
Answer:
- Growth rate of population is slow.
- Migration from rural to urban is slow.
Question 9.3.
Give the meaning of a ‘mega city’. [3]
Answer:
A mega city or megalopolis is a general term for cities together with their suburbs with a population of more than 10 million people.
Question 11.
Explain the significance of bio-energy to humankind in India. [3]
Answer:
The significance of bio-energy to humankind in India :
- Bio energy is a potential source of energy conversion.
- It can be converted into electrical energy, heat energy or gas for cooking.
- It will also process the waste and garbage and produce energy.
- This will improve economics life of rural areas in developing countries.
- It reduces environmental pollution, enhance self-reliance and reduces pressure on fuel and wood.
Question 17.
‘Trans-Canadian railway line is considered as the economic artery of Canada.’ Support the F statement with suitable examples. [5 × 1 = 5]
Answer:
Trans-Canadian railway line is considered as the economic artery of Canada by the following reasons :
- Trans-Canadian railway line is about 7050 km long rail-line in Canada, runs from Halifax in the east to Vancouver on the Pacific coast passing through Montreal, Ottawa, Winnipeg and Calgary.
- It was constructed in 1886, as part of an agreement to make British Columbia on the west coast join the Federation of States.
- It gained economic significance because it connected the Quebec-Montreal industrial Region with the wheat belt of Prairie region and the coniferous forest region in the north.
- Each of these regions became complementary to the other.
- A loop fine from Winnipeg to Thunder bay connects this rail-line with one of the important waterways of the world.
- This line is the economic artery of Canada, wheat and meat are the important exports on this route.
Question 20.
Examine the role of Inland waterways authority of India. Explain why inland water transport is an important mode of transport. [2 + 3 = 5]
Answer:
Inland waterway :
- The Inland waterways Authority of India was set up in 1986.
- It was set up for the development, maintenance and regulations of national waterways in the country.
- The authority has declared 3 inland waterways as national waterways.
- It has also identified 10 other inland waterways which can be upgraded.
- The famous Nehru Trophy Boat Race (Vallam Kali) is held in backwaters.
Importance of Inland Water Transport: India has the network of Inland water extending up to 14500 km. in the form of rivers, canals, backwater and creeks.
- It is suitable for carrying bulky goods.
- It carries both cargo and passengers.
- It is the cheapest mode of transport.
- It is fuel-efficient.
- It is eco-friendly.
CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Geography 2016 Outside Delhi Set – III
Note : Except for the following questions, all the remaining questions have been asked in previous set.
Question 1.
Which age group forms the working population ? [1]
Answer:
The working age population is between 15 to 59 years.
Question 3.
Explain any two features of foot loose industries. [ 1/2 + 1/2 = 1]
Answer:
- Footloose industries are not dependent on any particular raw material.
- They produce in small amount and employ small labour force.
Question 4.
Explain the meaning of ‘Volume of Trade’. [1]
Answer:
The actual tonnage of goods traded makes up the volume. However, services traded cannot be measured in tonnage. Therefore, the total value of goods and services traded is considered to be the volume of trade.
Question 5.
How is agricultural density of population different from physiological density of population ? [1]
Answer:
The Agricultural density of a population is the number of farmers per net cultivable area of farmland. Physiological density is the total number of people per net unit area of arable land.
Question 7.
Name the riverine port on the eastern coast of India. [1]
Answer:
Kolkata port.
Question 9.
Study the table given below and answer the questions that follow:
Continent-wise Distribution of Million Cities
| Continent | Early
1950 |
Mid
1970s |
Mid
2000 |
| Europe | 23 | 30 | 58 |
| Asia | 32 | 69 | 206 |
| North and Central America | 16 | 36 | 79 |
| South America | 8 | 17 | 43 |
| Africa | 3 | 8 | 46 |
| Australia | 2 | 2 | 6 |
| World Total | 84 | 162 | 438 |
Source : www.citypopulation.delworld.html
Question 9.1.
Name the two continents, one with highest growth rate and the other with lowest growth rate of million cities.
Answer:
Highest – Africa,
Lowest – Europe
Question 9.2.
Why is the number of million cities increasing in the world ?
Answer:
The number of million cities is increasing in the world due to rapid increase in urban population because of migration from rural areas to urban areas for employment and better education facilities.
Question 9.3.
Why is the age structure considered an important indicator of population composition ? Give one reason. [1]
Answer:
The term conurbation was coined by Patrick Geddes in 1915 and applies to a large area of urban development that results from the merging or originally seperate towns or cities
e.g., Greater London
Question 11.
Explain the importance of ‘Integrated Tribal Development Project’ implemented in Bharmaur region of Himachal Pradesh. [3]
Answer:
Bharmaur tribal area comprises Bharmaur and Holi tehsils of Chamba district of Himachal Pradesh. It is inhabited by ‘Gadd.?, a tribal community who practised transhumance and the economy is largely based on agriculture and allied activities such as sheep and goat rearing. Under the Fifth Five Year Plan, the tribal sub-plan was introduced in 1974 and Bharmaur was designated as one of the five Integrated Tribal Development Projects (ITDP) in Himachal Pradesh.
- This plan laid the highest priority on development of transport and communications, agriculture and allied activities, and social and community services.
- The most significant contribution of tribal sub plan in Bharmaur region is the development of infrastructure in terms of schools, health care facilities, potable water, roads, communications.
- The social benefits derived from ITDP include tremendous increase in literacy rate, improvement in sex ratio and decline in child marriage. The female literary rate in the region has also increased.
- The cultivation of pulses and other cash crops has increased and there is a declining importance of pastoralism.
Question 17.
“Land transport plays a vital role in the development of trade and tourism in the world”. Support the statement with suitable examples. [5]
Answer:
Transport helps in the assembly of raw materials and distribution of finished goods. It makes possible to move goods from the place of production to the place where they are to be consumed. In the earlier days, there were only local markets due to the absence of safe means of transport. Now-a-days, trade is not restricted to the boundaries of a nation, but has spread throughout the world. Development of the efficient means of transport has knit together all the nations of the world into the one big world market. Even the perishable articles like fish, dairy products, meat etc., are being transported to distant places of the world. But without good transport facilities, such a development in trade and commerce would not have been possible. In India, there are many highways linking the major towns and cities.
For example, National Highway No. 7 (NH 7), connecting Varanasi with Kanyakumari, is the longest in the country. The Golden Quadrilateral (GQ) or Super Expressway connects the four metropolitan cities — New Delhi, Mumbai, Bengaluru, Chennai, Kolkata and Hyderabad which has helped in the development of trade.
Transportation links diverse destinations and ferries people commodities and services between these ‘ places. Tourism is much about travel and therefore the role of transportation in its operation is vital. Railways are also a mode of land transport that helps to carry passengers over long distances. The Border Road Organization has constructed roads in f high altitude mountainous terrain joining Chandigarh with Manali (Himachal Pradesh) and Leh (Ladakh).
This road runs at an average altitude of 4,270 metres above the mean sea level and has promoted tourism in such high altitude areas as well.
Question 20.
Explain why rail transport countinues to remain the chief mode of transport for the masses in India. [5]
Answer:
Railway transport occupies a significant role in the transport system of a country because the development of trade, industry and commerce of a country largely depends on the development of railways.
- It facilitates long distance travel and transport of bulky goods which are not easily transported through motor vehicles.
- It is a quick and more regular form of transport because it helps in the transportation of goods with speed and certainty.
- It helps in the industrialization process of a country by easy transportation of coal and raw-materials at a cheaper rate.
- It helps in the quick movement of goods from one place to another at the time of emergencies like famines and scarcity.
- It encourages mobility of labour and thereby provides a great scope for employment.






