Table of Contents
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 SA2 Social Science Solved 2016 Set 7
1.By which Act was the United Kingdom formed?
Or
What is referred to as the Ho Chi Minh Trail?
2.Which state in India has the lowest road density?
3.Who led the protest against water privatisation in Bolivia?
4.Define coalition government
5.State any two social outcomes of democracy.
6.What is the main source of credit for the rural households in India?
7.Which type of countries have benefited most from globalisation?
8.Name any two products that require mandatory ISI standard certification.
9.Explain any three reasons for the conflict in the Balkans.
Or
What factors led to the outbreak of bubonic plague in the modern part of Hanoi in 1903?
10.How did Dr. B R Ambedkar try to improve the condition of the depressed class? Mention any three points.
11.State any three factors responsible for the growth of nationalism in India.
12.Why is coal the most important energy source in India even today? Give three reasons.
13.Give any three reasons for the shifting of sugar industries from north India to the western and southern Indian states.
14.You have recently travelled by train and are not satisfied with the facilities available.
(a)As a responsible citizen, have you brought the problems to the notice of the railway authorities?
(b)What action will you take when you find some passengers travelling without tickets?
(c)What values will you learn from the above situation?
15.Distinguish between the Pressure group and a Political party.
16.Discuss the different forms of the party system?
17.How is poverty a challenge to Democracy in India?
18.Discuss the loan activities of a bank.
19.How do producers and consumers benefit from foreign trade?
20.What are the advantages of consumer’s Right to be Informed?
21.Who was Garibaldi? Examine his contributions in the unification of Italy.
Or
Explain the features of the ‘Go East Movement’ in Vietnam.
22.How did the First World War help in the growth of National Movement in India?
23.Which is the most abundantly available fossil fuel in India? What are its three major forms? Write the main features of each form.
24.Tourism in India has grown substantially over the last three decades. Explain the statement by giving five reasons.
25.How do the pressure groups and movements exert influence on the politics of a country?
26.How does democracy lead to a peaceful and a harmonious life among the citizens? Explain.
27.In India about 80% of the farmers are small farmers, who need credit for cultivation.
(a)Why are banks unwilling to lend to small farmers?
(b)What are the other sources from which the small farmers borrow?
(c)Explain how the terms of credit can be unfavourable for the small farmers
(d)Suggest some ways by which small farmers can get cheap credit.
(e)What can be done to increase formal credit facilities to the people in the rural areas?
28.What were the main features of the Economic Reforms introduced in 1991 in India?
29.On the outline political map of India locate and label the following:
(i)Place associated with the Jallianwalla Bagh Tragedy.
(ii)Place associated with indigo planters movement.
(iii)Place associated with cotton mill workers protest.
30.Three features A, B and C are marked on the given political map of India. Identify these features with the help of the following information and write their correct names on the lines marked on the map.
A. Centre for Woollen Textile B. Major oil field C. Iron and Steel Plant
Answers
1.By which Act was the United Kingdom formed?
Or
What is referred to as the Ho Chi Minh Trail?
Ans.The United Kingdom was formed by the Act of Union.
Or
Ho Chi Minh Trail was an immense network of roads made to transport men and material from North to South Vietnam.
2.Which state in India has the lowest road density?
Ans.Jammu and Kashmir has the lowest road density in India.
3.Who led the protest against water privatisation in Bolivia?
Ans.The protest against water privatisation in Bolivia was led by FEDECOR.
4.Define coalition government
Ans.Government formed by two or more political parties in case no single party gets majority is called as the coalition government.
5.State any two social outcomes of democracy.
Ans.Two social outcomes of democracy are dignity and freedom of the citizens and abolition of untouchability and discrimination.
6.What is the main source of credit for the rural households in India?
Ans.Informal sources of credit like moneylenders, traders, relatives are the main source of credit for the rural households in India.
7.Which type of countries have benefited most from globalisation?
Ans.Developed countries have been the most beneficiaries from globalisation.
8.Name any two products that require mandatory ISI standard certification.
Ans.Electrical items and LPG cylinders require mandatory ISI standard certification
9.Explain any three reasons for the conflict in the Balkans.
Or
What factors led to the outbreak of bubonic plague in the modern part of Hanoi in 1903?
Ans.The Balkans comprised of modern-day Romania, Bulgaria, Albania, Greece, Macedonia, Croatia, Bosnia-Herzegovina, Slovenia, Serbia and Montenegro and a large part of this region was under the control of the Ottoman Empire. Some of the reasons that made this region very explosive and caused conflict are :
(i) The feelings of nationalism of these countries was in conflict with one another. They were fiercely jealous of each other and struggled to define their identity. They were extremely intolerant of one another.
(ii) The disintegration of the Ottoman Empire, which had throughout the nineteenth century, tried to strengthen itself through modernisation and reforms.
(iii) The breaking away of each of these nationalist groups one by one from the control of the Ottoman Empire and declaring themselves as independent with political rights, on the basis of history. They proved that once they had been independent but were subsequently subjugated.
(iv) Each of these countries attempted to gain more territory to their independent country.
(v) The Balkans became a scene of big power rivalry. Major European powers – Russia, Germany,
England, Austro-Hungary, manipulated nationalist aspirants to further their own aims. There was rivalry between the European powers over trade and colonies and naval and military superiority.
(vi) There was rivalry among the big powers to counter the hold of other powers over the Balkan region and extending their own control.
Or
(i) The latest ideas of architecture and modern engineering were used to build a new modern city in the French occupied region of Hanoi with wide avenues and well laid out sewer system, whilst the native region became the dumping ground and refuse from the city drained into rivers, which during rainy season overflowed into the streets.
(ii) The large sewers became ideal breeding grounds for rats and also served as a wonderful transport system for them. The rats entered into the homes of the French through the sewage pipes.
(iii) In order to overcome the rat menace a rat hunt scheme was devised by the colonisers who paid the natives to get rid of the rats. However, the natives took advantage of the scheme and did not kill the rats but just clipped their tails so that the process could be repeated.
(iv) Some natives began raising rats in their homes so the number of rats actually increased instead of decreasing.All this led to the outbreak of bubonic plague in 1903.
10.How did Dr. B R Ambedkar try to improve the condition of the depressed class? Mention any three points.
Ans. (i) In 1930, Dr B R Ambedkar organised the dalits (the untouchables) into an organisation called the Depressed Classes Association, now known as Schedule Castes.
(ii)His ideas for the Depressed Classes differed from that of Mahatma Gandhi. He wanted a separate electorate for the dalits.
(iii)Whilst at the Round Table Conference in London, he demanded a separate electorate for the dalits and the British colonisers conceded to his demands. This caused Mahatma Gandhi to fast unto death because he believed that a separate electorate for the dalits would slow the process of their integration into the main society.
(iv) He signed the Poona Pact with Gandhiji and the Congress, giving the Depressed classes to secure reserved seats for dalits in the Provincial and Central legislative Councils to be voted in the general elections.
11.State any three factors responsible for the growth of nationalism in India.
Ans.Factors responsible for the growth of nationalism in India
(i)Result of colonial exploitation.
(ii) Understanding of the true nature of the British rule.
(iii)Racial discrimination.
(iv)Role of Mahatma Gandhi and other leaders.
(v) Impact of nationalist literature, songs, poems and folklore.
12.Why is coal the most important energy source in India even today? Give three reasons.
Ans.Coal is the most important source of energy in India because
(i) India has abundant reserves of coal to meet a greater part of our energy requirements.
(ii)It is used for generation of thermal power in thermal power plants.
(iii)It is used as an energy resource both for domestic and industrial purposes.
13.Give any three reasons for the shifting of sugar industries from north India to the western and southern Indian states.
Ans.In recent years there is a tendency for the sugar mills to shift and concentrate in the southern and western states especially in Maharashtra. This is because the sugar cane produced has a higher sucrose content and it has cooler climate that ensures a longer crushing season. Most of the sugar industries are set up in the cooperative sector and cheap labour is available in the area.
14.You have recently travelled by train and are not satisfied with the facilities available.
(a)As a responsible citizen, have you brought the problems to the notice of the railway authorities?
(b)What action will you take when you find some passengers travelling without tickets?
(c)What values will you learn from the above situation?
Ans.(a) As a responsible citizen of India, I complained about the problems which I faced while travelling in the train to the railway authorities.
(b)When I found some passengers travelling without tickets, I told them that they might have to face punishment when the ticket collector would come for a check.
(c)The values learnt were that of responsibility, truth and respect for rules and regulations.
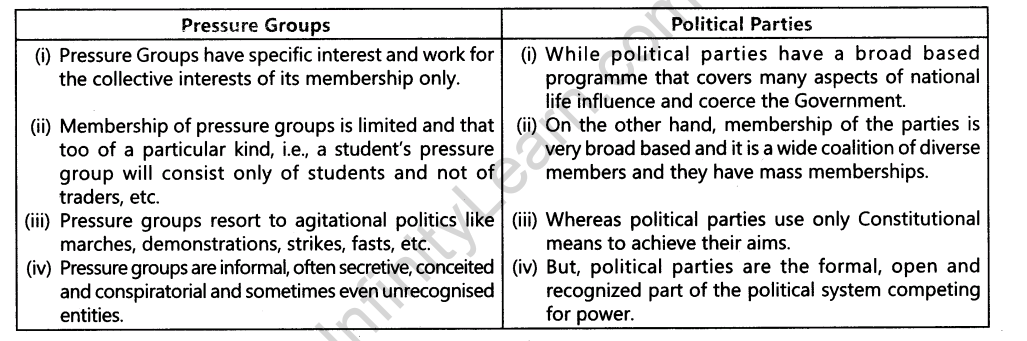
15.Distinguish between the Pressure group and a Political party.
Ans.
16.Discuss the different forms of the party system?
Ans.Basically there are three types of party systems:
(i) Single Party System: Under this system only one party is allowed to function, hence there is no opposition. This cannot be called a democratic system. Eg. China and Russia.
(ii) Bi-Party System: Under this system only two political parties exist in a state. One which comes in power and other acts as opposition. England and USA practice bi-party system.
(iii)Multiparty System: Under this system a number of political parties are free to function. The party with the majority of representatives, forms the government. India is the best example of a multi-party system.
17.How is poverty a challenge to Democracy in India?
Ans.Poverty has become a common phenomenon in India. Both the rural and the urban areas have a large number of people living below the poverty line. Following are the ways in which poverty becomes a challenge to democracy:
(i) The poor are not able to take an active part in public affairs because most of their time is spent in arranging basic necessities of life.
(ii) Poor people often lose faith in the democratic institutions as their situation remains the same year after year.
(iii) Poor people often misuse their right to vote. They are easily manipulated to sell their vote for money by influential and rich candidates.
18.Discuss the loan activities of a bank.
Ans.Loan Activities of Banks. Basically, banks borrow money to lend. Banks pay interest (suppose x%) from whom it borrows. After keeping a portion of deposits as reserves, banks lend to people who demand money as loan and bank charges interest (suppose y%) from them. The difference between what is charged from borrowers (y%) and what is paid to depositors is their main sources of income. After meeting all expenses of banks out of this income, the resultant is profit/loss for the bank.
19.How do producers and consumers benefit from foreign trade?
Ans.Foreign trade provides an opportunity for both producers and buyers to reach beyond the markets of their own countries. Goods travel from one country to another. There is huge competition among producer of one country and producer of another country. Competition among buyers also prevails. Thus foreign trade lead to integration of markets across countries. For example, during Diwali seasons, buyers in India have the option of choosing between Indian and the Chinese decorative lights and bulbs. Many shops have replaced Indian decorative lights with Chinese lights. For Chinese light manufacturers, this provides an opportunity to expand their business.
20.What are the advantages of consumer’s Right to be Informed?
Ans. Following are the advantages of consumer’s Right to be Informed:
(i)If a product is found defective, the consumer can ask for a replacement.
(ii)Consumer can make use of the information related to side effects, directions of use and precautions given on the label.
(iii)Consumer can protest or complain if the product is sold at more than the printed MRP.
21.Who was Garibaldi? Examine his contributions in the unification of Italy.
Or
Explain the features of the ‘Go East Movement’ in Vietnam.
Ans.(i)Garibaldi was the most celebrated Italian freedom fighter.
(ii)In 1833, he met Mazzini and joined the ‘Young Italy’ movement and participated in a republican uprising in Piedmont in 1834.
(iii)Though he was compelled to go in to exile till 1848, he supported Victor Emmanuel II in his efforts to unify the Italian states.
(iv)In 1860, Garibaldi led the famous expedition of the Thousand to South Italy. His volunteers called ‘Red Shirts’ made occupation of South Italy possible.
(v)In 1867, he led his volunteers to Rome to fight the papal states, the last obstacle to the unification of Italy. Though they were no match to the French Garrison who protected these states, the contribution and dedication of Garibaldi cannot be undermined. In 1870, Italy was unified when, during his war with Prussia, French troops were withdrawn and the papal state of Rome was freed.
Or
(i)The “Go East Movement” became popular in the first decade of the twentieth century. In 1907-08 about 300 Vietnamese students and nationalists, went to Japan to acquire modern education.
(ii)The primary objective of the “go east movement” was to acquire means and formulate plans to drive out the French from Vietnam, to overthrow the puppet tmperor and to re-establish the Nguyen Dynasty that had been deposed by the French colonisers.
(iii)They tried to obtain foreign arms and all kinds of help.
(iv)They appealed to the Japanese as fellow Asians, for help.
(v)The Vietnamese students also established a branch of the Restoration Society in Tokyo. However in 1908 the Japanese Ministry of Interiors clamped down on them and deported them.
22.How did the First World War help in the growth of National Movement in India?
Ans.The First World War played an important role in strengthening national movement in India.
The war created a new economic and political situation. It led to an increase in expenditure which was met by the additional taxes on Indian people.
The War led to a price rise—leading to extreme hardships for the common people.
Villages were called upon to supply soldiers and this forced recruitment in rural areas caused widespread anger.
Acute shortage of food accompanied by influenza epidemic led to famine and misery. The Indians began to realise, that they were unnecessarily drawn in a war which was for British imperialist interest. This feeling united the Indians against the British who began to demand reforms.
Fortunately during the period of war Gandhiji returned to India from South Africa and gave leadership to people by organising Satyagraha which was the mass struggle against foreign authorities.
23.Which is the most abundantly available fossil fuel in India? What are its three major forms? Write the main features of each form.
Ans.The most abundantly available fossil fuel in India is coal. The three major forms of coal are
(i) Lignite
(ii) Bituminous and
(iii) Anthracite
(i) Lignite is a low grade brown coal, which is soft with high moisture content.
(ii) Bituminous is the most popular coal used for commercial purposes mainly for smelting of Iron. It is found deep under the earth with high temperatures.
(iii) Anthracite is the highest quality hard coal.
24.Tourism in India has grown substantially over the last three decades. Explain the statement by giving five reasons.
Ans.(a) Over 2.6 million people visit India every year as tourists.
(b) It contributes to ? 21,825/- crores as foreign exchange.
(c) More than 15 million people are directly engaged in tourism industry.
(d) Foreign tourists visit India for heritage tourism, medical, economic, culture, business, adventure tourism, etc.
(e) It has made access easier in the North-eastern states and interior parts of Jammu Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh and Uttaranchal.
(f) It is suitable for sending valuable goods, life saving drugs, perishable commodities, mails etc. to distant places within a short time.
(g) It plays an important role for the defence of the country.
25.How do the pressure groups and movements exert influence on the politics of a country?
Ans.Pressure groups and movements exert influence on the politics in the following ways:
(i)They try to gain public support and sympathy for their goals by campaigning, organizing meetings, file petitions, etc.
(ii) They often organize protest activities like strikes, or disrupting government programmes.
(iii)Business groups often employ professionals or sponsor expensive advertisements and offer advise to the government.
(iv)In some instances the pressure groups are either formed or led by the leaders of the political parties or act as the expanded arms of the political parties
(v) Sometimes political parties grow out of movements.
(vi) In most cases, the leadership of the political party comes from the interest or movement groups
26.How does democracy lead to a peaceful and a harmonious life among the citizens? Explain.
Ans. Democracy leads to a peaceful and harmonious life among citizens as it gives to its citizens a sound political system based on social equality. We can prove the statement by citing the following instances:
In the Political Sphere
•Democracy provides a conducive political environment to citizens for their popular participation in politics.
•Every citizen has the Right to Vote and Right to Contest Elections.
In the Economic Sphere
•Democracy stands for equal economic status to all citizens. There is not a large gap between the rich and the poor.
•In democracy the government undertakes extensive social welfare schemes and achieves universal literacy rate.
In the Social Sphere
•In the social sphere, democracy tries to help its citizens to lead a peaceful and harmonious life by accommodating various social divisions and providing social equality to its citizens.
• Democratic governments try to resolve differences, respect differences and try mechanisms which can negotiate differences.
In this way, Democracy is not a mere form of government. It is also a form of society as well as a social order which promotes dignity and freedom of the individual. It improves the quality of decision making and allows room for correcting mistakes.
27.In India about 80% of the farmers are small farmers, who need credit for cultivation.
(a)Why are banks unwilling to lend to small farmers?
(b)What are the other sources from which the small farmers borrow?
(c)Explain how the terms of credit can be unfavourable for the small farmers
(d)Suggest some ways by which small farmers can get cheap credit.
(e)What can be done to increase formal credit facilities to the people in the rural areas?
Ans. (a) As the farmers find it difficult to provide necessary documents/formalities and collateral security required for
loan, these banks might be unwiling to lend to small farmers.
(b) These farmers usually borrow from informal sources of credit like moneylenders, employers, relatives, friends, etc.
(c) Terms of credit for small farmers if they borrow from informal sources may carry a very high rate of interest which means that larger part of the earnings is used to repay loan.
(d) Farmers can get cheap credit through Cooperatives and SHGs.
(e) Following are the ways to increase the formal credit facilities to the people in the rural areas:
(i) Setting up of Grameen Banks in the rural areas.
(ii) Making the process of granting loans more simple and suited to the needs of the rural people.
(iii) Provisions of setting up of different cooperative societies in the villages.
(iv) Encouraging the villagers to set up Self Help Groups.
28.What were the main features of the Economic Reforms introduced in 1991 in India?
Ans.Main features of Economic reforms introduced in 1991 in India were:
(i) Deregulation of Industries.
(ii) Liberalised Policy towards foreign capital and technology.
(iii) Reduced Role for the Public Sector.
(iv) Disinvestment in Public Enterprises.
(v) Liberalisation of Import Licencing.
(vi) Rationalisation of Tariff Structure.
(vii) Reforms in Foreign Exchange Management.
(viii) Reforms in Financial Sector.
29.On the outline political map of India locate and label the following:
(i)Place associated with the Jallianwalla Bagh Tragedy.
(ii)Place associated with indigo planters movement.
(iii)Place associated with cotton mill workers protest.
Ans.
30.Three features A, B and C are marked on the given political map of India. Identify these features with the help of the following information and write their correct names on the lines marked on the map.
A. Centre for Woollen Textile B. Major oil field C. Iron and Steel Plant
Ans.




