Table of Contents
NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science Ch 1 Crop Production And Management
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management is an essential resource for students following the CBSE syllabus. This chapter provides comprehensive answers to the exercises in the NCERT textbook, helping students grasp the fundamental concepts of agricultural practices, types of crops, and the various methods of crop management.
Infinity Learn, an online educational platform, offers detailed NCERT solutions that are designed to enhance the learning experience of students. These Class 8 NCERT solutions are crafted by subject experts to ensure that students have a clear understanding of the topic. The explanations are straightforward and easy to comprehend, making them ideal for effective exam preparation.
In Class 8 Science Ch 1, students will learn about the different stages of crop production such as preparation of soil, sowing, adding fertilizers, irrigation, protecting from weeds, harvesting, and storage. The NCERT solutions class 8 Science provided by Infinity Learn cover all these topics in depth, offering step-by-step explanations for each process involved in crop production and management.
By utilizing NCERT solutions from Infinity Learn, students can strengthen their foundation in Science and perform better in their exams. These solutions are aligned with the CBSE syllabus for class 8 Science and are updated regularly to ensure that students have access to the most accurate and relevant information.

The Class 8 HOTS Course enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills through engaging activities and advanced learning techniques, ensuring academic excellence.
Class 8 Science Ch 1 NCERT Solutions Download PDF
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production And Management Extra Questions
Textbook Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Questions and Answers
1. Select the correct word from the following list and fill in the blanks.
- float, water, crop, nutrients, preparation
- The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called _____________.
- The first step before growing crops is _____________ of the soil.
- Damaged seeds would _____________ on top of water.
- For growing a crop, sufficient sunlight and _____________ and _____________ from the soil are essential.
Ans.
- crop
- preparation
- float
- water and nutrients
2. Match items in column A with those in column B.
| A | B |
| (i) Kharif crops | (a) Food for cattle |
| (ii) Rabi crops | (b) Urea and superphosphate |
| (iii) Chemical fertilisers | (c) Animal excreta, cow dung urine and plant wastes |
| (iv) Organic manure | (d) Wheat, gram, pea |
| (e) Paddy and maize |
Ans.
- e
- d
- b
- c
3. Give two examples of each.
- Kharif crop
- Rabi crop
Ans.
- Kharif crop – Paddy, maize etc.
- Rabi crop – Wheat, gram etc.
4. Write a paragraph in your own words on each of the following.
- Preparation of soil
- Sowing
- Weeding
- Threshing
Ans.
Preparation of soil
i) The preparation of soil is the first step before growing a crop.
ii) The preparation the of soil is to turn the soil and loosen it which allows the roots to penetrate deep into the soil.
iii) The loose soil allows the roots to breathe easily even when they go deep into the soil.
iv) Turning and loosening of soil brings the nutrient-rich soil to the top so that plants can use these nutrients.
v) The process of loosening or turning of soil is called tilling or ploughing. This is done by using a plough.
Sowing
i) Sowing is the most important part of the crop production. It can be done either through traditional tool or seed drill.
ii) Before sowing, good quality seeds which give a high yield are selected by the farmers.
iii) During sowing, an appropriate distance between the seeds is important to avoid overcrowding of plants.
Weeding
i) The removal of weeds is called ‘Weeding’. Hoe is a simple tool which is used for weeding.
ii) Weeding is necessary since weeds compete with the crop plants for water, nutrients, space and light.
iii) Weeding is also done by using certain chemicals called Weedicides.
d) Threshing
i) The process of separation of harvested grain seeds from the chaff is called ‘Threshing’.
ii) Now a days, this is carried out with the help of a machine called ‘combine’ which is in fact a combined harvester and thresher.
5. Explain how fertilisers are different from manure.
Ans.
| Fertilisers | Manures |
| A fertiliser is an inorganic salt. | Manure is a natural substance obtained by the decomposition of cattle dung, human waste and plant residues. |
| A fertiliser is prepared in factories. | Manure is prepared in the fields. |
| A fertiliser does not provide any humus to the soil. | Manure provides a lot of humus to the soil. |
| Fertilisers are very rich in plant nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorous and potassium. | Manure is relatively less rich in plant nutrients. |
6. What is irrigation? Describe two methods of irrigation which conserve water.
Ans.
Supply of water to crop plants at appropriate intervals is called irrigation.
Two methods of irrigation which help in conservation of water are – Sprinkler system and Drip system.
a) Sprinkler system
i) This system is more useful on the uneven land, having fewer water supplies.
ii) In this method, water is supplied using pipes to one or more central locations within the field.
iii) When water is allowed to flow under high pressure with the help of a pump, it gets sprinkled on the crop plants.
iv) It is very useful for sandy soil.
b) Drip system
i) This is the most efficient method of irrigation where water is delivered at or near the roots of plants, drop by drop.
ii) This is the best technique for watering fruit plants, gardens and trees.
iii) This method is important in areas where water availability is poor.
7. If wheat is sown in the kharif season, what would happen? Discuss.
Ans.
If wheat is sown in the kharif season (from June to October), then the whole crop might get destroyed because of many factors such as lack of optimum temperature, adaptability, availability of pests etc.
Therefore, wheat crop should not be sown during this season.
8. Explain how soil gets affected by the continuous plantation of crops in a field.
Ans.
- Plants require nutrients for their proper growth and functioning.
- Continuous plantation of crops in a field makes the soil poorer (deficit) in certain
- As a result, availability of nutrients in the soil decreases.
- This reduces the soil fertility and crop yield.
9. What are weeds? How can we control them?
Ans.
Undesirable plants that grow naturally along with crop plants and reduces the crop yield are known as weeds. Eg. Xanthium, Parthenium etc.
Weeds can be controlled by:
- removing them manually. This is done with the help of a Khurpi.
- using certain chemicals called weedicides like 2, 4 – Dichlorophenoxy acetic acid.
- crop rotation method.
10. Arrange the following boxes in proper order to make a flowchart of sugarcane crop production.
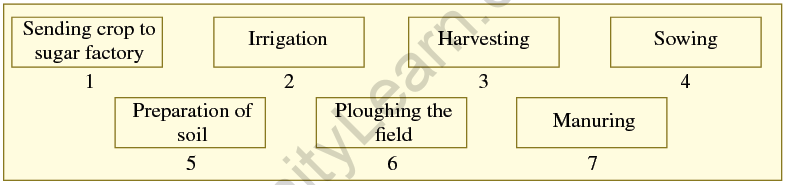
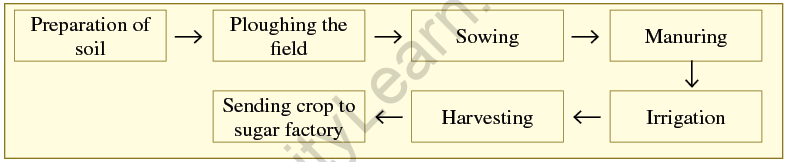
Ans.
Flowchart of sugarcane crop production:
11. Complete the following word puzzle with the help of the clues given below.
Down
1. Providing water to the crops.
2. Keeping crop grains for a long time under proper conditions.
5. Certain plants of the same kind are grown on a large scale.
Across
3. A machine used for cutting the matured crop.
4. A rabi crop, which is also one of the pulses.
6. A process of separating the grain from the chaff.
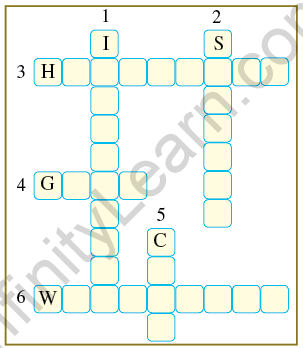
Ans.
Down
1. IRRIGATION
2.STORAGE
5.CROP
Cross
3. HARVESTER
4. GRAM
6. WINNOWING
- Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
- Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
- Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
- Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame
- Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Chapter 8 Cell – Structure and Functions
- Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals
- Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence
- Chapter 11 Force and Pressure
- Chapter 12 Friction
- Chapter 13 Sound
- Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
- Chapter 16 Light
- Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System
- Chapter 18 Pollution of Air and Water
Chapter 1 of NCERT Science Class 8: Crop Production and Management Overview
Readers will be able to learn everything they need to know about crop production and management in this section. This material will assist students in answering the questions in this chapter.
Let’s begin with the fundamentals. A crop is a group of plants of the same type that are planted and farmed for the purpose of providing food. This is carried out on a vast tract of arable land. Crops come in a variety of shapes and sizes. The following are the various sorts of crops:
Rabi Crops: These crops are grown from October to March, throughout the winter season.
Kharif Crops: These crops are sown from July through October, during the rainy season.
The soil must be prepared for the crop before any seed can be planted. This is done to ensure that the seeds are correctly sewn.
Tilling vs. ploughing
Ploughing or tilling is the process of loosening and turning the soil. This is accomplished with the use of a plough.
Plough: A plough, as previously said, is a device used mostly by farmers for various purposes such as loosening the soil and providing fertilisers to the land. A plough can also be used for weed removal and soil scraping. A plough shaft is the major component of a plough, which is usually composed of wood logs.
Hoe: A hoe is a digging instrument that can be used to dig up soil. This tool can also be used to eliminate weeds and loosen the soil in preparation for planting a sapling.
Cultivator: A cultivator is a piece of equipment that attaches to a tractor. It aids in the loosening of soil. Because cultivators are faster than ploughs, many farmers prefer to use them instead of ploughs.
Sowing might begin when the soil has been prepped. Sowing is the act of putting seeds into the ground. It is vital to highlight that the quality of the seed is one of the most critical aspects in determining the crop’s yield. As a result, a person should always choose the best seeds. Seeds that are good can be selected by immersing them in water. If there are any dead or damaged seeds, they will float to the surface.
Another component of a plough is the plough share, which is a triangular iron strip. The shaft has a handle on the other end. The opposite end is secured to a support beam. After being placed on the bull’s neck, this beam is pulled by the bull. A guy can operate a wooden plough as well. Nowadays,
Farmers exclusively employed traditional tools before the introduction of modern agricultural procedures, tools, and technology, which may be of interest to readers. Scythes, shovels, ploughs, and pickaxes are examples of traditional implements. The traditional seed sowing equipment was shaped like a funnel. When the farmer placed the seeds within the funnel, the equipment operated. The seeds will be placed in two or three sharp-end tubes. The tool’s ends will pierce the earth and plant the seeds within it.
Seed drills are now commonly used for sowing. Tractors and seed drills are used together. This tool guarantees that seeds are sown in a consistent manner. All seeds are planted at a specific depth and are then covered with soil. A nursery is a facility where young trees and plants are raised for the purpose of being sold.
The germination of seeds occurs after the seeds have been sown. Following that, the plant emerges from the seed and begins to grow. The farmer’s next job is to apply manure or fertilizers. It’s worth noting that manures and fertilizers are both compounds that can be added to the soil to boost the soil’s Solution fertility. Manure is made from organic stuff such as human waste, farm waste, and cow dung, whereas fertilizers are made from inorganic salt. Fertilizers are made in factories as well. Manures can be made on farms as well. Fertilizers only need to be applied in minimal amounts to the soil. Manures, on the other hand, must be added in bigger quantities due to their lower nutrient content.
Fertilizers also do not offer any humus to the soil, whereas manures do. Before deciding whether or not to use manure or fertilizers, a farmer must examine all of these differences.
While thinking about this, keep in mind that excessive fertilizer use can lead to pollution. In some situations, it can also alter the pH of the soil. Some farmers prefer to leave their fields fallow. This aids in the natural replenishment of the land’s nutrients and minerals. The land can be used again when some time has passed.
Crop rotation is another good way to help the soil restore itself. Crop rotation means that the same crop isn’t cultivated every year. This keeps the soil’s fertility from eroding. Another important aspect of cultivating crops is crop protection.
Weeds are unwanted plants that grow alongside the main crop in a natural environment. Weeds are hazardous to crops because they compete with them for nutrients, water, light, and space.
Tilling is a procedure that can be carried out after the crops have been planted. This method aids in the killing and uprooting of weeds. Weeds can also be removed by physically uprooting them from the soil or cutting them down to the ground level. The manual removal approach is what it’s called. Weedicides, which are chemicals intended to kill weeds, are also utilized by some farmers. Weedicides do not impact the main crop, so students should remember that. After that, harvesting takes place.
Harvesting is the process of cutting the crop once it has reached maturity.
Harvesting can be accomplished using one of two approaches. These are the methods:
- A sickle can be used in this approach.
- The mechanical method of harvesting with a harvester, which is a massive machine.
The method of threshing can also be used to separate the grains from the chaff. This procedure can be carried out either manually or with the assistance of machinery. Separating grain seeds from the chaff is also done by winnowing. However, this strategy makes use of the wind. The lighter chaff will fly away in the wind, while the heavier grains will fall down.
After the grain has been separated, the grains must be stored. After harvesting, the grains should be kept in silos and granaries. Grain should be stored in a dry, pest-free environment free of fungal or rat infection. The storage area should also be fumigated to ensure that it is free of germs.
For pupils who are unfamiliar with the term, a granary is a storage facility for freshly harvested food grains. Animal husbandry also refers to the care and management of agricultural animals. To obtain milk, eggs, or meat, this is done.
Benefits of Infinity Learn NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1
There are numerous advantages to obtaining INFINITY LEARN’s NCERT solutions for class 8 science chapter 1 pdf. If you want to learn more about those advantages, see the list of advantages for downloading class 8th science chapter 1 solutions below.
- Students can sign up for live online classes.
- Students can memorize all of the answers in order to improve their final science exam scores.
- All of the responses are 100 percent accurate and dependable.
- The most brilliant and experienced subject matter experts in India write the answers.
- Students can access academic help 24 hours a day, seven days a week.
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Ch 1 Crop Production And Management
What is NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 about?
Chapter 1 of Class 8 Science introduces students to Crop Production and Management. It covers agricultural practices, types of crops, crop rotation, and various aspects of crop management.
Why are NCERT Solutions important for Class 8 Science Chapter 1?
NCERT Solutions provide comprehensive answers to the textbook questions, helping students understand the concepts better and improve their problem-solving skills.
How can NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 help in exams?
NCERT Solutions act as a valuable study resource, aiding students in preparing for exams by offering well-explained solutions and boosting their confidence in answering questions effectively.
Are NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 available online?
Yes, NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 are readily available online. Students can access them for free on Infinity Learn website.
Can NCERT Solutions be used for self-study?
Absolutely! NCERT Solutions are designed to be user-friendly and can be used for self-study to strengthen conceptual understanding and improve subject knowledge.
Are the NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 accurate?
Yes, NCERT Solutions provided by reputable sources are accurate as they are prepared by subject matter experts and adhere to the NCERT curriculum guidelines.
How can NCERT Solutions help in understanding crop production and management?
NCERT Solutions break down complex concepts related to crop production and management into simple, easy-to-understand explanations, making it easier for students to grasp the topics.
Can NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 be downloaded in PDF format?
Yes, Infinity Learn website offers NCERT Solutions in PDF format, allowing students to download and access them offline for convenient studying.
How can NCERT Solutions improve my performance in Class 8 Science?
NCERT Solutions can enhance your performance by providing step-by-step solutions, clarifying doubts, and helping you practice effectively, leading to better understanding and improved grades.
Are NCERT Solutions sufficient for Class 8 Science exam preparation?
NCERT Solutions serve as an essential resource for exam preparation, but it is advisable to supplement them with additional study materials, practice questions, and mock tests for comprehensive preparation.