Table of Contents
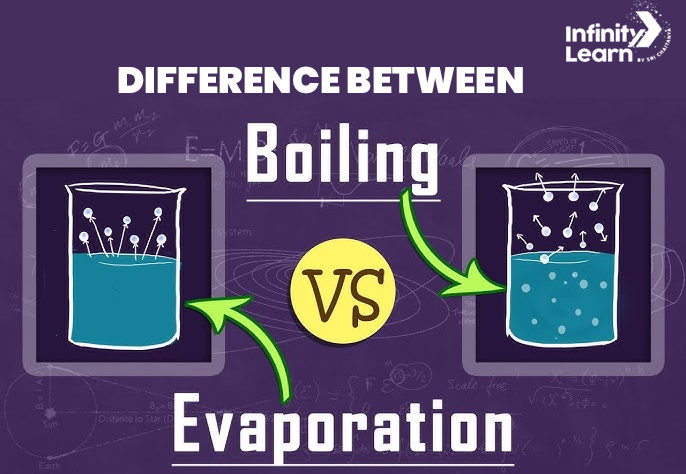
Evaporation is the transformation of liquid into vapor at temperatures below the boiling point, primarily occurring at the liquid’s surface. A classic example of evaporation is the sun’s heat causing water to vaporize from the soil. Conversely, boiling is the rapid vaporization of a liquid when its temperature reaches its boiling point, happening throughout the entire liquid mass.
The most notable distinction is where these processes take place: evaporation is surface-level, while boiling involves the whole liquid. Knowing the boiling point formula can further aid in understanding these differences.
What is Evaporation?
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. This process happens below the boiling point of the liquid, meaning it can occur at a wide range of temperatures, not just at the liquid’s boiling point. The most common example of evaporation is gradually drying water from a surface or clothing.
In evaporation, molecules at the surface of the liquid gain sufficient energy to overcome the liquid’s surface tension and enter the air as vapor. This energy is typically provided by heat from the surroundings. Factors like temperature, surface area, air movement, and humidity can affect the rate of evaporation.
In nature, evaporation is a crucial part of the water cycle, contributing to cloud formation and the overall weather patterns on Earth. It’s fundamental in various scientific fields, including physics, chemistry, and meteorology.
Factors Influencing the Rate of Evaporation
Evaporation, a key phase change in the water cycle, is influenced by several factors determining how quickly a liquid turns into vapor. Understanding these factors helps differentiate between natural processes and their environmental effects.
- Surface Area: The evaporation rate is proportional to the exposed surface area. A larger surface area allows more molecules to escape into the air, thus increasing the evaporation rate. This principle explains why spreading out clothes helps them dry faster.
- Temperature: Higher temperatures contribute to a faster rate of evaporation. As temperature rises, molecules gain more kinetic energy, increasing their likelihood of overcoming intermolecular forces and escaping as vapor. This is evident when clothes dry quicker in the sun. The relationship is defined as:
- Humidity: Humidity, the amount of water vapor in the air, inversely affects the evaporation rate. High humidity means the air is already saturated with water vapor, reducing the rate at which water can evaporate.
- Wind Speed: An increase in wind speed can enhance the evaporation rate. Wind moves water vapor away from the surface, reducing local humidity and allowing more liquid to evaporate. This is why clothes dry faster on a windy day.
Each factor plays a significant role in evaporation, affecting everything from daily weather to the global climate. Understanding these can help better predict and manage natural and artificial systems involving evaporation.
What is Boiling?
Boiling is a rapid vaporization of a liquid that occurs when a liquid is heated to its boiling point, the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the surrounding pressure. This process results in the formation of bubbles within the liquid that rise to the surface and release into the air as steam or vapor.
When a liquid boils, the heat energy absorbed breaks the intermolecular bonds within the liquid, allowing molecules to escape as gas. This phase change happens throughout the entire liquid body, not just at the surface. The specific temperature at which boiling occurs varies for different substances due to their unique chemical and physical properties.
Boiling is a key concept in cooking, chemistry, and various industrial processes. In cooking, it’s used to prepare a wide range of foods, while in industrial and scientific settings, it’s important for distillation, sterilization, and many other applications. The boiling point of a liquid can also provide important information about its purity and properties.
What is Boiling Point and How Does it Differ from Evaporation?
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which its vapor pressure equals the surrounding pressure, leading the liquid to turn into vapor. This concept is crucial in understanding the what is difference between evaporation and boiling. While evaporation can occur at various temperatures below the boiling point and typically at the liquid’s surface, boiling is a specific, rapid process that occurs throughout the liquid at the boiling point.
Factors Affecting Boiling Point
- Atmospheric Pressure: Central to the evaporation and boiling difference, atmospheric pressure significantly influences the boiling point. Higher atmospheric pressure requires more energy to break intermolecular bonds, thus raising the boiling point. Conversely, lower pressure leads to a lower boiling point. This explains why water boils below 100°C in high altitudes with lower pressure.
- Impurities: The presence of impurities in a substance elevates its boiling point. For instance, while pure water boils at 100°C, water with dissolved substances boils at a higher temperature. This phenomenon is due to the impurities disrupting the liquid’s normal boiling behavior, requiring more energy for the liquid to enter the vapor phase. Understanding how impurities affect boiling points is key to differentiate between boiling and evaporation.
These factors are essential in understanding the boiling point and its differentiation from evaporation, providing a comprehensive view of the physical behaviors of substances under varying conditions.
Difference between Evaporation and Boiling
Understanding the what is difference between evaporation and boiling is crucial, as they are often mistaken for one another. Grasping the evaporation and boiling difference not only clarifies common misconceptions but also enhances comprehension of these physical processes.
To differentiate between boiling and evaporation, it’s essential to recognize their distinct characteristics and similarities. Refer to the table for differences between evaporation and boiling:
| Difference between Evaporation and Boiling | ||
| Aspect | Evaporation | Boiling |
| Definition | Evaporation is a natural process where the liquid changes into gas, often due to increased temperature or pressure. | Boiling is a rapid process where continuous heating vaporizes the liquid. |
| Location of Occurrence: | Usually occurs at the surface of the heated liquid. | Occurs throughout the entire mass of the liquid. |
| Visibility of Bubbles | Bubbles are not visible during evaporation. | The bubbling effect is prominent during boiling. |
| Rate of Process | Evaporation is a relatively slow process. | Boiling is a much quicker process. |
FAQs on Difference Between Evaporation and Boiling
What are the 3 differences between evaporation and boiling?
Evaporation occurs at temperatures below the boiling point and usually at the surface of the liquid, whereas boiling occurs at a specific temperature throughout the liquid. Evaporation is a slow process, while boiling is rapid, forming visible bubbles.
What are the 5 similarities between boiling and evaporation?
Both processes involve changing a liquid to a gas, require heat, decrease the liquid's quantity, are part of the water cycle, and are influenced by environmental factors like pressure and temperature. These similarities underscore their roles in phase changes
What is boiling class 9?
In class 9, boiling is taught as the rapid vaporization of a liquid at its boiling point, where the liquid's vapor pressure equals the surrounding pressure. It's a fundamental concept explaining how substances change from liquid to gas at specific temperatures.
What are boiling and evaporation examples?
An example of boiling is water turning to steam at 100°C in a kettle. An example of evaporation is a puddle drying up on a warm day, as water slowly turns to vapor at temperatures below its boiling point
What are 5 examples of evaporation?
Common examples of evaporation include drying clothes on a line, sweat cooling the body, a puddle shrinking under the sun, morning dew disappearing, and a wet sidewalk drying after rain, all illustrating evaporation's role in everyday life








