Table of Contents
Potassium chloride, often represented by the chemical formula KCl, is a compound composed of potassium (K) and chloride (Cl) ions. Here are some notes on potassium chloride, including its formula, structure, and chemical and physical properties:
Formula and Structure of Potassium Chloride:
The formula for potassium chloride is KCl, indicating that each unit of the compound contains one potassium ion (K+) and one chloride ion (Cl–). The potassium ion has a positive charge, while the chloride ion carries a negative charge.
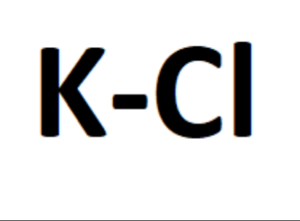
Chemical Properties of Potassium Chloride:
- Ionic Bonding: Potassium chloride is formed through ionic bonding, where the potassium atom donates one electron to the chlorine atom. This transfer of electrons leads to the formation of the K+ cation and Cl- anion, resulting in the overall neutral compound.
- Solubility: Potassium chloride is highly soluble in water. When dissolved in water, the ionic compound dissociates into potassium and chloride ions, which are surrounded by water molecules in a process called hydration.
- Electrolyte: Potassium chloride is an electrolyte, meaning it conducts electricity when dissolved in water or in molten form. The dissociation of the compound into ions allows for the flow of electric current.
- Reactivity: Potassium chloride is relatively inert chemically. However, it can participate in some reactions, such as precipitation reactions with other salts, or reactions involving the exchange of ions.
Physical Properties of Potassium Chloride:
- Appearance: Potassium chloride commonly exists as a colourless or white crystalline solid. It has a crystal lattice structure, where the positive potassium ions and negative chloride ions are arranged in a repeating pattern.
- Melting and Boiling Points: Potassium chloride has a high melting point of approximately 770°C (1418°F) and a boiling point of around 1420°C (2588°F). These high temperatures indicate the strength of the ionic bonds within the compound.
- Density: The density of potassium chloride depends on its form and temperature. In its solid state, its density is around 1.98 g/cm³. However, as a molten liquid, its density decreases.
- Taste: Potassium chloride has a slightly salty taste. It is often used as a salt substitute for individuals who need to limit their sodium intake.
- Medical and Industrial Applications: Potassium chloride has various applications in the medical and industrial fields. It is used as a nutritional supplement, in medical treatments, as a fertilizer, in food processing, and in the manufacturing of other potassium compounds.
These are some key points about potassium chloride, including its formula, structure, and chemical and physical properties. Potassium chloride is a widely used compound with diverse applications in various industries.
Solved Examples on Potassium chloride Formula:
Example 1: What is the total number of atoms in one molecule of potassium chloride?
Solution:
The formula for potassium chloride is KCl, which indicates that one molecule of potassium chloride consists of one potassium (K) atom and one chloride (Cl) atom. To calculate the total number of atoms, we add the number of potassium atoms and the number of chloride atoms.
Number of potassium atoms = 1
Number of chloride atoms = 1
Total number of atoms in one molecule of potassium chloride = Number of potassium atoms + Number of chloride atoms
= 1 + 1
= 2
Therefore, there are two atoms in one molecule of potassium chloride.
Example 2: Determine the molar mass of potassium chloride.
Solution:
To calculate the molar mass of potassium chloride, we need to find the atomic masses of potassium (K) and chlorine (Cl) from the periodic table and add them together.
Atomic mass of potassium (K) = 39.10 g/mol
Atomic mass of chlorine (Cl) = 35.45 g/mol
Molar mass of potassium chloride (KCl) = Atomic mass of potassium + Atomic mass of chlorine
= 39.10 g/mol + 35.45 g/mol
= 74.55 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of potassium chloride is 74.55 g/mol.
Note: The molar mass of a compound represents the mass of one mole of that compound, expressed in grams per mole (g/mol).
Frequently asked Questions on Potassium chloride Formula:
1: Is potassium chloride safe to consume?
Answer: Potassium chloride is generally safe for consumption when used in appropriate amounts. It is commonly used as a salt substitute and in medical treatments. However, individuals with specific health conditions or on certain medications should consult with a healthcare professional before using potassium chloride.
2: What are the uses of potassium chloride?
Answer: Potassium chloride has various uses. It is used as a nutritional supplement, particularly for individuals who need to replenish potassium levels. It is also used in medical treatments, such as intravenous infusions. Additionally, potassium chloride is used as a fertilizer in agriculture and in the manufacturing of other potassium compounds.
3: Can potassium chloride be used as a salt substitute?
Answer: Yes, potassium chloride can be used as a salt substitute. It provides a similar salty taste to sodium chloride (table salt) but with a reduced sodium content. However, it is important to note that individuals with certain health conditions, such as kidney problems or potassium-restricted diets, should consult with a healthcare professional before using potassium chloride as a salt substitute.
4: Does potassium chloride have any side effects?
Answer: While potassium chloride is generally safe, it may have side effects in some individuals. Common side effects may include stomach upset, diarrhea, or nausea. In rare cases, excessive intake of potassium chloride can lead to hyperkalemia, a condition characterized by high potassium levels in the blood. It is important to follow recommended dosage guidelines and consult with a healthcare professional if any concerns arise.
5: How is potassium chloride administered in medical treatments?
Answer: Potassium chloride can be administered in medical treatments through various routes, including oral tablets or solutions, intravenous infusion, or intramuscular injection. The specific method of administration depends on the medical condition being treated, the dosage prescribed, and the healthcare provider’s recommendation.




