Table of Contents
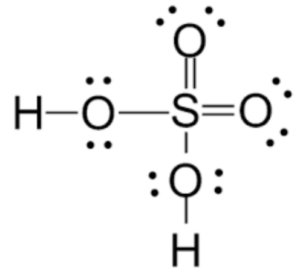
Sulphuric acid, also known as H2SO4, is a highly corrosive and strong mineral acid. It is commonly referred to as oil of vitriol. Sulphuric acid is composed of two hydrogen ions (H+), one sulfur atom (S), and four oxygen atoms (O).
Formula: H2SO4
Equations involving Sulphuric Acid:
- Dissociation in Water: Sulphuric acid readily dissociates in water, releasing hydrogen ions (H+) and sulphate ions (SO42-). The equation for this dissociation is: H2SO4 → 2H+ + SO42-
- Neutralization Reaction: Sulphuric acid reacts with bases in a neutralization reaction to form a salt and water. The equation for a generic neutralization reaction with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is: H2SO4 + 2NaOH → Na2SO4 + 2H2O
- Dehydration Reaction: Sulphuric acid can act as a dehydrating agent due to its strong affinity for water. It can remove water molecules from substances, such as alcohols, resulting in the formation of corresponding alkenes.
For example: H2SO4 + C2H5OH → C2H4 + H2SO4.H2O
- Oxidation Reactions: Sulphuric acid is a strong oxidizing agent and can participate in various oxidation reactions.
For example, it can oxidize copper (Cu) to form copper(II) sulphate (CuSO4):
H2SO4 + Cu → CuSO4 + SO2 + H2O
Sulphuric acid is a highly corrosive substance and must be handled with extreme care. It is important to follow proper safety protocols and use appropriate protective equipment when working with sulphuric acid due to its hazardous nature.
Physical properties of Sulphuric Acid:
- State: Sulphuric acid is typically found in a liquid state at room temperature. It is a dense, oily liquid that can vary in viscosity depending on its concentration.
- Colour: Pure sulphuric acid is a colourless liquid. However, the presence of impurities or higher concentrations can give it a slightly yellow or brownish tint.
- Odour: Sulphuric acid has no distinct odour. It is often described as odourless, although some people may detect a faint acidic or sour smell.
- Boiling Point: Sulphuric acid has a relatively high boiling point of approximately 337 degrees Celsius (639 degrees Fahrenheit). However, the boiling point can change with variations in concentration.
- Solubility: Sulphuric acid is highly soluble in water. It forms a homogenous solution with water, and the process of dissolving sulphuric acid in water is highly exothermic (releases heat). The solubility of sulphuric acid decreases as the temperature decreases.
- Conductivity: Sulphuric acid is an excellent conductor of electricity when it is dissolved in water. It dissociates into hydrogen ions (H+) and sulphate ions (SO4²–) in the aqueous solution, allowing for the flow of electric current.
- Corrosiveness: Sulphuric acid is highly corrosive and can cause severe burns upon contact with skin, eyes, or other tissues. It can also corrode many materials, including metals, organic substances, and certain plastics.
Chemical properties of Sulphuric Acid:
- Strong Acid: Sulphuric acid is a strong acid, meaning it readily donates hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water. It is classified as a diprotic acid because it can release two hydrogen ions per molecule. The dissociation of sulphuric acid in water is nearly complete.
- Acid-Base Reactions: Sulphuric acid reacts with bases in neutralization reactions to form salts and water. The hydrogen ions from sulphuric acid combine with the hydroxide ions from the base to produce water, while the remaining ions form the salt. For example: H2SO4 + 2NaOH → Na2SO4 + 2H2O
- Dehydrating Agent: Sulphuric acid is a powerful dehydrating agent. It has a strong affinity for water and can remove water molecules from other substances, such as carbohydrates or alcohols. This dehydration reaction is often used in laboratory procedures and industrial processes.
- Oxidizing Agent: Sulphuric acid can act as an oxidizing agent, particularly under certain conditions. It can oxidize various substances by accepting electrons and undergoing reduction itself. For example, it can oxidize metals like iron (Fe) or copper (Cu) to form iron(III) sulphate (Fe2(SO4)3) or copper(II) sulphate (CuSO4).
- Esterification: Sulphuric acid is commonly used in esterification reactions, where it reacts with alcohols to form esters and water. The sulphuric acid serves as a catalyst in this process. The reaction involves the removal of a water molecule from the alcohol and the carboxylic acid. For example: CH3CH2OH + CH3COOH → CH3COOCH2CH3 + H2O
- Reactive with Organic Compounds: Sulphuric acid can react with various organic compounds, including sugars, alkenes, and alkyl halides. These reactions often involve the addition or elimination of functional groups, leading to the formation of new compounds.
Solved Examples on Sulphuric acid formula:
Example 1: Calculation of Molar Mass Calculate the molar mass of sulphuric acid (H2SO4).
The molar mass of hydrogen is 1.01 g/mol, the molar mass of sulphur is 32.07 g/mol, and the molar mass of oxygen is 16.00 g/mol.
To calculate the molar mass of sulphuric acid (H2SO4), we add the molar masses of two hydrogen atoms, one sulphur atom, and four oxygen atoms.
Molar Mass = (Number of hydrogen atoms × Molar mass of hydrogen) + (Number of sulphur atoms × Molar mass of sulphur) + (Number of oxygen atoms × Molar mass of oxygen)
Molar Mass = (2 × 1.01 g/mol) + (1 × 32.07 g/mol) + (4 × 16.00 g/mol)
Molar Mass = 2.02 g/mol + 32.07 g/mol + 64.00 g/mol
Molar Mass = 98.09 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of sulphuric acid (H2SO4) is 98.09 g/mol.
Example 2: Stoichiometry in a Reaction Sulphuric acid (H2SO4) reacts with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to form sodium sulphate (Na2SO4) and water (H2O). If you mix 20 grams of sulphuric acid with excess sodium hydroxide, what is the theoretical yield of sodium sulphate?
The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is:
H2SO4 + 2NaOH → Na2SO4 + 2H2O
According to the stoichiometry of the balanced equation, 1 mole of sulphuric acid reacts with 2 moles of sodium hydroxide to produce 1 mole of sodium sulphate.
First, we calculate the number of moles of sulphuric acid using its molar mass:
Moles of H2SO4 = (Mass of H2SO4 ÷ Molar mass of H2SO4)
= (20 g ÷ 98.09 g/mol)
= 0.204 moles
Since the ratio of moles of sulphuric acid to moles of sodium sulphate is 1:1, the number of moles of sodium sulphate produced is:
Moles of Na2SO4 = Moles of H2SO4
= 0.204 moles
Finally, we convert the moles of sodium sulphate to grams using its molar mass:
Mass of Na2SO4 = (Moles of Na2SO4 × Molar mass of Na2SO4) = (0.204 moles × 142.04 g/mol) = 29.03 grams
Therefore, the theoretical yield of sodium sulphate in the reaction is 29.03 grams.
Frequently asked Questions on Sulphuric acid formula
- Is sulphuric acid dangerous?
Yes, sulphuric acid is highly corrosive and can cause severe burns upon contact with the skin, eyes, or other tissues. It is also harmful if inhaled or ingested. Proper safety precautions should be followed when handling sulphuric acid.
- What is the concentration of commercial sulphuric acid?
Commercial sulphuric acid is available in various concentrations, typically ranging from 1 M (mol/L) to 18 M. The concentration is usually indicated on the label or specified by the supplier.
- How is sulphuric acid used in industrial applications?
Sulphuric acid has numerous industrial applications, including the production of fertilizers, detergents, dyes, explosives, and pharmaceuticals. It is also used in petroleum refining, metal processing, and wastewater treatment.
- What safety precautions should be taken when working with sulphuric acid?
When working with sulphuric acid, it is essential to wear protective clothing, gloves, and eye protection. Adequate ventilation should be ensured, and the acid should be handled in a well-ventilated area. It should be stored in a safe and secure manner, away from incompatible materials.
- How should spills or accidents involving sulphuric acid be handled?
In the event of a spill or accident involving sulphuric acid, it is important to immediately neutralize the acid with a suitable neutralizing agent, such as sodium bicarbonate or calcium carbonate. Proper cleanup procedures should be followed, and appropriate safety protocols should be implemented.






