Table of Contents
Difference Between Ideal and Non Ideal Solution:When comparing ideal and non-ideal solutions, it’s essential to understand how they differ in terms of behavior and interactions. Ideal solutions follow Raoult’s law precisely, with no significant change in intermolecular forces. However, non-ideal solutions deviate from this, displaying either positive or negative deviations due to stronger or weaker interactions. This distinction helps explain why certain solutions behave differently in various conditions. Let’s have a look into the key differences, examples, and factors influencing both ideal and non-ideal solutions.
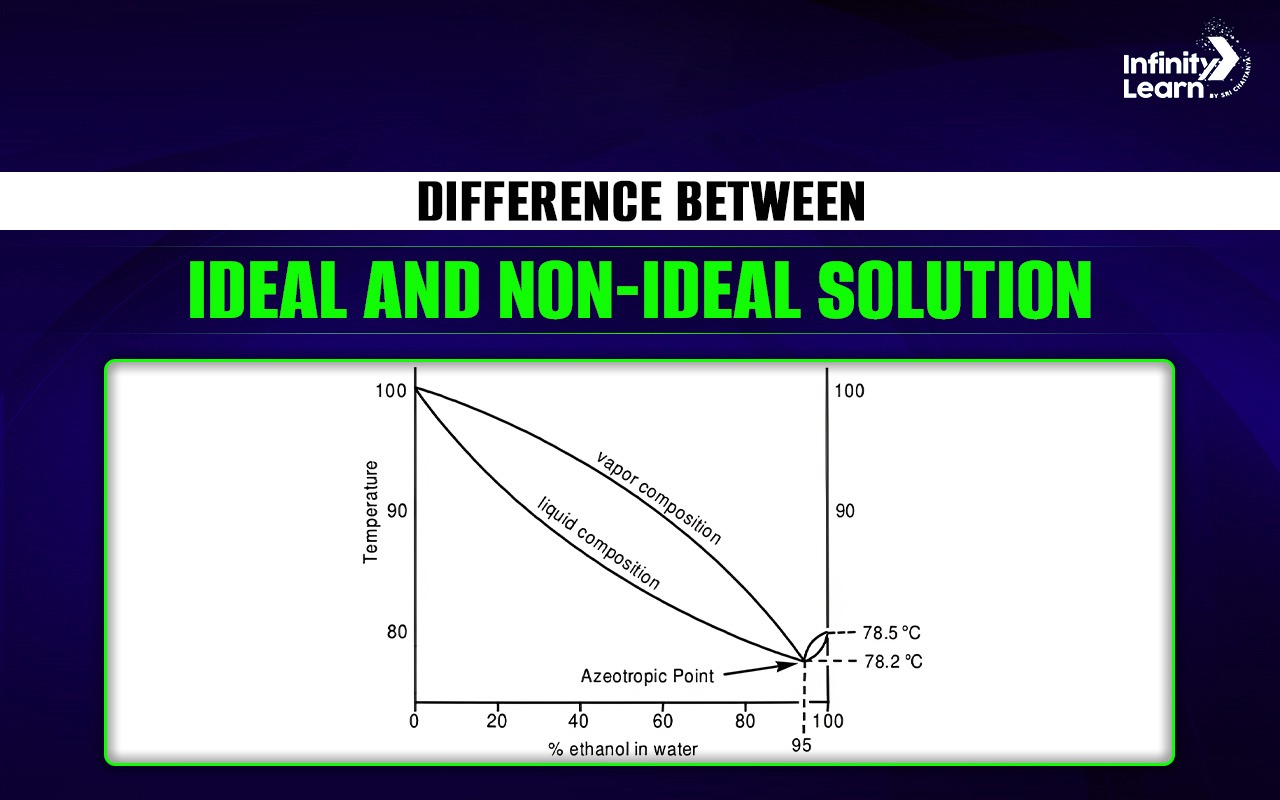
Ideal and Non Ideal Solution
In an ideal solution, the components mix without interacting, meaning their behavior is based purely on the amounts of each substance. There is no change in properties like vapor pressure or boiling point compared to individual substances.
On the other hand, non-ideal solutions show interactions between molecules, leading to deviations. These can be positive (molecules push apart) or negative (molecules pull closer), impacting how the solution behaves. Factors such as molecular size, polarity, and intermolecular forces play a big role in these deviations. The following notes explain these differences in detail with examples.
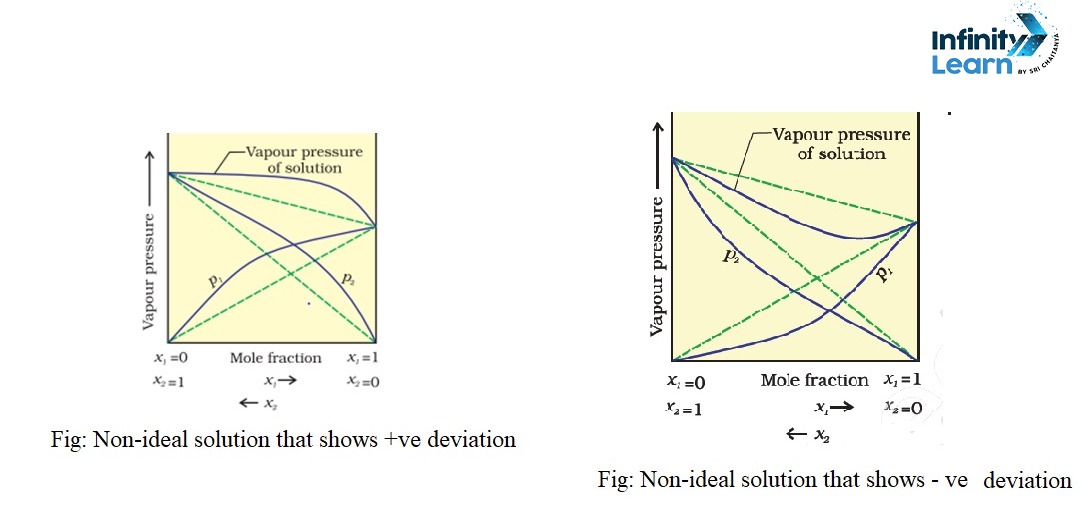
What is Ideal Solution?
An ideal solution is a type of mixture where the components blend together perfectly without any changes in the physical properties such as volume and enthalpy. In these solutions, the interactions between molecules of different components are identical to those between molecules of the same component. As a result, ideal solutions follow Raoult’s Law at all concentrations and temperatures, meaning that the vapor pressure of the solution is directly proportional to the mole fraction of its components.
For example, when you mix benzene and toluene, the resulting solution behaves as an ideal solution because the two liquids have similar molecular structures and sizes. They exhibit no significant heat change (ΔHmix = 0) or volume change (ΔVmix = 0) when mixed. Their interactions with each other are essentially the same as their interactions within themselves.
Also Check: NEET Chemistry Chapter-wise Weightage 2025
What is Non Ideal Solution?
A non-ideal solution, on the other hand, does not adhere to Raoult’s Law. In these solutions, the molecular interactions between different components are either stronger or weaker than those between molecules of the same component. This causes deviations in properties like vapor pressure, enthalpy, and volume. Non-ideal solutions can show either positive deviation (higher vapor pressure than expected) or negative deviation (lower vapor pressure than expected).
An example of a non-ideal solution is a mixture of ethanol and acetone. When these two liquids are mixed, they show a positive deviation from Raoult’s Law because the interactions between ethanol and acetone molecules are weaker than those within the pure substances. This results in an increase in vapor pressure and heat being absorbed during the mixing process.
In summary, while ideal solutions behave predictably without any change in physical properties, non-ideal solutions display complex behaviors due to varying molecular interactions.
Also Check: How To Study Chemistry For NEET 2025
Difference Between Ideal and Non Ideal Solution
| Property | Ideal Solution | Non-Ideal Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Raoult’s Law | Follows Raoult’s Law at all concentrations and temperatures. | Does not follow Raoult’s Law, showing positive or negative changes. |
| Enthalpy of Mixing (ΔHmix) | Zero (ΔHmix = 0). When combined, no heat is released or absorbed. | Not zero. Heat is either absorbed or released during mixing. |
| Volume of Mixing (ΔVmix) | Zero (ΔVmix = 0). The total volume equals the sum of both parts. | Not zero. The sum of the pieces does not equal the overall volume. |
| Intermolecular Interactions | The interactions between all components are similar. | Interactions between components are different from each other. |
| Examples | Benzene and toluene, hexane and heptane. | Ethanol and acetone (positive deviation), phenol and aniline (negative deviation). |
| Deviation from Raoult’s Law | No deviation. | Positive deviation: Vapor pressure is higher. Negative deviation: Vapor pressure is lower. |
| Formation of Azeotropes | Does not form azeotropes. | Can form azeotropes. |
| Nature of Components | Components are similar in size and polarity. | Components may differ in terms of polarity, size, or shape. |
Conclusion
Ideal solutions can be found in the real world, even though ideal gases don’t exist. In fact, very diluted solutions often act like ideal solutions because the interactions between solute molecules and solvent molecules are minimal. What makes an ideal solution different from a non-ideal one is that in an ideal solution, all molecules experience the same type of intermolecular interactions. In contrast, non-ideal solutions have different forces of interaction between solute and solvent molecules, leading to deviations from ideal behavior.
Difference Between Ideal and Non Ideal Solution FAQs
What is the difference between ideal and non-ideal fluids?
Ideal fluids are hypothetical, having no viscosity and incompressibility, meaning they flow without resistance. Non-ideal fluids are real-world fluids with viscosity and compressibility, meaning they resist flow and experience energy loss.
What is the difference between non-ideal and ideal gases?
Ideal gases follow the ideal gas law (PV = nRT) and have no intermolecular forces; their behavior is predictable at all temperatures and pressures. Non-ideal gases deviate from this law at high pressure and low temperature due to interactions between gas molecules.
What are ideal solutions with an example?
Mixtures that have the same interactions between the molecules of the solute and solvent as the pure components are called ideal solutions. Toluene and benzene together exhibits optimal behavior as an example.
What are the five characteristics of solutions?
Homogeneous mixture. Uniform composition. Particles do not settle over time. Solute particles are small, usually on a molecular scale. Cannot be separated by filtration.
What are the properties of an ideal solution?
The mixture's volume is the total of its component volumes. During mixing, no heat is absorbed or released. The interactions between solute and solvent are identical to the interactions between like molecules.








